Abstract
Aims/hypothesis
Upregulation of the functional beta cell mass is required to match the physiological demands of mother and fetus during pregnancy. This increase is dependent on placental lactogens (PLs) and prolactin receptors, but the mechanisms underlying these events are only partially understood. We studied the mRNA expression profile of mouse islets during pregnancy to gain a better insight into these changes.
Methods
RNA expression was measured ex vivo via microarrays and quantitative RT-PCR. In vivo observations were extended by in vitro models in which ovine PL was added to cultured mouse islets and MIN6 cells.
Results
mRNA encoding both isoforms of the rate-limiting enzyme of serotonin biosynthesis, tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH), i.e. Tph1 and Tph2, were strongly induced (fold change 25- to 200-fold) during pregnancy. This induction was mimicked by exposing islets or MIN6 cells to ovine PLs for 24 h and was dependent on janus kinase 2 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 5. Parallel to Tph1 mRNA and protein induction, islet serotonin content increased to a peak level that was 200-fold higher than basal. Interestingly, only a subpopulation of the beta cells was serotonin-positive in vitro and in vivo. The stored serotonin pool in pregnant islets and PL-treated MIN6 cells was rapidly released (turnover once every 2 h).
Conclusions/interpretation
A very strong lactogen-dependent upregulation of serotonin biosynthesis occurs in a subpopulation of mouse islet beta cells during pregnancy. Since the newly formed serotonin is rapidly released, this lactogen-induced beta cell function may serve local or endocrine tasks, the nature of which remains to be identified.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
During pregnancy, more insulin is needed to support growth and energy homeostasis of mother and fetus [1]. To meet this enhanced metabolic demand, the functional beta cell mass is increased [2, 3]. Flexibility of the functional beta cell mass is mediated by lactogenic hormones, prolactin and placental lactogen (PL) [2], which bind to prolactin receptors (PRLRs), leading to activation of the janus kinase 2 (JAK2)–signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5) pathway [4, 5]. In addition to this pathway, PRLRs can also transduce their signal via the RAS–RAF–mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways [6]. The exact gene network responsible for the adaptations of islets to pregnancy is not fully known. A recent study showed that the expression of a large number of genes was altered during pregnancy, including the two genes encoding tryptophan hydroxylases (TPH) [7]. Serotonin is a monoamine known to control processes in the brain and gastrointestinal tract [8, 9]. More and more studies have indicated that serotonin influences growth and differentiation of tissues [10] such as the mammary gland [11], the nervous system [12], bone [13] and liver [14]. Serotonin is synthesised from tryptophan via a two-step pathway (Electronic supplementary material [ESM] Fig. 1a) [15]. The first and flux-generating step consists of hydroxylation of tryptophan to 5-hydroxytryptophan, which is catalysed by TPH. Two non-allelic isoforms of this enzyme exist: the non-neuronal TPH1 and the neuronal TPH2 [16, 17]; their production pattern is non-overlapping, with TPH1 being produced in the pineal gland and the enterochromaffin cells, while TPH2 is present in the neurons of the raphe nuclei and the enteric nervous system [9, 18]. Around 95% of the body’s serotonin is produced by enterochromaffin cells [9]. Overflow of gut serotonin is taken up and concentrated in platelets, where it participates in platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction [15]. Since circulating serotonin cannot cross the blood–brain barrier, local production is required. The last step of serotonin biosynthesis is catalysed by dopa decarboxylase, which is abundantly expressed in beta cells [19]. Serotonin exerts its effect via a large family of receptors [20]. In addition, recent evidence suggests that cytosolic serotonin regulates exocytosis in thrombocytes [21] and in pancreatic beta cells [22] by serotonylation, a newly identified post-translational modification.
Because of the great interest in serotonin biology and the important change in mRNA expression of Tph genes in islets of pregnant mice [7], we measured serotonin biosynthesis and release in islets of pregnant females. We also investigated the role of PLs in the upregulation of Tph gene expression.
Methods
Preparation of islets and tissues
All experiments with laboratory animals were approved by the committee for animal welfare at the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven. Islets of Langerhans from C57BL6/J (Janvier, Le Genest-Saint-Isle, France) female mice were collagenase-isolated as previously described [23]. Other tissues were dissected from 10- to 12-week-old C57Bl6/J (Janvier) mice. Fetal tissue was isolated on pregnancy day (P) 15.5. Embryonic stem cells were isolated as previously described [24]. Tissues were rinsed in PBS, frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C. Mouse beta cells were purified from islets of Ripyy mice producing eYFP under the rat insulin promoter [25].
