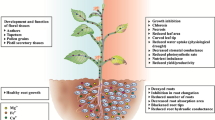
Abstract
Acetamiprid is a broad-spectrum insecticide, belonging to the neonicotinoid compounds group, which has been extensively applied throughout the globe. Recently, indiscriminate use of these compounds was reported to cause fatal impacts on non-targeted soil organisms. Hence, the present study aimed to examine the impact of acetamiprid on Indian indigenous earthworm, Perionyx excavatus. Acute toxicity revealed an LC50 concentration of 0.25 µg/cm2 for filter paper test/72 h and 400 µg/kg for artificial soil test/14 days. Oxidative stress (ROS) and various biomarkers including superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione S-transferase, malondialdehyde content and DNA damage were measured. The results of the biomarker responses confirmed the acetamiprid exposure can cause toxicity to P. excavatus. In addition, cell density (20 × 102 cell mL/mg) and cell viability (40%) were significantly (p < 0.05) reduced. Further, the ecotoxicological assessment made through this study can be utilized as good evidence to toxicity of neonicotinoids to non-targeted indigenous organisms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeel M, Ma C, Ullah S, Rizwan M, Hao Y, Chen C, Xing B (2019) Exposure to nickel oxide nanoparticles insinuates physiological, ultrastructural, and oxidative damage: a life cycle study on Eisenia fetida. Env Poll 254: 113032.
Bonmatin JM, Giorio C, Girolami V, Goulson D, Kreutzweiser D, Krupke C, Liess M, Long E, Marzaro M, Mitchell EA (2015) Environmental fate and exposure; neonicotinoids and fipronil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22: 35–67.
Chowdhary AB, Singh J, Quadar J, Singh S, Dutta R, Angmo D, Vig AP (2022) Earthworm’s show tolerance and avoidance response to pesticide clothianidin: effect on antioxidant enzymes. Int j sci environ technol 1–10.
Cossi PF, Herbert, LT, Yusseppone MS, Pérez AF, Kristoff G (2020) Toxicity evaluation of the active ingredient acetamiprid and a commercial formulation (Assail® 70) on the non-target gastropod Biomphalaria straminea (Mollusca: Planorbidae). Ecotoxicol. Environ Saf 192: 110248.
Fang K, Han L, Liu Y, Fang J, Wang X, Liu T (2021). Enantioselective bioaccumulation and detoxification mechanisms of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to mandipropamid. Sci Total Environ 796: 149051.
Gao Y, Wang L, Zhang X, Shi C, Ma L, Zhang X, Wang G (2022). Similarities and differences among the responses to three chlorinated organophosphate esters in earthworm: evidences from biomarkers, transcriptomics, and metabolomics. Sci Total Environ 815: 152853.
Han Y, Zhu L, Wang J, Wang J, Xie H, & Zhang S (2014) Integrated assessment of oxidative stress and DNA damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) exposed to azoxystrobin. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 107: 214–219.
Hladik ML, Main AR, Goulson D (2018) Environmental risks and challenges associated with neonicotinoid insecticides. Environ Sci Technol 3329–3335.
Kaur H, Hundal SS, Singh J (2022) Imidacloprid affects the reproductive performance and genotoxicity in Eudrilus eugeniae and Metaphire posthuma. Int j sci environ technol 1–10.
Lackmann C, Velki M, Bjedov D, Ečimović S, Seiler TB, Hollert H (2021) Commercial preparations of pesticides exert higher toxicity and cause changes at subcellular level in earthworm Eisenia andrei. Environ Sci Eur 33(1): 1–15.
Lackmann C, Šimić A, Ečimović S, Mikuška A, Seiler TB, Hollert H, Velki M (2023). Subcellular responses and avoidance behavior in Earthworm Eisenia andrei exposed to Pesticides in the Artificial Soil. Agriculture 13: 271.
Li B, Xia X, Wang J, Zhu L, Wang J, Wang G (2018) Evaluation of acetamiprid-induced genotoxic and oxidative responses in Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 161: 610–615.
Li M, Yang Y, Xie J, Xu G, Yu Y (2019). In-vivo and in-vitro tests to assess toxic mechanisms of nano ZnO to earthworms. Sci Total Environ 687:71–6.
Liu T, Wang X, You X, Chen D, Li Y, Wang F (2017) Oxidative stress and gene expression of earthworm (Eisenia fetida) to clothianidin. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 142: 489–496.
Liu T, Wang X, Chen D, Li Y, Wang F (2018) Growth, reproduction and biochemical toxicity of chlorantraniliprole in soil on earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 150: 18–25.
Ma T, Chen LK, Wu L, Zhang H, Luo Y (2016). Oxidative stress, cytotoxicity, and genotoxicity in earthworm Eisenia fetida at different di-n-butyl phthalate exposure levels. PLoS One11: e0151128.
Ma X, Li H, Xiong J, Mehler WT, You J (2019) Developmental toxicity of a neonicotinoid insecticide, acetamiprid to zebrafish embryos. J Agric Food Chem 67(9) 2429–2436.
Murano H, Suzuki K, Kayada S, Saito M, Yuge N, Arishiro T, Isoi T (2018) Influence of humic substances and iron and aluminum ions on the sorption of acetamiprid to an arable soil. Sci Total Environ 615: 1478–1484.
Narayanan M, Murugan JM, Kandasamy G, Kandasamy S, Nasif O, Rajendran M, Pugazhendhi A (2022). The biotransformation potential of Bacillus cereus on β-cypermethrin to protect the earthworm (Perionyx excavatus) on insecticide-contaminated soil. Arch Agron Soil Sci 68:944–55.
