Abstract
Aims/hypothesis
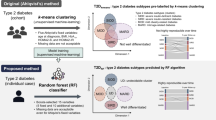
Five clusters based on clinical characteristics have been suggested as diabetes subtypes: one autoimmune and four subtypes of type 2 diabetes. In the current study we replicate and cross-validate these type 2 diabetes clusters in three large cohorts using variables readily measured in the clinic.
Methods
In three independent cohorts, in total 15,940 individuals were clustered based on age, BMI, HbA1c, random or fasting C-peptide, and HDL-cholesterol. Clusters were cross-validated against the original clusters based on HOMA measures. In addition, between cohorts, clusters were cross-validated by re-assigning people based on each cohort’s cluster centres. Finally, we compared the time to insulin requirement for each cluster.
Results
Five distinct type 2 diabetes clusters were identified and mapped back to the original four All New Diabetics in Scania (ANDIS) clusters. Using C-peptide and HDL-cholesterol instead of HOMA2-B and HOMA2-IR, three of the clusters mapped with high sensitivity (80.6–90.7%) to the previously identified severe insulin-deficient diabetes (SIDD), severe insulin-resistant diabetes (SIRD) and mild obesity-related diabetes (MOD) clusters. The previously described ANDIS mild age-related diabetes (MARD) cluster could be mapped to the two milder groups in our study: one characterised by high HDL-cholesterol (mild diabetes with high HDL-cholesterol [MDH] cluster), and the other not having any extreme characteristic (mild diabetes [MD]). When these two milder groups were combined, they mapped well to the previously labelled MARD cluster (sensitivity 79.1%). In the cross-validation between cohorts, particularly the SIDD and MDH clusters cross-validated well, with sensitivities ranging from 73.3% to 97.1%. SIRD and MD showed a lower sensitivity, ranging from 36.1% to 92.3%, where individuals shifted from SIRD to MD and vice versa. People belonging to the SIDD cluster showed the fastest progression towards insulin requirement, while the MDH cluster showed the slowest progression.
Conclusions/interpretation
Clusters based on C-peptide instead of HOMA2 measures resemble those based on HOMA2 measures, especially for SIDD, SIRD and MOD. By adding HDL-cholesterol, the MARD cluster based upon HOMA2 measures resulted in the current clustering into two clusters, with one cluster having high HDL levels. Cross-validation between cohorts showed generally a good resemblance between cohorts. Together, our results show that the clustering based on clinical variables readily measured in the clinic (age, HbA1c, HDL-cholesterol, BMI and C-peptide) results in informative clusters that are representative of the original ANDIS clusters and stable across cohorts. Adding HDL-cholesterol to the clustering resulted in the identification of a cluster with very slow glycaemic deterioration.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.

Introduction
A recent study stratified people with any form of diabetes into five clusters based on six clinical variables, i.e. age, GAD antibodies, BMI, HbA1c, insulin resistance (HOMA2-IR) and beta cell function estimates (HOMA2-B) [1]. The five clusters were characterised by autoimmunity (severe autoimmune diabetes [SAID]), insulin deficiency (severe insulin-deficient diabetes [SIDD]), insulin resistance (severe insulin-resistant diabetes [SIRD]), high BMI (mild obesity-related diabetes [MOD]) and the last without any extreme characteristics other than high age (mild age-related diabetes [MARD]) [1]. Clustering of people with diabetes has been repeated successfully in several other studies based on these variables in people of European descent and of other ethnicities and based on different clinical measures [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. In addition, the original and subsequent papers have shown that people in different clusters have different risks for a number of diabetes-related outcomes [1,2,3,4]. The autoimmunity and insulin-deficient clusters were defined by high HbA1c at diagnosis, had higher risk for ketoacidosis and retinopathy [2, 7], and progressed more rapidly onto insulin relative to the other clusters [1]. Moreover, a recent study comprising multiple cohorts enriched for cardiovascular risk assigned people to the clusters identified by Ahlqvist et al [1] based on the distance to the respective cluster centres. In this study, people in the SIDD cluster showed higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events [5]. For the insulin-resistant cluster, a higher frequency of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease has been observed and people in this group were at increased risk of developing chronic kidney disease [1]. As HOMA2 calculations require fasting insulin or C-peptide and fasting glucose, their measurement is not routine in clinical practice.