Cell culture
MIN6 cells were cultured in DMEM (Invitrogen-Gibco, Karlsruhe, Germany) 25 mmol/l glucose equilibrated with 5% CO2 and 95% air at 37°C and supplemented with 15% (vol./vol.) decomplemented FCS, 70 μmol/l β-mercaptoethanol, 4 mmol/l glutamax, 50 U/ml penicillin and 50 μg/ml streptomycin. MIN6 cells were used between passages 20 and 30. For immunocytochemistry, MIN6 cells were seeded on glass coverslips coated with Fibronectin-like engineered protein polymer plus (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) in a 12 well plate and incubated for 24 h in DMEM (25 mmol/l glucose, 2% [vol./vol.] decomplemented FCS, 4 mmol/l glutamax) with 0 or 500 ng/ml ovine PL (Prospec, Rehovot, Israel). For the inhibitor experiments, MIN6 cells were serum-starved for 24 h. Next they were pre-incubated for 15 to 30 min with one of the three inhibitors: tyrphostin AG490 (50 μmol/l; Sigma-Aldrich), mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1&2 (MEK1/2)-inhibitor-1 (10 μmol/l; Calbiochem-Merck Biochemicals, Darmstadt, Germany) or wortmannin (100 nmol/l; Sigma-Aldrich). Thereafter, they were incubated with or without 500 ng/ml PL, together with wortmannin for 7 h or together with tyrphostin AG490 or MEK1/2-inhibitor-1 for 24 h. For overexpression experiments, AMAXA technology (Lonza, Cologne, Germany) was used. Briefly, using the X13 program, 5×106 MIN6 cells were electroporated with 2 μg plasmid DNA and 100 μl nucleofector V (Lonza), and recovered for 7 h in RPMI (Invitrogen-Gibco; 11 mmol/1 glucose, 15% [vol./vol.] decomplemented FCS) medium.
Islet monolayer
Extracellular matrix-coated plates and coverslips were produced as previously described [26]. In these coated plates, isolated islets were cultured in RPMI medium (10% [vol./vol.] decomplemented FCS, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, 4 mmol/l glutamax) for 7 days to form a monolayer. On day 7, islets were stimulated with 0 or 500 ng/ml PL.
RNA extraction
Total RNA from mouse islets, pure beta cells and MIN6 cells was extracted using a kit (Absolutely RNA microprep; Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA). Total RNA was extracted from the other tissues as previously described [27]. Total RNA quantity and quality were determined using a spectrophotometer (ND-1000; NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA) and a bioanalyser (2100; Agilent, Waldbronn, Germany), respectively.
mRNA expression analysis via microarray
Microarray analysis was conducted on different tissues with MOE430-2.0 arrays (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA, USA) as described [27]. To analyse the time series of pregnant islets, total RNA (100 ng) was used to hybridise the arrays (MoGene_1.0_ST; Affymetrix) according to manufacturer’s manual 701880Rev4 as described previously [23]. The different conditions were compared with each other pairwise on the basis of p < 0.001 and a fold change of ≥1.5.
Quantitative RT-PCR
Following cDNA synthesis using a reverse transcriptase kit (RevertAid H Minus; Fermentas, St Leon-Rot, Germany), quantitative RT-PCR (Absolute QPCR mix; Abgene-Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was performed on a Rotorgene (Corbett Research, Mortlake, NSW, Australia) to estimate mRNA expression of different genes. The gene encoding RNA polymerase II (Polr2a) was used for normalisation. For primers and probes see ESM Table 1. For Tph2 we used a Taqman gene expression assay (Mm00557717_m1; Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA).
Protein levels
Total protein extracts were obtained from freshly isolated islets or MIN6 cells, which were lysed in extraction buffer (50 mmol/l Tris, pH8; 1% [vol./vol.] NP-40; 150 mmol/l NaCl; 1 mmol/l EDTA). Protein extracts (100 μg for islets, 20 μg for MIN6 cells) were separated by SDS-PAGE (10% [vol./vol.] Tris/glycine gel; Invitrogen, Paisley, UK). The gels were blotted on polyvinylidene fluoride membranes and, after blocking with 4% (wt/vol.) milk, incubated with primary antibody (ESM Table 2). Thereafter, they were incubated with peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (ESM Table 2). Detection was by ECL-system (GE Healthcare-Amersham, Diegem, Belgium).
