Abstract
Purpose
Although plasma therapy of thrombotic micro-angiopathies (TMAs) has dramatically improved survival, the outcome remains fatal in up to 15 % of patients. We investigated the causes and risk factors of death in patients with TMA.
Methods
Retrospective matched case–control national-registry study of 57 patients who died within 180 days of TMA diagnosis and 48 survivors matched on age, gender, and baseline platelet count and creatinine level. The study period was 1995–2007. Factors associated with mortality were identified using a conditional logistic regression model.
Results
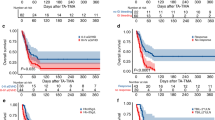
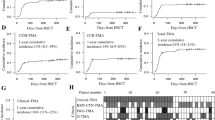
Median time from TMA symptom onset to death was 7 (5–14) days. The leading causes of death were nosocomial infections, myocardial infarction, stroke, and pulmonary embolism. Cases and controls did not differ significantly regarding haemolysis parameters, ADAMTS13 activity, or neurological or gastrointestinal involvement. TMA was more frequently related to HIV or cancer in patients who died. Compared to survivors, non-survivors more often had cardiac involvement at diagnosis (38 vs. 6 %, p = 0.03) and less often received plasma exchange therapy (60 vs. 92 %, p = 0.004). Only two factors were independently associated with mortality by multivariate analysis: cardiac involvement at diagnosis (odds ratio, 5.96; 95 % confidence interval, 1.06–33.4) and plasma exchange therapy (odds ratio, 0.25; 95 % confidence interval, 0.06–0.99).
Conclusion
Our data emphasise the adverse prognostic significance of cardiac abnormalities and support routine plasma exchange in patients with TMA. Given the high risk of cardiac and neurological complications, adequate monitoring should be proposed to these patients in appropriate hospital settings.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moake JL (2002) Thrombotic microangiopathies. N Engl J Med 347:589–600
Bell WR, Braine HG, Ness PM, Kickler TS (1991) Improved survival in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome. Clinical experience in 108 patients. N Engl J Med 325:398–403
George JN, Vesely SK, Terrell DR (2004) The Oklahoma Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura-Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (TTP-HUS) Registry: a community perspective of patients with clinically diagnosed TTP-HUS. Semin Hematol 41:60–67
Moake JL, Rudy CK, Troll JH, Weinstein MJ, Colannino NM, Azocar J, Seder RH, Hong SL, Deykin D (1982) Unusually large plasma factor VIII: von Willebrand factor multimers in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med 307:1432–1435
Tsai HM, Lian EC (1998) Antibodies to von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med 339:1585–1594
Furlan M, Robles R, Galbusera M, Remuzzi G, Kyrle PA, Brenner B, Krause M, Scharrer I, Aumann V, Mittler U, Solenthaler M, Lammle B (1998) von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and the hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med 339:1578–1584
Veyradier A, Meyer D (2005) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and its diagnosis. J Thromb Haemost 3:2420–2427
Fujimura Y, Matsumoto M (2010) Registry of 919 patients with thrombotic microangiopathies across Japan: database of Nara Medical University during 1998–2008. Intern Med 49:7–15
Malak S, Wolf M, Millot GA, Mariotte E, Veyradier A, Meynard JL, Korach JM, Malot S, Bussel A, Azoulay E, Boulanger E, Galicier L, Devaux E, Eschwège V, Gallien S, Adrie C, Schlemmer B, Rondeau E, Coppo P, des Microangiopathies Thrombotiques (TMA-Rare Diseases Reference Center) (2008) Human immunodeficiency virus-associated thrombotic microangiopathies: clinical characteristics and outcome according to ADAMTS13 activity. Scand J Immunol 68:337–344
Rock GA, Shumak KH, Buskard NA, Blanchette VS, Kelton JG, Nair RC, Spasoff RA (1991) Comparison of plasma exchange with plasma infusion in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Canadian Apheresis Study Group. N Engl J Med 325:393–397
Coppo P, Bussel A, Charrier S, Adrie C, Galicier L, Boulanger E, Veyradier A, Leblanc T, Alberti C, Azoulay E, Le Gall JR, Schlemmer B (2003) High-dose plasma infusion versus plasma exchange as early treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore) 82:27–38
Darmon M, Azoulay E, Thiery G, Ciroldi M, Galicier L, Parquet N, Veyradier A, Le Gall JR, Oksenhendler E, Schlemmer B (2006) Time course of organ dysfunction in thrombotic microangiopathy patients receiving either plasma perfusion or plasma exchange. Crit Care Med 34:2127–2133
