Abstract
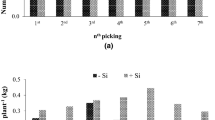
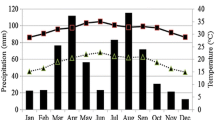
Selenium (Se) is an essential micronutrient for human beings and plants are the current main sources of Se element in Asian diet. Therefore a feasible way to increase people’s Se intake is to increase Se content in plants. In this paper, we focus on how the tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum) yield and quality are influenced by the effect of irrigation amount, Se-enriched and high-calcium organic fertilizer and compound fertilizer amount respectively. The results from a two-year experiment show that the combination of Se-enriched organic fertilizer and compound fertilizer can significantly increase the tomato yield comparing with the use of NPK organic or compound fertilizer. It is also shown that by applying more Se-enriched and high-calcium organic fertilizer the contents of Se, Lycopene, Vitamin C (Vc) and soluble sugar in tomato fruit can be increased considerably. It was found that the highest Se content was achieved using 100% Se-enriched organic fertilizer combined with irrigation at 100% in 2016 and 100% Se-enriched organic fertilizer with irrigation at 80% in 2017. Deficit irrigation (80%) can help to increase Water Use Efficiency (WUE) and the Se and VC contents in tomato yield. Therefore in order to improve the Se-enriched tomato yield and quality, it is suggested to apply 100% Se-enriched organic fertilizer and adopt the deficit irrigation at 80%.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altansuvd J, Nakamaru YM, Kasajima S, Ito H, Yoshida H (2014) Effect of long-term phosphorus fertilization on soil Se and transfer of soil Se to crops in northern Japan. Chemosphere 107:7–12
Arif M, Llyas M, Rias M (2017) Biochar improves phosphorus use efficiency of organic-inorganic fertilizers, maize-wheat productivity and soil quality in a low fertility alkaline soil. Field Crop Res 214:25–37
Badr MA, Abou-Hussein SD, EI-Tohamy WA (2016) Tomato yield nitrogen uptake and water use efficiency as affected by planting geometry and level of nitrogen in an arid region. Agric Water Manag 169:90–97
Chang C, Yin R, Wang X, Shao S, Chen C, Zhang H (2019) Selenium translocation in the soil-rice system in the Enshi seleniferous area, Central China. Sci Total Environ 669:83–90
Chen J, Wang J, Li L, Lin J, Yang K, Ma Z, Xu Z (2012) Integrated risk evaluation of multiple disasters affecting longyan yield in Fujian Province, East China. J Appl Ecol 23:819–826
Feng T, Zhou X, Yu Y, Yang J, Ma J, Xue L (2016) Influence of irrigation amount on yield and quality of tomato in greenhouse. North. Hortic 54–58
Farooq MU, Zhu J (2019) The paradox in accumulation behavior of cadmium and selenium at different planting times in rice. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:22421
Gerçek S, Demirkaya M, Işik D (2017) Water pillow irrigation versus drip irrigation with regard to growth and yield of tomato grown under greenhouse conditions in a semi-arid region. Agric Water Manag 180:172–177
Guo X, Jie X, Li M (2010) Effects of single and combined fertilization of Se and Co on growth and yield of alfalfa. J Plant Nutr 16:998–1005
He H, Dong Z, Peng Q, Wang X, Fan C, Zhang X (2017) Impacts of coal fly ash on plant growth and accumulation of essential nutrients and trace elements by alfalfa (Medicago sativa) grown in a loessial soil. J Environ Manag 197:428–439
Heeb A, Bengt L, Savage GP, Ericsson T (2006) Impact of organic and inorganic fertilizers on yield, taste, and nutritional quality of tomatoes. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 169:535–541
Huang W, Wang D, Huang S, Song Y, Yin Y (2018) Effect of tillage methods and irrigation amount on yield and quality of tomato under mulch drip irrigation. North Hortic 73–76
Jing F, Yang Z, Chen X, Liu W, Liu W (2019) Potentially hazardous element accumulation in rice tissues and their availability in soil systems after biochar amendments. J Soil Sedim 19:2957–2970
Li BY, Zhou DM, Cang L (2007) Soil micronutrient availability to crops as affected by long-term inorganic and organic fertilizer applications. Soil Till Res 96:166–173
Li HF, Lombi E, Stroud JL (2010) Selenium speciation in soil and rice: influence of water management and Se fertilization. J Agric Food Chem 58:11837–11843
Li H, Cao H, Guo L, Wu X (2016) Effect of furrow irrigation pattern and irrigation amount on comprehensive quality and yield of greenhouse tomato. Scientia Agr Sin 21:4179–4191
Li S, Li J, Zhang B, Li G, Li Y, Li D (2017a) Effect of different organic fertilizers application on tomato quality and flavor. China Soil Fertil Sci 2:114–119
Li Y, Yang J, Shi H, Li Y (2017b) Assessment of sustainable urban transport development based on entropy and unascertained measure. PLoS ONE 12:e0186893
Li Z, Liang D, Peng Q (2017c) Interaction between selenium and soil organic matter and its impact on soil selenium bioavailability. A review. Geoderma 295:69–79
Luo H, Li F (2018) Tomato yield, quality and water use efficiency under different drip fertigation strategies. Sci Hortic 235:181–188
Natasha SM, Niazi NK, Khalid S, Murtaza B, Bibi I, Rashid MI (2018) A critical review of selenium biogeochemical behavior in soil-plant system with an inference to human health. Environ Pollut 234:915–934