Immunocytochemistry
After stimulation with vehicle or PL, cells were washed with PBS and fixed with 4% (wt/vol.) paraformaldehyde. Next cells were washed with PBS, permeabilised with 0.2% (vol./vol.) Triton X-100 and washed again. For TPH1 staining, the cells were immersed in 0.1% (wt/vol.) SDS at 37°C to recover the antigen. The cells were then washed and immersed in Hoechst solution and thereafter washed and blocked with 5% (wt/vol.) BSA. After blocking, primary antibodies (ESM Table 2) were added for 1 h at room temperature in 1% (wt/vol.) BSA, after which cells were again washed. Finally, the cells were incubated with secondary antibodies (AlexaFluor; Invitrogen) (ESM Table 2) for 1 h at room temperature in 1% (wt/vol.) BSA and washed again. Images were obtained with a laser scanning confocal microscope (LSM510; Carl Zeiss Meditec, Jena, Germany) using a 63× oil objective or with an inverted microscope (Ti-E; Nikon, Brussels, Belgium) using 40× and 60× oil objectives.
Immunohistochemistry
The Tph1-knockout (KO) mice were obtained by knock-in of the lacZ gene and disruption of Tph1 in embryonic stem cells as previously described [28]. The Tph1-null mutation was backcrossed on to a C57BL6/J background. Pancreases were dissected from pregnant wild-type and Tph1-KO mice, and fixed in 4% (wt/vol.) paraformaldehyde. Binding of primary serotonin antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) (ESM Table 2) was detected with biotinylated anti-rat Ig in combination with streptavidin horseradish peroxidase; diaminobenzidine was used as substrate (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark). See also ESM Methods.
Insulin/serotonin release and content
To determine serotonin content, MIN6 cells and islets were homogenised in serotonin buffer (0.01 mol/l HCl, 1 mmol/l EDTA, 4 mmol/l sodium metabisulfite) by 3 min sonication. Other tissues were homogenised by douncing. After centrifugation (20,000 g) for 15 min at 4°C and addition of 0.1% (wt/vol.) ascorbic acid, lysates were stored at −20°C.
Freshly isolated islets from P15.5 pregnant female mice were incubated for 1 h in batches of 50 at 37°C. Incubation was in Krebs HEPES buffer (20 mmol/l HEPES, pH7.4; 119 mmol/l NaCl; 4.75 mmol/l KCl; 2.5 mmol/l CaCl2; 1.2 mmol/l MgSO4; 1.2 mmol/l KH2PO4; 5 mmol/l NaHCO3, 0.5% [wt/vol.] BSA) containing either 5 or 20 mmol/l glucose. After 1 h, medium was removed and stored at −20°C for measurement of insulin and serotonin release.
After 24 h incubation with PL, MIN6 cells were pre-incubated for 1 h in Earl’s HEPES buffer (0.5% [wt/vol.] BSA; 124 mmol/l NaCl; 5.3 mmol/l KCl; 0.8 mmol/l MgSO4; 1 mmol/l NaH2PO4; 10 mmol/l HEPES; 1.8 mmol/l CaCl2; 14.3 mmol/l NaHCO3; pH 7.35) containing 2 mmol/l glucose, 10 μmol/l clorgyline (Sigma-Aldrich), a monoamine oxidase A inhibitor and 0.1% (wt/vol.) ascorbic acid. Next, cells were incubated in 2 or 20 mmol/l glucose. After 1 h, medium was recovered for quantification of insulin and serotonin release using commercial ELISA kits (LDN, Nordhorn, Germany; Mercodia, Uppsala, Sweden, respectively).
Statistics
All data are expressed as mean ± SEM, except the microarray analysis where data are mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed on experiments with n ≥ 3 animals/samples. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed Student’s t test or Welch’s t test, except for the monolayer experiments, where a Z test with value 1 (value of control sample) was used.