The aim of the current study is to perform a systematic replication and cross-validation of clustering based on five routine clinical variables in three large international cohorts (Diabetes Care System [DCS], All New Diabetics in Scania [ANDIS], Genetics of Diabetes Audit and Research Tayside Study [GoDARTS]). In ANDIS, we directly compare the current clusters with those identified in the original study [1].
Methods
Cohort descriptions
Data from 15,940 individuals with type 2 diabetes from three cohorts, DCS (Netherlands), GoDARTS (Scotland) and ANDIS (Sweden), were used in this cross-sectional study within the RHAPSODY consortium. RHAPSODY (Risk Assessment and ProgreSsiOn of Diabetes, https://imi-rhapsody.eu) is an Innovative Medicine Initiative project and one of the aims is to improve the segmentation of people with type 2 diabetes, supporting the implementation of novel strategies for diabetes prevention and treatment. Inclusion criteria for RHAPSODY were age of diagnosis ≥35, clinical data available within 2 years after diagnosis, GAD negative, no missing data in one of the five clinical measures used for clustering and the presence of genome-wide association study (GWAS) data.
Hoorn DCS cohort
The Hoorn DCS cohort is an open prospective cohort started in 1998 with currently over 14,000 individuals with type 2 diabetes from the north-west part of the Netherlands [10]. The study has been approved by the Ethical Review Committee of the Vrije Universiteit University Medical Center, Amsterdam. People visit DCS annually to monitor their diabetes. During this visit, multiple measurements are collected as part of routine care, including anthropometric and laboratory measurements. Measurements were used anonymously. Individuals were informed about the use of their data and were offered an opt-out. All laboratory measurements were done on samples taken in a fasted state. HbA1c measurements were performed using the turbidimetric inhibition immunoassay for haemolysed whole EDTA blood (Cobas c501, Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany, run CV 1.6%) [10]. HDL-cholesterol (mmol/l) was measured enzymatically (Cobas c501, Roche Diagnostics). C-peptide was measured on a DiaSorin Liaison (DiaSorin, Saluggia, Italy). In total, 2953 individuals matched the inclusion criteria.
GoDARTS
For clinical purposes, individuals with diabetes mellitus from the Tayside region of Scotland (n = 391,274; January 1996) were added to the Diabetes Audit and Research Tayside Study (DARTS) register [11]. Retrospective and prospective longitudinal anonymised data were collected, including data on prescribing and biochemistry and clinical data. All laboratory measurements were measured in a non-fasted state. People with type 2 diabetes were asked to participate in the Genetics of DARTS study (GoDARTS), which currently includes over 10,000 individuals with type 2 diabetes [11]. The GoDARTS study was approved by the Tayside Medical Ethics Committee. Informed consent was obtained from all participants. C-peptide was measured on a DiaSorin Liaison. In total, 5509 individuals matched the inclusion criteria.
ANDIS
The ANDIS cohort aims to recruit all people with incident diabetes within Scania County, Sweden. Recruitment started in January 2008 until November 2016. People are included in the study close to diagnosis, with a median of 40 days (IQR 12–99). All laboratory measurements were measured in a fasted state. HbA1c measurements were obtained from the Clinical Chemistry database. C-peptide was determined with an electro-chemiluminescence immunoassay on a Cobas e411 (Roche Diagnostics) or by a radioimmunoassay (Human C-peptide radioimmunoassay; Linco, St Charles, MO, USA; or Peninsula Laboratories, Belmont, CA, USA). In total, 7478 individuals matched the inclusion criteria.
