Abstract
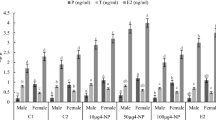
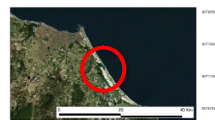
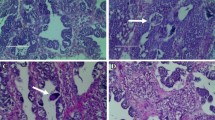
This study was conducted to measure 17β-estradiol (E2) levels in Laguna de Bay, Philippines and to examine feral male common carp for evidence of exposure to estrogenic pollutants. Analysis of water samples revealed E2 concentrations of 630 and 550 ng/L from the east and west bay of the lake, respectively. Plasma vitellogenin (VTG) in captured fish ranged from 506 to 4083 ng/mL. In comparison to the reference and west bay groups, fish from the east bay had higher plasma VTG concentrations and reduced gonadosomatic index (GSI). Ovotestis was not observed although some individuals had endocrine-related histopathological alterations in the testis. The degree of biologic effects induced by estrogenic pollutants in tropical freshwater systems like Laguna de Bay need to be further investigated to provide a better comprehension of the fates and effects of these compounds under tropical conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avar P, Zrínyi Z, Maász G, Takátsy A, Lovas S, G-Tóth L, Pirger Z (2016) β-estradiol and ethinyl-estradiol contamination in the rivers of the Carpathian Basin. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:11630. doi:10.1007/s11356-016-6276-2
Chavez HM, Casao EA, Villanueva EP, Paras MP, Guinto MC, Mosqueda MB (2006) Heavy metal and microbial analyses of janitor fish (Pterygoplichthys spp.) in Laguna de Bay, Philippines. J Environ Sci Manag 9(2):31–40
Chen C-Y, Wen T-Y, Wang G-S, Cheng H-W, Lin Y-H, Lien G-W (2007) Determining estrogenic steroids in Taipei waters and removal in drinking water treatment using high-flow solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Sci Total Environ 378:352–365
Chou PH, Lin YL, Liu TC, Chen KY (2015) Exploring potential contributors to endocrine disrupting activities in Taiwan’s surface waters using yeast assays and chemical analysis. Chemosphere 138:814–820
Duong CN, Ra JS, Cho J, Kim SD, Choi HK, Park J, Kim KW, Inam E, Kim SD (2010) Estrogenic chemicals and estrogenicity in river waters of South Korea and seven Asian countries. Chemosphere 78:286–293
EPA (2005) Environmental Protection Agency – Danish Ministry of the Environment. Survey of estrogenic activity in the Danish aquatic environment. Environ Project Nr 977:1–170
Gimeno S, Komen H, Venderbosch PWM, Bowmer T (1998) Disruption of sexual differentiation in genetic male common carp (Cyprinus carpio) exposed to an alkylphenol during different life stages. Environ Sci Technol 31:2884–2890
Gross-Sorokin MY, Roast SD, Brighty GC (2006) Assessment of feminization of male fish in English rivers by the environment agency of England and Wales. Environ Health Perspect 114:147–151
Hale RC, La Guardia MJ (2002) Emerging contaminants of concern in coastal and estuarine environments. In: Newman MC, Roberts MH Jr, Hale RC (eds) Coastal and estuarine risk assessment. CRC Press/Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, p 41–72
Hashimoto S, Bessho H, Hara A, Nakaura M, Iguchi T, Fujita J (2000) Elevated serum vitellogenin levels and gonadal abnormalities in wild male flounder (Pleuronectes yokohamae) from Tokyo Bay, Japan. Mar Environ Res 49:37–53
Hassanin J, Kuwahara S, Nurdihayat Y, Tsukamoto Y, Ogawa K, Hiramitsu K, Sasaki F (2002) Gonadosomatic index and testis morphology of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) in rivers contaminated with estrogenic chemicals. J Vet Med Sci 64(10):921–926
Jobling S, Beresford N, Nolan M, Rodgers-Gray T, Brighty GC, Sumpter JP, Tyler CR (2002a) Altered sexual maturation and gamete production in wild roach (Rutilus rutilus) living in rivers that receive treated sewage effluents. Biol Reprod 66:272–281
Jobling S, Coey S, Whitmore JG, Kime DE, Van Look KJW, McAllister BG, Beresford N, Henshaw AC, Brighty G, Tyler CR, Sumpter JP (2002b) Wild intersex roach (Rutilus rutilus) have reduced fertility. Biol Reprod 67:515–524
Kumar V, Johnson AC, Nakada N, Yamashita N, Tanaka H (2012) De-conjugation behavior of conjugated estrogens in the raw sewage, activated sludge and river water. J Hazard Mater 227–228:49–54
Lahr J, Kuiper R, Van Mullem A, Verboom B, Jol J, Schout P, Grinwis G, Rouhani T, Pieters J, Gerritsen A, Giesy J, Vethaak A (2006) A field survey of estrogenic effects in freshwater and marine fish in the Netherlands. In: Vethaak D, Schrap M, de Voogt P (eds) Estrogens and xenoestrogens in the aquatic environment: an integrated approach for field monitoring and effect assessment. Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC), The Hague, p 168–173
Ma T, Wan X, Huang Q, Wang Z, Liu J (2005) Biomarker responses and reproductive toxicity of the effluent from a Chinese large sewage treatment plant in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Chemosphere 59:281–288