Zhan H, Streiff MB, King KE, Segal JB (2010) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura at the Johns Hopkins Hospital from 1992 to 2008: clinical outcomes and risk factors for relapse. Transfusion 50:868–874
Hosler GA, Cusumano AM, Hutchins GM (2003) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome are distinct pathologic entities. A review of 56 autopsy cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med 127:834–839
Coppo P, Bengoufa D, Veyradier A, Wolf M, Bussel A, Millot GA, Malot S, Heshmati F, Mira JP, Boulanger E, Galicier L, Durey-Dragon MA, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Ramakers M, Pruna A, Bordessoule D, Gouilleux V, Scrobohaci ML, Vernant JP, Moreau D, Azoulay E, Schlemmer B, Guillevin L, Lassoued K (2004) Severe ADAMTS13 deficiency in adult idiopathic thrombotic microangiopathies defines a subset of patients characterized by various autoimmune manifestations, lower platelet count, and mild renal involvement. Medicine (Baltimore) 83:233–244
Veyradier A, Obert B, Houllier A, Meyer D, Girma JP (2001) Specific von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in thrombotic microangiopathies: a study of 111 cases. Blood 98:1765–1772
Brand J (1999) Development, implementation and evaluation of multiple imputation strategies for the statistical analysis of incomplete data sets. Leiden and Erasmus University, Rotterdam
van Buuren S, Boshuizen H, Knook D (1999) Multiple imputation of missing blood pressure covariates in survival analysis. Stat Med 18:681–694
Gami AS, Hayman SR, Grande JP, Garovic VD (2005) Incidence and prognosis of acute heart failure in the thrombotic microangiopathies. Am J Med 118:544–547
Hawkins BM, Abu-Fadel M, Vesely SK, George JN (2008) Clinical cardiac involvement in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a systematic review. Transfusion 48:382–392
Gandhi K, Aronow WS, Desai H, Amin H, Sharma M, Lai HM, Singh P (2009) Cardiovascular manifestations in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a single-center experience. Clin Cardiol 33:213–216
Hughes C, McEwan JR, Longair I, Hughes S, Cohen H, Machin S, Scully M (2009) Cardiac involvement in acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: association with troponin T and IgG antibodies to ADAMTS 13. J Thromb Haemost 7:529–536
Sane DC, Streer NP, Owen J (2009) Myocardial necrosis in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: pathophysiology and rationale for specific therapy. Eur J Haematol 82:83–92
Perez L, Ramappa P, Guzman JA (2008) Myocardial injury in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a frequent, perplexing complication. Int J Cardiol 128:257–260
Bobbio-Pallavicini E, Gugliotta L, Centurioni R, Porta C, Vianelli N, Billio A, Tacconi F, Ascari E (1997) Antiplatelet agents in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). Results of a randomized multicenter trial by the Italian Cooperative Group for TTP. Haematologica 82:429–435
Thachil J (2010) The myths about platelet transfusions in immune-mediated thrombocytopenias. Br J Haematol 150:494–495
Gottschall JL, Pisciotta AV, Darin J, Hussey CV, Aster RH (1981) Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: experience with whole blood exchange transfusion. Semin Thromb Hemost 7:25–32
Harkness DR, Byrnes JJ, Lian EC, Williams WD, Hensley GT (1981) Hazard of platelet transfusion in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. JAMA 246:1931–1933
Swisher KK, Terrell DR, Vesely SK, Kremer Hovinga JA, Lammle B, George JN (2009) Clinical outcomes after platelet transfusions in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Transfusion 49:873–887
Benhamou Y, Assie’ C, Boelle PY, Buffet M, Grillberger R, Malot S, Wynckel A, Presne C, Choukroun G, Poullin P, Provôt F, Gruson D, Hamidou M, Bordessoule D, Pourrat J, Mira JP, Le Guern V, Pouteil-Noble C, Daubin C, Vanhille P, Rondeau E, Palcoux JB, Mousson C, Vigneau C, Bonmarchand G, Guidet B, Galicier L, Azoulay E, Rottensteiner H, Veyradier A, Coppo P (2012) Development and validation of a predictive model for death in acquired severe ADAMTS13 deficiency-associated idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: the French TMA Reference Center experience. Haematologica (Epub ahead of print)
Acknowledgment
Supported by a grant from the Assistance-Publique Hôpitaux de Paris.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peigne, V., Perez, P., Resche Rigon, M. et al. Causes and risk factors of death in patients with thrombotic microangiopathies. Intensive Care Med 38, 1810–1817 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-012-2638-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-012-2638-5