Statistical analysis
Clustering was performed on five risk factors for type 2 diabetes progression [12]: age at first visit (years); BMI (kg/m2); HbA1c (mmol/mol); HDL-cholesterol (mmol/l); and C-peptide (nmol/l). C-peptide was included as a proxy of insulin resistance and, to some extent, beta cell function (electronic supplementary material [ESM] Table 1) in absence of fasting glucose in GoDARTS (preventing the use of HOMA). HDL-cholesterol levels were included as lower HDL-cholesterol has previously been recognised as a risk factor for time to insulin requirement [12]. Clustering was performed separately in each cohort and stratified by sex. Clusters were defined based on k-means using the kmeansruns function in the R package fpc (https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/fpc/index.html). The optimal number of clusters was determined using the gap statistic across the three cohorts [13], this being defined as the point where the curve of the gap statistic vs the number of clusters flattened, with little added value of increasing the number of clusters. The stability of the clusters was assessed in two ways. The clusters identified here in ANDIS using C-peptide instead of HOMA2 were compared with their previously published clusters based on HOMA2 [1]. Second, identified clusters were cross-validated between cohorts to assess their stability. For this, individuals from cohort A were assigned to clusters based on the cluster centres of each of the clusters identified in cohort B. This approach will quantify the probability that an individual in cohort A will be assigned to the same cluster, but based on the clustering model for cohort B. Next, predicted clusters in cohort A based on the clusters of cohort B were compared with the ‘real’ clusters of cohort A. This was done for each of the three pairwise comparisons (DCS–GoDARTS, DCS–ANDIS, GoDARTS–ANDIS). Agreement between clusters was assessed based on the specificity and sensitivity.
Time to insulin requirement was defined as the period until an individual started sustained (more than 6 months in duration) insulin treatment or required insulin, defined as ≥2 HbA1c measurements >69 mmol/mol (8.5%) at least 3 months apart and when on ≥2 non-insulin glucose-lowering drugs. Cox proportional hazard models were used where one cluster was tested against the other clusters as a reference group in each individual cohort. Thereafter, results were meta-analysed using random effects meta-analysis using the metagen function from the meta package (https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/meta/index.html). Analyses were performed using R statistics (version 3.6.2; https://www.r-project.org/). Figures were produced using the R packages ggplot2 (v3.3.0) (https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggplot2/index.html) and omicCircos (v1.22.0) (http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/OmicCircos.html).
Results
Clustering in three large cohorts based on clinical measures
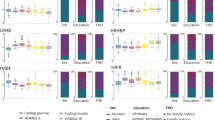
In this cross-sectional study, 15,940 individuals from three cohorts were included, for which baseline characteristics are given in Table 1. The characteristics of the three cohorts were generally comparable, with the majority male participants and an average age of around 60 years. Individuals were clustered based on age, BMI, HbA1c, C-peptide and HDL-cholesterol. The optimal number of clusters was based on the gap statistic across the three cohorts. In GoDARTS the optimal number of clusters was five, with lower gap statistics from six onwards. In DCS and ANDIS, the increase in gap statistic showed a clear stabilisation after five clusters. Therefore, we considered five the most optimal number of clusters (ESM Fig. 1a). The first cluster comprised 13–17% of the individuals included. It was characterised by high HbA1c, but, compared with the other clusters, participants were younger with lower BMI, C-peptide and HDL-cholesterol levels. When compared with the original clusters in ANDIS [1], this cluster was most similar to the SIDD cluster with a sensitivity (SEM) of 90.7% (CI 88.4%, 92.6%; Fig. 1, ESM Fig. 1b) [1]. Between 9% and 22% of individuals clustered to a cluster with high C-peptide levels and age, but relatively lower HbA1c and HDL-cholesterol levels, suggestive of insulin resistance. Indeed, compared with the ANDIS clusters, this cluster resembled most the SIRD cluster with an SEM of 92.4% (CI 89.7%, 94.6%; Fig. 1, ESM Fig. 1b) [1]. The third cluster comprised participants with high BMI and the youngest age and relatively lower levels of HbA1c and HDL-cholesterol. It was most similar to the originally described MOD cluster with an SEM of 80.6% (CI 78.4%, 82.7%) and comprised 18–23% of the individuals included in the study. The fourth and fifth clusters were most similar to the MARD cluster and showed a combined sensitivity of 79.1% (CI 77.5%, 80.6%) against the MARD cluster in ANDIS (Fig. 1, ESM Fig. 1b) [1]. The fourth cluster, which was also the largest, encompassing 29–35% of the individuals, showed no extreme characteristics and was termed mild diabetes (MD). The fifth cluster was characterised by higher age and HDL-cholesterol and was termed mild diabetes with high HDL-cholesterol (MDH), and comprised 16–19% of the individuals (Fig. 1). Between male and female participants there were small differences in characteristics, but the overall differences between clusters were similar across both sexes (ESM Fig. 2).
