Abstract
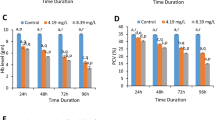
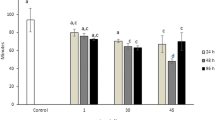
Poecilia reticulata were exposed to herbicide Roundup Transorb® for micronucleus test, nuclear abnormalities and comet assay. The exposure-concentrations were based on CL50–96 h following 0, 1.41, 2.83, 4.24 and 5.65 μL L−1 for 24 h. Micronucleus and comets were significantly increased in the gill erythrocyte cells after herbicide exposure compared with the non-exposed group. Results showed a gradual increase in the number of damaged cells, indicating a concentration-dependent effect and that this herbicide was mutagenic and genotoxic to P. reticulata and this effect could be attributed to a combination of compounds contained in the formulation with the active ingredient glyphosate.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayllón F, Garcia-Vasquez E (2001) Micronuclei and other nuclear lesions as in trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 49:221–225
Bolis CL, Piccolella M, Dalla Valle AZ, Rankin JC (2001) Fish as model in pharmacological and biological research. Pharmacol Res 44:265–280
Bolognesi C, Bonatti S, Degan P, Gallerani E, Peluso M, Rabboni R, Roggieri P, Abbondandolo A (1997) Genotoxic activity of glyphosate and its technical formulation Roundup®. J Agric Food Chem 45:1957–1962
Cadet J, Douki T, Gasparutto D, Ravana JL (2003) Oxidative damage to DNA: formation, measurement and biochemical features. Mutat Res 531:5–23
Çaglar S, Kolankaya D (2008) The effect of sub-acute and subchronic exposure of rats to the glyphosate-based herbicide. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol l25:57–62
CAS (2010) Division of the American Chemical Society. www.cas.org/proucts/index.html. Accessed 10 Jul 2010
Çavas T, Konen S (2007) Detection of cytogenetic and DNA damage in peripheral erythrocytes of goldfish (Carassius auratus) exposed to a glyphosate formulation using the micronucleus test and the comet assay. Mutagenesis 22:263–268
Clements C, Ralph S, Petras M (1997) Genotoxicity of selected herbicides in Rana catesbeiana tadpoles using the alkaline single-cell gel DNA electrophoresis (comet). Environ Mol Mutagen 29:277–288
Constantz GD (1989) Reproductive biology of poeciliid fishes. In: Meffe GK, Snelson FF (eds) Ecology and evolution of live bearing fishes (Poecciliidae). Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, pp 35–50
Dimitrov BD, Gadeva PG, Benoa DK, Bineva MV (2006) Comparative genotoxicity of the herbicides Roundup®, stomp and reglone in plant and mammalian test systems. Mutagenesis 21:375–382
Fenech M, Cheng WP, Kirsch-Volders M, Holland N, Bonassi S, Zeiger E, Human micronucleus project (2003) Human project: detailed description of the scoring criteria for the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay using isolated human lymphocyte cultures. Mutat Res 534:65–75
Fenech M, Kirsch-Volders M, Natarajan AT, Surralles J, Crott JW, Parry J, Norppa H, Eastmond DA, Tucker JD, Thomas P (2011) Molecular mechanisms of micronucleus, nucleoplasmic bridges and nuclear bud formation in mammalian and human cells. Mutagenesis 26:125–132
Goldsborough LG, Brown DJ (1993) Dissipation of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in water and sediments of boreal forest ponds. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:1139–1147
Gopalan HNB, Njagi GDE (1981) Mutagenicity testing of pesticides. III. Drosophila: recessive sex-linked lethals. Genetics 97(suppl):s44
Grisolia CK (2002) A comparison between mouse and fish micronucleus test using cyclophosphamide, mitomycin C and various pesticides. Mutat Res 518:145–150
Howe CM, Berrill M, Pauli BD, Helbing CC, Werry K, Veldhoen N (2004) Toxicity of glyphosate-based pesticides to four North American frog species. Environ Toxicol and Chem 23:1928–1938
Kolpin D, Thurman M (2006) Urban contributions of glyphosate and its degradate AMPA to streams in the United States. Sci Total Environ 354:191–197
Langiano VC, Martinez CB (2008) Toxicity and effects of a glyphosate-based herbicide on the Neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Comp Biochem Physiol Toxicol Pharmacol 147:222–2231
Li AP, Long TJ (1998) An evaluation of the genotoxic potential of glyphosate. Fundam Appl Toxicol 10:537–546
Mañas F, Peralta L, Raviolo J, Ovando HG, Weyers A, Ugnia L, Cid MG, Larripa I, Gorla N (2009) Genotoxicity of glyphosate assessed by the comet assay and cytogenetic tests. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 28:37–41
Moriya M, Ohta T, Watanabe K, Miyazawa T, Kato K, Shirasu Y (1983) Further mutagenicity studies on pesticides in bacterial reversion assay systems. Mutat Res 116:185–216
OECD (1997) Organization for economic co-operation and development. Guideline for the testing of chemicals. Mammalian erythrocyte micronucleus tests 474, Paris
Paz-Y-Miño C, Sánchez ME, Arévalo M, Muñoz JM, Witte T, De-la-Carrera GO, Leone PE (2007) Evaluation of DNA damage in an Ecuadorian population exposed to glyphosate. Genet Mol Biol 30:456–460
Peluso M, Munnia A, Bolognesi C, Parodi S (1998) P-Poslabeling detection of DNA adducts in mice treated with the herbicide Roundup. Environ Mol Mutagen 31:55–59
Plhalová L, Mácová S, Doleželová P, Maršálek P, Svobodová Z, Pištěková V, Bedáňová I, Voslářová E, Modrá H (2010) Comparison of terbutryn acute toxicity to Danio rerio and Poecilia reticulata. Acta Vet Brno 79:593–598
Rank J, Jensen AG, Skov B, Pederson LH, Jensen K (1993) Genotoxicity testing of the herbicide Roundup® and its active ingredient glyphosate isopropylamine using the mouse bone marrow micronucleus test, Salmonella mutagenicity test, and Allium cepa anaphase–telophase test. Mutat Res 300:29–36
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Williams GM, Kroes R, Munro IC (2000) Safety evaluation and risk assessment of the herbicide Roundup® and its active ingredient, glyphosate for humans. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol l31:117–165
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Council of Scientific and Technologic Development (CNPq-Brazil). J. de Souza Filho had a fellowship from CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Souza Filho, J., Sousa, C.C.N., Da Silva, C.C. et al. Mutagenicity and Genotoxicity in Gill Erythrocyte Cells of Poecilia reticulata Exposed to a Glyphosate Formulation. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91, 583–587 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1103-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1103-7