Abstract
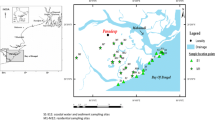
In this study, the contamination of arsenic, cadmium, nickel and vanadium in the surface sediments of Khazar Abad, in the southern part of the Caspian Sea was analyzed in 2019 using ecotoxicological indices. The geoaccumulation index (Igeo) values showed that the sediment samples of the study area could be classified as ‘unpolluted’ to ‘strongly polluted’, while, the values of toxic units (TUs) with an average value of 0.591 indicated that all samples could be classified as ‘at low toxicity level’. Moreover, the ecotoxic risk level (TRI) in the studied sediments was classified at the level of ‘no toxic risk’ for Cd and ‘considerable toxic risk’ for As and Ni. On the whole, the results showed that the levels of contamination were higher in the areas where industrial, domestic and agricultural wastewater was discharged (i.e. S4, S7, S10, S11 and S12). Finally, to avoid and/or reduce ecotoxicological dangers, periodic monitoring of PTEs in the coastal strip of the southern part of the Caspian Sea is recommended.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agah H (2021) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment, fish, and human hair from Chabahar Bay, Makoran, Iran. Mar Pollut Bull 169:112345
Alizadeh Ketek Lahijani H, Naderi Beni A, Tavakoli V (2018) Heavy metals in coastal sediments of South Caspian Sea: natural or anthropogenic source? Casp J Environ Sci 16(1):45–61)
Azimzadeh B, Khademi H (2013) Estimation of background concentration of selected heavy metals for pollution assessment of surface soils of Mazandaran Province, Iran. J Water Soil 27(3):548–559 (In Persian)
Baniamam M, Mashinchian Moradi A, Riyahi Bakhtiari A, Fatemi MR, Ejlali Khanghah K (2019) Distribution and pollution level of nickel and vanadium in sediments from south part of the Caspian Sea, Iran. Ind J Geo Mar Sci 48(05):765–771
Beg MU, Al-Muzaini S, Saeed T, Jacob PG, Beg KR, Al-Bahloul MK, Al-Matrouk K, Al-Obaid T, Kurian A (2001) Chemical contamination and toxicity of sediment from a coastal area receiving industrial effluents in Kuwait. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 41(3):289–297
Chai L, Li H, Yang Z, Min X, Liao Q, Liu Y, Men S, Yan Y, Xu J (2017) Heavy metals and metalloids in the surface sediments of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan, China: distribution, contamination, and ecological risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:874–885
Cüce H, Kalipci E, Ustaoglu F, Baser V, Türkmen M (2022) Ecotoxicological health risk analysis of potential toxic elements accumulation in the sediments of Kızılırmak River. Int J Environ Sci Technol. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03869-z
Davodpour R, Sobhanardakani S, Cheraghi M, Abdi N, Lorestani B (2019) Honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) as a potential bioindicator for detection of toxic and essential elements in the environment (Case study: Markazi Province, Iran). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 77(3):344–358
El-Tokhi M, Abdelgawad E, Lotfy M (2008) Impact of Heavy metals and Petroleum hydrocarbons contamination of the East Port Said Port area, Egypt. Appl Sci Res 4:1788–1798
Habibi H, Sobhanardakani S, Cheraghi M, Lorestani B, Kiani Sadr M (2022) Analysis, sources and health risk assessment of trace elements in street dust collected from the city of Hamedan, west of Iran. Arab J Geosci 15:168
Hosseini SM, Sobhanardakani S, Batebi Navaei M, Kariminasab M, Aghilinejad SM, Regenstein JM (2013) Metal content in caviar of wild Persian sturgeon from the southern Caspian Sea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(8):5839–5843
Jafari N (2010) Review of pollution sources and controls in Caspian Sea region. J Ecol Nat Environ 2(2):25–29
Kalani N, Riazi B, Karbassi A, Moattar F (2021) Measurement and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals accumulated in sediment and water collected from Gomishan international wetland, Iran. Water Sci Technol 84(6):1498–1508
Khademi N, Riyahi-Bakhtiari A, Sobhanardakani S, Rezaie-Atagholipour M, Burger J (2015) Developing a bioindicator in the Northwestern Persian Gulf, Iran: trace elements in bird eggs and in coastal sediments. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 68(2):274–282
Khalijian A, Lorestani B, Sobhanardakani S, Cheraghi M, Tayebi L (2021) Source identification and evaluation of contamination of some elements in surface sediments collected from Farahabad Coast, South part of Caspian Sea. Environ Water Eng. doi: https://doi.org/10.22034/JEWE.2021.314718.1671 (In Persian)
Lu X, Wang L, Lei K, Huang J (2009) Contamination assessment of copper, lead, zinc,manganese and nickel in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater 161(2–3):1058–1062