Characteristics of the clusters. (a–e, g–k, m–q) Characteristics of the five clusters across the three cohorts; DCS (a–e), GoDARTS (g–k) and ANDIS (m–q); x-axis, cluster; y-axis, age, BMI, HbA1c, HDL-cholesterol and C-peptide. (f, l, r) Frequency and percentage of individuals in each of the clusters; DCS (f), GoDARTS (l) and ANDIS (r)
Clusters cross-validate between the three cohorts
To assess the stability across cohorts, clusters were cross-validated between cohorts. Clusters generally cross-validated well between the three cohorts (ESM Fig. 3, ESM Table 2). The SIDD and MDH clusters showed the highest sensitivity of the five clusters identified, ranging from 85.6% (CI 83.5%, 87.6%) to 97.1% (CI 94.8%, 98.5%) in SIDD and from 73.3% (CI 69.5%, 77.0%) to 92.9% (CI 91.3%, 94.3%) in MDH (ESM Fig. 3, ESM Table 2). The SIRD and MD clusters performed generally worst in terms of sensitivity, with sensitivities ranging from 36.1% (CI 32.3%, 39.9%) to 92.3% (CI 90.1%, 94.2%) in SIRD and from 40.8% (CI 38.9%, 42.7%) to 78.1% (CI 75.9%, 80.2%) in MD. Individuals clustered to SIRD were classified as MD and vice versa (ESM Fig. 3, ESM Table 2). The sensitivity of the MOD cluster ranged from 55.0% (CI 52.6%, 57.3%) to 93.2% (CI 91.5%, 94.7%).
Clusters are different in their progression to insulin requirement
Next, we assessed differences between clusters in terms of progression towards insulin initiation or requirement. As expected, the SIDD cluster showed the fastest progression (HR 3.40 [CI 1.72, 6.72]) compared with the other clusters (Table 2, ESM Fig. 4). The SIRD group showed slower progression (0.59 [0.46, 0.76]). The clusters MD and MDH also showed differences in their progression, where MDH showed the slowest progression compared with the other clusters (0.44 [0.33, 0.59]), also slower than MD (0.81 [0.63, 1.06]).
Discussion
Based on five clinical variables, people with type 2 diabetes from three large European cohorts were assigned to five separate clusters. Clusters were successfully cross-validated against the clustering reported by Ahlqvist et al [1] but also between cohorts included.
Even though we used slightly different variables for clustering, i.e. C-peptide and HDL-cholesterol instead of HOMA2 measures [1], people were clustered largely to the same clusters in a direct comparison with previously published clusters in ANDIS. The insulin-deficient cluster (SIDD) was defined by a high HbA1c, the insulin-resistant cluster (SIRD) by a high C-peptide and the obese cluster (MOD) by a high BMI. The previously identified MARD cluster [1] could be further divided into two clusters of people with a low (MD cluster) and a high HDL-cholesterol (MDH cluster). Including HDL-cholesterol resulted in two clusters with mild characteristics, where one had high HDL-cholesterol and one cluster had generally a low HDL-cholesterol. A subset of the SIRD cluster was classified as MD, which is most likely due to the use of C-peptide and HDL-cholesterol instead of HOMA2 measures.