Olaetxea M, Hita DD, Garcia A, Fuentes M, Baigorri R, Mora V, Garnica M, Urrutia O, Erro J, Zamarreñ AM, Berbara RL, Garcia-Mina JM (2018) Hypothetical framework integrating the main mechanisms involved in the promoting action of rhizospheric humic substances on plant root- and shoot- growth. Appl Soil Ecol 123:521–537
Peng Q, Wang M, Cui Z (2017) Assessment of bioavailability of selenium in different plant-soil systems by diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT). Environ Pollut 225:637–643
Saleque MA, Abedin MJ, Bhuiyan NI, Zaman SK, Panaullah GM (2004) Long-term effects of inorganic and organic fertilizer sources on yield and nutrient accumulation of lowland rice. Field Crop Res 86:53–65
Sarma B, Gogoi N, Bharali M, Mali P (2017) Field evaluation of soil and wheat responses to combined application of hardwood biochar and inorganic fertilizers in acidic sandy loam soil. Exp Agric 54:1–13
Shahrokhnia MH, Sepaskhah AR (2016) Effects of irrigation strategies, planting methods and nitrogen fertilization on yield, water and nitrogen efficiencies of safflower. Agric Water Manag 172:18–30
Sharma VK, McDonald TJ, Sohn M (2015) Biogeochemistry of selenium. A review. Environ Chem Lett 13:49–58
Su HQ, Chen GF, Zhu CR (2010) A combination forecasting model for corn yield based on entropy weight. J Sheny Agric Univ 4:125–127
Sui J, Wang J, Gong S (2018) Assessment of maize yield-increasing potential and optimum N level under mulched drip irrigation in the Northeast of China. Field Crop Res 215:132–139
Sun Y, Wu W, Liu Y, Meng F (2017) Effects of organic and mineral fertilizers on nitrogen utilization and losses. J China Agric Univ 22:37–46
Sutton KF, Lanini TW, Mitchell JP, Miyao EM, Shresta A (2006) Weed control, yield, and quality of processing tomato production under different irrigation, tillage, and herbicide systems. Weed Technol 20:831–838
Tonfack LB, Bernadac A, Youmbi E, Mbouapouognigni VP (2009) Impact of organic and inorganic fertilizers on tomato vigor, yield and fruit composition under tropical andosol soil conditions. Fruits 64:167–177
Wang D, Huang W, Liu Y, Wang Y, Huang Y, Song Y (2015) Effects of integration of irrigation and fertilization(drip fertigation) on growth, fiber yield and quality of kenaf. J South Agric 46:204–209
Wang D, Li F, Nong M (2017) Response of yield and water use efficiency to different irrigation levels at different growth stages of Kenaf and crop water production function. Agric Water Manag 179:177–183
Wang X, Yan YM (2013) Entropy coefficient assessment of mulch drip irrigation scheme in tobacco fields. Adv Mater Res 726–731:3077–3083
Yan J (2014) 15N tracing technique based evaluation of entropy weight coefficients of water and nitrogen coupling schemes for flue-cured tobacco. J Northwest A&F Univ 42:25–31
Zhang E, Tan F, Wang Y, Zhang S, Duan Y, Zhou F (2015) Effects of NPK fertilizers and organic manure on nutritional quality, yield of tomato and soil enzyme activities. Acta Hortic Sin 42:2059
Zhang G, Zhou L, Cai D, Wu Z (2017) Anion-responsive carbon nanosystem for controlling selenium fertilizer release and improving selenium utilization efficiency in vegetables. Carbon 129:711–719
Zhang Q, Wang H, Kong Q, Li F, An M, Luo T (2018) Effects of wetting and drying alternated irrigation on soil selenium forms and rice Selenium accumulation in Se-enriched soil. J Soil Water Conserv 32:327–331
Zhang Y, Li C, Wang Y, Hu Y, Chris P, Zhang J, Li X (2016) Maize yield and soil fertility with combined use of compost and inorganic fertilizers on a calcareous soil on the North China Plain. Soil Till Res 155:85–94
Zhao F, Sun J, Jiang Y (2018) Effect of rhizosphere aeration by subsurface drip irrigation with tanks on the growth of ‘Red Globe’ grape seedling and its absorption, distribution and utilization of urea- 15N. Sci Hortic 236:207–213
Zhong F, Hou M, He B, Chen I (2017) Assessment on the coupling effects of drip irrigation and organic fertilization based on entropy weight coefficient model. PeerJ 5:e3855
Zhou B, Sun X, Ding Z, Ma W (2017) Multisplit nitrogen application via drip irrigation improves Maize grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency. Crop Sci 57:65
Zhou C, Hu Y, Zeng J, Yang J, Chen L (2015) Effects of soil factors on the Selenium absorption characteristics of tea plant. J Tea Sci 5:429–436
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the research Grants from Guangxi Science and Technology Program Project of China (GuiKe AA17202037, GuiKe AD19245169, GuiKe AD18281072), Yulin Science and Technology Program Project(Yushikeneng 20194301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WH analyzed the data, contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. YZ performed the experiments, DW conceived and designed the experiments, reviewed drafts of the paper, NW translation papers, revision of the paper.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, W., Zhu, Y., Wang, D. et al. Assessment on the Coupling Effects of Drip Irrigation and Se-Enriched Organic Fertilization in Tomato Based on Improved Entropy Weight Coefficient Model. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106, 884–891 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03156-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03156-0