Miles-Richardson SR, Kramer VJ, Fitzgerald SD, Render JA, Yamini B, Barbee SJ, Giesy JP (1999) Effects of waterborne exposure of 17β-estradiol on secondary sex characteristics and gonads of fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). Aquat Toxicol 47:129–145
Nash JP, Kime DE, Van der Ven LT, Wester PW, Brion F, Maack G, Stahischmidt-Aliner P, Tyler CR (2004) Long-term exposure to environmental concentrations of the pharmaceutical ethynylestradiol causes reproductive failure in fish. Environ Health Perspect 112(17):1725–1733
Nepomuceno DN (2010) Improving water security for the future: learning from the IWRM experience in Laguna de Bay. http://www.tecniberia.es/jornadas/documentos/papers/3_DOLORA%20NEPOMUCENO_PAPER.pdf. Accessed 28 May 2016
Nie M, Yan C, Dong W, Liu M, Zhou J, Yang Y (2015) Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment of estrogens in surface water, suspended particulate matter, and sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. Chemosphere 127:109–116. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.01.021
OECD (2010) Guidance document on the diagnosis of endocrine-related histopathology in fish gonads. OECD series on testing and assessment no. 123. Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris, p 182
Pait AS, Nelson JO (2002) Endocrine disruption in fish: an assessment of recent research and results. NOAA technical memorandum 149. US Department of Commerce, Baltimore, p 13–15
Paraso MG, Capitan SS (2012) Vitellogenin induction and gonad abnormalities in male common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) introduced to Laguna de Bay, Philippines. Philipp J Vet Anim Sci 38:34–44
Paraso MGV, Espaldon MVO, Alcantara AJ, Sevilla CC, Alaira SA, Sobremisana MJ, Ravalo RO, Macan KRD, Valdez CA (2010) A survey of waste management practices of selected swine and poultry farms in Laguna, Philippines. J Environ Sci Manag 13(2):44–52
Partnerships in Environmental Management for the Seas of East Asia (PEMSEA), Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) and the Laguna Lake Development Authority (2013) Total Pollutant Loading Study in the Laguna de Bay–Pasig River–Manila Bay Watershed. http://www.pemsea.org/sites/default/files/Total-Pollutant-Loading-Study-Laguna-de-Bay-Pasig-River-Manila-Bay-Watershed.pdf. Accessed 18 May 2016
Pereira JJ, Mercaldo-Allen R, Kuropat C, Luedke D, Sennefelder G (1993) Effect of cadmium accumulation on serum vitellogenin levels and hepatosomatic and gonadosomatic indices of winter flounder (Pleuronectes americanus). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 24(4):427–431
Santos-Borja AC, Nepomuceno DN (2003) Experience and lessons learned brief for Laguna de Bay, Philippines. Proceedings of the Lake Basin Management 26 Initiative ILEC/LakeNet Regional Workshop for Asia: sharing experience and lessons learned in Lake Basin Management. Manila, Philippines.
Söffker M, Tyler CR (2012) Endocrine disrupting chemicals and sexual behaviors in fish – a critical review on effects and possible consequences. Crit Rev Toxicol 42(8):653–668
Swartz CH, Reddy S, Benotti MJ, Yin H, Barber LB, Brownawell BJ, Rudel RA (2006) Steroid estrogens, nonylphenol ethoxylate metabolites, and other wastewater contaminants in groundwater affected by a residential septic system in Cape Cod, MA. Environ Sci Technol 40:4894–4902
Vajda AM, Norris DO (2011) Endocrine-active chemicals in fishes. In: Norris DO and Lopez KH (eds) Hormones and reproduction of vertebrates, Vol 1: Fishes, 1st Ed. Academic Press, London, p 245–264
Wright-Walters M, Volz C (2009) Municipal wastewater concentrations of pharmaceutical and xeno-estrogens: wildlife and human health implications. In: Uzochukwu GA (ed) Proceedings of the 2007 National Conference on Environmental Science and Technology. Springer, New York, p 103–113
Zaroogian G, Gardner G, Horowitz DB, Gutjahr-Gobell R, Haebler R, Mills L (2001) Effect of 17beta-estradiol, o, p’-DDT, octylphenol and p, p’-DDE on gonadal development and liver and kidney pathology in juvenile male summer flounder (Paralichthys dentatus). Aquat Toxicol 54(1–2):101–112
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Research Council of the Philippines for funding this study, and the Institute of Chemistry and the Limnological Station of the University of the Philippines Los Baños for the use of their laboratory equipment and facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paraso, M.G.V., Morales, J.K.C., Clavecillas, A.A. et al. Estrogenic Effects in Feral Male Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) from Laguna de Bay, Philippines. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98, 638–642 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2060-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2060-3