In addition to a comparison with the original ANDIS clusters, in the current study we also cross-validated the clusters across cohorts. Clusters cross-validated generally well and the best sensitivity was observed in the SIDD and MDH clusters. For SIRD and MD a lower sensitivity was observed. Individuals that were classified in one cohort to SIRD or MOD were classified as MD in a second cohort and vice versa. The characteristics of particularly SIRD and MD are very similar, with the sole difference being higher levels of C-peptide in the SIRD cluster. This could explain the difference in classification in the two cohorts.
A limitation of the current study is that individuals in DCS and GoDARTS were not clustered based on clinical data collected at the time of diagnosis prior to treatment. Different treatment regimens could have had an influence on the clustering. However, it should be noted that ANDIS was clustered based on data collected at the time of diagnosis and in GoDARTS a smaller group was treated at baseline compared with DCS. Therefore, treatment effects did not seem to have a major influence on the clustering or the cross-validation.
The progression towards insulin requirement of the identified clusters resembled that of the original clusters in ANDIS [1]. The SIDD group showed the fastest progression, followed by MOD. The SIRD group showed a generally slower progression in our study. The MDH cluster that we additionally identified showed the slowest progression of all clusters. This shows that adding HDL-cholesterol to the clustering allows the identification of a separate group among those with mild diabetes with very low risk of glycaemic deterioration towards insulin requirement.
Conclusion
In the current study, clusters were identified in three cohorts, based on five different clinical characteristics. We show that clusters based on random or fasted C-peptide instead of HOMA2 measures resemble those based on HOMA2 measures. By adding HDL-cholesterol, we identified one additional cluster with mild characteristics. Cross-validation between cohorts showed that there was generally a good resemblance between cohorts. Together, our results show that the clustering is generally stable across cohorts, and also when the clustering includes C-peptide instead of HOMA measures. The novel MDH cluster represents a group of people with mild diabetes and very low risk of glycaemic deterioration towards insulin requirement.
Data availability
Steering committees of the individual cohorts will consider reasonable requests for sharing of de-identified patient-level data.
Abbreviations
- ANDIS:
-
All New Diabetics in Scania
- DCS:
-
Diabetes Care System
- GoDARTS:
-
Genetics of Diabetes Audit and Research Tayside Study
- MARD:
-
Mild age-related diabetes
- MD:
-
Mild diabetes
- MDH:
-
Mild diabetes with high HDL-cholesterol
- MOD:
-
Mild obesity-related diabetes
- RHAPSODY:
-
Risk Assessment and ProgreSsiOn of DIabetes
- SIDD:
-
Severe insulin-deficient diabetes
- SIRD:
-
Severe insulin-resistant diabetes
References
Ahlqvist E, Storm P, Karajamaki A et al (2018) Novel subgroups of adult-onset diabetes and their association with outcomes: a data-driven cluster analysis of six variables. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 6:361–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30051-2
Safai N, Ali A, Rossing P, Ridderstråle M (2018) Stratification of type 2 diabetes based on routine clinical markers. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 141:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2018.05.014
Zaharia OP, Strassburger K, Strom A et al (2019) Risk of diabetes-associated diseases in subgroups of patients with recent-onset diabetes: a 5-year follow-up study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 7(9):684–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30187-1
Dennis JM, Shields BM, Henley WE, Jones AG, Hattersley AT (2019) Disease progression and treatment response in data-driven subgroups of type 2 diabetes compared with models based on simple clinical features: an analysis using clinical trial data. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 7(6):442–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30087-7
Kahkoska AR, Geybels MS, Klein KR et al (2020) Validation of distinct type 2 diabetes clusters and their association with diabetes complications in the DEVOTE, LEADER and SUSTAIN-6 cardiovascular outcomes trials. Diabetes Obes Metab 22(9):1537–1547. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.14063