OECD (1984) Guideline for testing of chemicals no. 207. Earthworm, acute toxicity test. Organization for economic cooperation and development, Paris France.
Parente CE, da Silva EO, Júnior SFS, Hauser-Davis RA, Malm O, Correia FV, Saggioro EM (2021) Fluoroquinolone-contaminated poultry litter strongly affects earthworms as verified through lethal and sub-lethal evaluations. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 207: 111305.
Pereira PC, Soares LO, Júnior SF, Saggioro EM, Correia FV (2020). Sub-lethal effects of the pesticide imazalil on the earthworm Eisenia andrei: reproduction, cytotoxicity, and oxidative stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:33474–85.
Pietrzak D, Kania J, Kmiecik E, Malina G, Wątor K (2020) Fate of selected neonicotinoid insecticides in soil–water systems: current state of the art and knowledge gaps. Chemosphere 255:126981.
Qadri HA, Qamar A, Maheshwari N (2023). Oxidative stress, DNA damage, and histological alterations in Bombyx mori exposed orally to pesticide dimethoate. Physiol Entomol 48: 1–13.
Renaud M, Akeju T, Natal-da-Luz T, Leston S, Rosa J, Ramos F, Azevedo-Pereira HM (2018) Effects of the neonicotinoids acetamiprid and thiacloprid in their commercial formulations on soil fauna. Chemosphere 194: 85–93.
Roubalová R, Procházková P, Dvořák J, Škanta F, Bilej M (2015) The role of earthworm defense mechanisms in ecotoxicity studies. Invertebr Surviv J 12(1): 203–213.
Saggioro EM, do Espirito Santo DG, Júnior SFS, Hauser-Davis RA, Correia FV (2019) Lethal and sublethal effects of acetamiprid on Eisenia andrei: behavior, reproduction, cytotoxicity, and oxidative stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183: 109572.
Saha S, Mondal R, Mukherjee S, Sarkar M, Kole RK (2017) Persistence of acetamiprid in paddy and soil under West Bengal agro-climatic conditions. Environ Monit Assess 189(4): 150.
Simon-Delso N, Amaral-Rogers V, Belzunces LP, Bonmatin JM, Chagnon M, Downs C, Wiemers M (2015). Systemic insecticides (neonicotinoids and fipronil): trends, uses, mode of action and metabolites. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(1): 5–34.
Singh S, Sharma A, Khajuria K, Singh J, Vig AP (2020) Soil properties changes earthworm diversity indices in different agro-ecosystem. BMC ecology 20(1): 1–14.
Solé, M (2021). Biomarkers in earthworms. Interaction and Fate of Pharmaceuticals in Soil-Crop Systems: The Impact of Reclaimed Wastewater 311–337.
Song Y, Zhu LS, Wang J, Wang JH, Liu W, Xie H (2009) DNA damage and effects on antioxidative enzymes in earthworm (Eisenia foetida) induced by atrazine. Soil Biol Biochem 41(5): 905–909.
Sujeeth NK, Aravinth R, Thandeeswaran M, Angayarkanni J, Rajasekar A, Mythili R, Gnanadesigan M (2023). Toxicity analysis and biomarker response of Quinalphos Organophosphate Insecticide (QOI) on eco-friendly exotic Eudrilus eugeniae earthworm. Environ Monit Assess 195: 274.
Wang X, Zhu X, Peng Q, Wang Y, Ge J, Yang G, Shen W (2019) Multi-level ecotoxicological effects of imidacloprid on earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Chemosphere 219: 923–932.
USEPA, 2012. Ecological effects test guidelines - OCSPP 850.3100: earthworm sub chronic toxicity test. EPA 712-C-016. Available at. https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/P100IREJ.PDF?Dockey=P100IREJ.PDF
Wang G, Xia X, Yang J, Tariq M, Zhao J, Zhang M, Zhang W (2020) Exploring the bioavailability of nickel in a soil system: physiological and histopathological toxicity study to the earthworms (Eisenia fetida). J Hazard Mater 383: 121169.
Wood TJ, Goulson D (2017) The environmental risks of neonicotinoid pesticides: a review of the evidence post 2013. Environ Sci and Pollut Res 24:17285–325.
Yan X, Wang J, Zhu L, Wang J, Li S, Kim YM (2021) Oxidative stress, growth inhibition, and DNA damage in earthworms induced by the combined pollution of typical neonicotinoid insecticides and heavy metals. Sci Total Environ 754: 141873.
Yatoo AM, Ali MN, Zaheen Z, Baba ZA, Ali S, Rasool S, Sheikh TA, Sillanpää M, Gupta PK, Hamid B, Hamid B (2022). Assessment of pesticide toxicity on earthworms using multiple biomarkers: a review. Environ Chem Lett 20:2573–96.
Zhu L, Li B, Wu R, Li W, Wang J, Wang J, Zhu L (2020) Acute toxicity, oxidative stress and DNA damage of chlorpyrifos to earthworms (Eisenia fetida): the difference between artificial and natural soils. Chemosphere 255: 126982.
Zoumenou BSG, Aïna MP, Imorou Toko I, Igout A, Douny C, Brose F, Scippo, ML (2019). Occurrence of acetamiprid residues in water reservoirs in the cotton basin of Northern Benin. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102(1), 7–12.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Department of Biotechnology- BioCaRe Scheme (No. BT/PR18289/BIC/101/754/2016) and University Grants Commission- NFST Fellowship program (No: 201920-NFST-TAM-00427), India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Elango, D., Kayalvizhi, N. & Jayanthi, P. Effects of a Neonicotinoid on Indigenous Earthworm Perionyx excavatus Biochemical and Histopathological Alterations. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 110, 93 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-023-03731-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-023-03731-7