Abstract
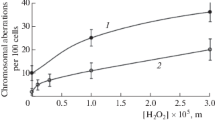
Hospital effluents are serious problems in developing countries like Brazil, and when not treated adequately, can cause mutagenic effects on live organisms. Biomonitors, like Allium cepa L., which is one of the most used plant species when monitoring effluent genotoxicity, have been used to alert the world population about environmental contamination and genotoxic chemical emissions. The Allium cepa test was used to evaluate the genotoxicity of a hospital effluent in Santa Maria, Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil. During the study, chromosomal disruptions, anaphasic bridges, and micronuclei during telophase were observed, indicating environmental toxicity risk.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayres M, Ayres JRM (2003) BioEstat 3.0: aplicações estatísticas nas aréas das ciências biológicas e médicas. Belém, Sociedade Civil Mamiraua, Brasília, p 291
Bassi MD, Moretton J (2003) Mutagenicity of antineoplastic drug residues treated in health care waste autoclave. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 71:170–175. doi:10.1007/s00128-003-0145-7
Costa RMA, Menk CFM (2000) Biomonitoramento de mutagênese ambiental. In: Biotecnologia (ed) Ciência & Desenvolvimento, vol 2. pp 24–26
El-Shahaby AO, Abdel Migid HM, Soliman MI, Mashaly IA (2003) Genotoxicity screening of industrial wastewater using the Allium cepa chromosome aberration assay. Pak J Biol Sci 6:23–28
Fiskejö G (1993) The Allium test. In: Wastewater monitoring. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 8:291–298. doi:10.1002/tox.2530080306
Gadano A, Gurni A, López P, Ferraro G, Carballo M (2002) In vitro genotoxic evaluation of the medicinal plant Chenopodium ambrosioides. L. J Ethnopharmacol 81:11–16. doi:10.1016/S0378-8741(01)00418-4
Guerra M, Lopes MJS (2002) Como observar cromossomos—Um guia de técnicas em citogenética vegetal, animal e humana. FUNPEC, vol 1. Ribeirão Preto, p 131
Paz M, Muzio H, Mendelson A, Magdaleno A, Tornello NB, Moretton J (2006) Evaluation of genotoxicity of Buenos Aires city hospital wastewater samples. J Braz Soc Ecotoxicol 1(1):1–6
Rank J (2003) The method of Allium anaphase–telophase chromosome aberration assay. Ekologiia (Vilnius) 1:38–41
Silva J, Erdtmann B, Henriques JAP (2003) Genética toxicológica. Alcance, Porto Alegre, pp 70–74
Vicentini VEP, Camparoto ML, Teixeira RO, Mantovani MS (2001) Averrhoa carambola L., Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels and Cissus sicyoides L.: medicinal herbal tea effects on vegetal and test systems. Acta Scientiarum 23(2):593–598
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bagatini, M.D., Vasconcelos, T.G., Laughinghouse, H.D. et al. Biomonitoring Hospital Effluents by the Allium cepa L. Test. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82, 590–592 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9666-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9666-z