Zou X, Zhou X, Zhu Z, Ji L (2019) Novel subgroups of patients with adult-onset diabetes in Chinese and US populations. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 7(1):9–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(18)30316-4
Anjana RM, Baskar V, Nair ATN et al (2020) Novel subgroups of type 2 diabetes and their association with microvascular outcomes in an Asian Indian population: a data-driven cluster analysis: the INSPIRED study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 8(1):1506. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001506
Bennet L, Nilsson C, Mansour-Aly D, Christensson A, Groop L, Ahlqvist E (2020) Adult-onset diabetes in Middle Eastern immigrants to Sweden: novel subgroups and diabetic complications-the all new diabetes in scania cohort diabetic complications and ethnicity. Diabetes Metab Res Rev e3419. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.3419
Bancks MP, Casanova R, Gregg EW, Bertoni AG (2019) Epidemiology of diabetes phenotypes and prevalent cardiovascular risk factors and diabetes complications in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003-2014. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 158:107915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107915
van der Heijden AA, Rauh SP, Dekker JM et al (2017) The Hoorn Diabetes Care System (DCS) cohort. A prospective cohort of persons with type 2 diabetes treated in primary care in the Netherlands. BMJ Open 7(5):e015599
Hebert HL, Shepherd B, Milburn K et al (2018) Cohort Profile: Genetics of Diabetes Audit and Research in Tayside Scotland (GoDARTS). Int J Epidemiol 47(2):380–381j. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyx140
Zhou K, Donnelly LA, Morris AD et al (2014) Clinical and genetic determinants of progression of type 2 diabetes: a DIRECT study. Diabetes Care 37(3):718–724. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc13-1995
Yan M, Ye K (2007) Determining the number of clusters using the weighted gap statistic. Biometrics 63(4):1031–1037. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1541-0420.2007.00784.x
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support of the Health Informatics Centre, University of Dundee for managing and supplying the anonymised data.
Authors’ relationships and activities
KS is CEO of Lipotype GmbH. KS and CK are shareholders of Lipotype GmbH. MJG is an employee of Lipotype GmbH. GAR has received grant funding and consultancy fees from Sun Pharmaceuticals and Les Laboratoires Servier. MKH is an employee of Janssen Research & Development, LLC. AF and IP are employees of Eli Lilly Regional Operations GmbH. The authors declare that there are no relationships or activities that might bias, or be perceived to bias, their work.
Funding
This project has received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking under grant agreement number 115881 (RHAPSODY). This Joint Undertaking receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation programme and EFPIA. This work is supported by the Swiss State Secretariat for Education‚ Research and Innovation (SERI) under contract number 16.0097-2. The opinions expressed and arguments employed herein do not necessarily reflect the official views of these funding bodies. ERP was supported by a Wellcome Trust Investigator Award (102820/Z/13/Z). GAR was supported by a Wellcome Trust Senior Investigator Award (WT098424AIA) and Investigator Award (212625/Z/18/Z), by MRC Programme Grants (MR/R022259/1, MR/J0003042/1, MR/L020149/1) and by Diabetes UK Project Grants (BDA/11/0004210, BDA/15/0005275, BDA 16/0005485).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RCS, LAD, JWJB, LM’tH and ERP designed the study and drafted the manuscript. RCS, LAD, HF, GAB and MÅ performed the analyses. ID, DK and MI set up a federated node system for data analysis. RCS, DMA, LAD, HF, EA, AA, MJG, MK, FM, TS, AW, CLQ and MI were involved in the data pre-processing and quality control. GNG, AF, MKH, DMA, IP, TJP, BT, VL, LG, PWF, GAR, MJG, CK, KS, CLQ, AA, PR, AW and TS contributed to the data acquisition and project logistics. All authors contributed to the data interpretation. All authors critically revised the manuscript and approved the final version. RCS, LAD, JWJB, LM’tH and ERP are the guarantors of the work.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM
(PDF 829 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Slieker, R.C., Donnelly, L.A., Fitipaldi, H. et al. Replication and cross-validation of type 2 diabetes subtypes based on clinical variables: an IMI-RHAPSODY study. Diabetologia 64, 1982–1989 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-021-05490-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-021-05490-8