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines forfresh water ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Mazloomi S, Esmaeili-Sari A, Bahramifar N, Moeinaddini M (2017) Assessment of the metals and metalloids level in street dust of the east and west of Tehran. Iran J Health Environ 10(2):281–292 (In Persian)
Nasrabadi T, Bidhendi GN, Karbassi A, Mehrdadi N (2010) Evaluating the efficiency of sediment metal pollution indices in interpreting the pollution of Haraz River sediments, southern Caspian Sea basin. Environ Monit Assess 171(1):395–410
Nejat S, Hermidas Bavand D, Farshchi P (2018) Environmental challenges in the Caspian Sea and international responsibility of its littoral states. Casp J Environ Sci 16(2):97–110
Nowrouzi M, Pourkhabbaz A (2014) Application of geoaccumulation index and enrichment factor for assessing metal contamination in the sediments of Hara Biosphere Reserve, Iran. Chem Speciat Bioavailab 26(2):99–105
Pedersen F, Bjornestad E, Andersen HV, Kjolholt J, Poll C (1998) Characterization of sediments from Copenhagen Harbour by use of biotests. Water Sci Technol 37(6–7):233–240
Rosales-Hoz L, Carranza-Edwards A, Celis-Hernandez O (2007) Environmental implications of heavy metals in surface sediments near Isla de Sacrificios, Mexico. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 78(5):353–357
Sabet Aghlidi P, Cheraghi M, Lorestani B, Sobhanardakani S, Merrikhpour H (2020) Analysis, spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of arsenic and some heavy metals of agricultural soils, Case study: South of Iran. J Environ Health Sci Eng 18(2):665–676
Sekabira K, Oryem Origa H, Basamba TA, Mutumba G, Kakudidi E (2010) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in the urban stream sediments and its tributaries. Int J Environ Sci Tech 7(3):435–446
Saghali M, Baqraf R, Patimar R, Hosseini SA, Baniemam M (2014) Determination of heavy metal (Cr, Zn, Cd and Pb) concentration in water, sediment and benthos of the Gorgan Bay (Golestan province, Iran). Iran J Fish Sci 13(2):449–455
Sobhanardakani S (2018a) Health risk assessment of inorganic arsenic through groundwater drinking pathway in some agricultural districts of Hamedan, west of Iran. Avicenna J Environ Health Eng 5(2):73–77
Sobhanardakani S (2018b) Human health risk assessment of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn through consumption of raw and pasteurized cow’s milk. Iran J Publ Health 47(8):1172–1180
Sobhanardakani S (2019) Ecological and human health risk assessment of heavy metals content of atmospheric dry deposition, a case study: Kermanshah, Iran. Biol Trace Elem Res 187(2):602–610
Sobhanardakani S, Ghoochian M, Taghavi L (2016) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediment of the Darreh-Morad Beyg River. Iran J Health Sci 4(3):22–34
Sobhanardakani S, Tayebi L, Hosseini SV (2018) Health risk assessment of arsenic and heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Co, Pb, and Sn) through consumption of Caviar of Acipenser persicus from Southern Caspian Sea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(3):2664–2671
Tabari S, Saeedi Saravi SS, Bandany GA, Dehghan A, Shokrzadeh M (2010) Heavy metals (Zn, Pb, Cd and Cr) in fish, water and sediments sampled form Southern Caspian Sea, Iran. Toxicol Ind Health 26(10):649–656)
Xu X, Lu X, Han X, Zhao N (2015) Ecological and health risk assessment of metal in resuspended particles of urban street dust from an industrial city in China. Curr Sci 108:72–79
Xu DQ, Wang YH, Zhang RJ, Guo J, Zhang W, Yu KF (2016) Distribution, speciation, environmental risk, and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the karst aquatic environment of the Lijiang River, Southwest China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(9):9122–9133
Zhang G, Bai J, Zhao Q, Lu Q, Jia J, Wen X (2016) Heavy metals in wetland soils along a wetland-forming chronosequence in the Yellow River Delta of China: levels, sources and toxic risks. Ecol Ind 69:331–339
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Hamedan Branch, Islamic Azad University for providing facilities to conduct and complete this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khalijian, A., Lorestani, B., Sobhanardakani, S. et al. Ecotoxicological Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements (as, Cd, Ni and V) Contamination in the Sediments of Southern Part of Caspian Sea, the Case of Khazar Abad, Mazandaran Province, Iran. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 109, 1142–1149 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03621-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03621-4