Results
Induction of the two TPH isoforms in islets during pregnancy
Ex vivo mRNA expression analysis of islets isolated from non-pregnant mice vs mice at P15.5, revealed that one of the most highly induced genes in islets during pregnancy is Tph1 (MOE430_2.0 microarrays), which encodes the rate-limiting enzyme of serotonin biosynthesis, TPH1 (ESM Fig. 1b), confirming a recent analysis [7]. The strong upregulation was also observed by quantitative RT-PCR (Fig. 1a) and at the protein level (Fig. 1c). With the exception of a modest increase in the small intestine, Tph1 mRNA was not induced in any other tested tissue during pregnancy (Fig. 1a). At variance with currently accepted thinking that expression of the two non-allelic Tph genes is divided between neuronal and non-neuronal cells [9, 16, 18], we found that Tph1 and Tph2 were strongly induced in islets from pregnant females (Fig. 1b, ESM Fig. 1c). Even under non-pregnant conditions, low expression of Tph1 and Tph2 mRNA was detectable in beta cells. Indeed, Tph2 was more highly expressed in primary beta cells than in tumoural MIN6 cells, whereas Tph1 mRNA was more abundant in MIN6 cells (Fig. 1d, e). We further analysed the expression of both genes in islets using a time course analysis and MoGene_1.0_ST array to cover the 2nd and 3rd week of pregnancy, as well as mice 10 days postpartum. As shown in Fig. 2a, expression of Tph1 in islets increased markedly during the 2nd week of pregnancy, peaking around P12.5 to P15.5, after which Tph1 mRNA decreased again. However, Tph2 (Fig. 2b) reached a plateau at P9.5, which lasted until P18.5. The characteristic time course of Tph1 expression in islets was confirmed by quantitative RT-PCR (ESM Fig. 2a) and could be clearly separated from its rather constant expression in duodenum and jejunum (ESM Fig. 2a). In addition to the tryptophan hydroxylases, Ddc, the gene encoding the enzyme that catalyses the final step of serotonin synthesis, was also significantly upregulated during pregnancy (ESM Fig. 1d, ESM Fig. 2b). Therefore, expression of all genes encoding the enzymes involved in serotonin biosynthesis was found to be strongly induced in islets from pregnant mice. In contrast, mRNA encoding the enzymes needed for conversion of serotonin into melatonin was so low as to be undetectable (data not shown).
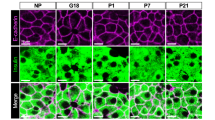
Co-expression of Tph1 and Tph2 in islets of pregnant mice. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of mRNA encoding Tph1 (a) and Tph2 (b) in islets and in tissue as indicated from non-pregnant (white bars) and P15.5 females (black bars). Results are mean ± SEM of three to seven independent experiments (see also ESM Fig. 1). c Representative western blot of TPH1 protein levels in islets isolated from non-pregnant (NP) and P15.5 mice. β-Actin was used as control for protein load. Microarray analysis (Affymetrix MOE430_2.0) of mRNA encoding Tph1 (d) and Tph2 (e) in islets of non-pregnant (NP) female mice, FACS-purified beta cells (male mice) and other tissues as indicated. Primary beta cells expressed more Tph2 and less Tph1 than the MIN6 cell line. Brain and small intestine were used as controls. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 for difference between tested conditions
Time course of islet Tph1 and Tph2 mRNA expression and serotonin content during pregnancy. Expression of Tph1 (a) and Tph2 mRNA (b) in islets isolated from non-pregnant (NP) mice, pregnant mice on different days of pregnancy as indicated and mice at 10 days postpartum (10 dpp). Expression was determined with the MoGene_1.0_ST array. Values are mean ± SD, n = 3–4. Tph1 mRNA expression peaked around P12.5 to P15.5, whereas that of Tph2 plateaued from P9.5 onwards. Expression of both declined after delivery. See ESM Fig. 2a for Tph1 expression in intestine at different time points during pregnancy. c Time course of serotonin content in islets isolated from mice as indicated (n = 2–11). For the content of different parts of the intestine, see ESM Fig. 3. a–c *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 for difference between non-pregnant and pregnant, or between indicated conditions. d Correlation analysis between islet Tph1 or (e) Tph2 mRNA expression and serotonin content. The correlation between Tph1 (r = 0.951) and serotonin was better than that between Tph2 (r = 0.812) and serotonin. f Serotonin immunostaining (brown) of pancreatic sections from pregnant mice. Serotonin was used as blocking agent. Only a subset of the islet cells was stained with an intensity similar to the time-dependent ELISA measurement of serotonin content of isolated islets (c). No immunostaining was detected in Tph1-KO mice
Increased serotonin content in islets during pregnancy
To assess the functional consequence of these mRNA changes, we measured serotonin content in islets isolated from pregnant and non-pregnant female mice (Fig. 2c). The basal serotonin content in islets from non-pregnant mice was close to the lower detection threshold (0.004 pmol/islet). During pregnancy, however, islet serotonin content increased ∼200-fold (Fig. 2c), with a time course very similar to that of Tph1 expression (r = 0.951) (Fig. 2d), but less so to that of Tph2 expression (r = 0.812) (Fig. 2e). Immunhistochemistry confirmed this temporal profile of serotonin content during pregnancy (Fig. 2f). In contrast, the small changes during pregnancy in intestinal Tph1 expression (ESM Fig. 2a) were not associated with changes in serotonin content (ESM Fig. 3).
Placental lactogens induce
Tph1 and Tph2 expression in islets during pregnancy Because traces of Tph1 and Tph2 expression can be found in beta cells under non-pregnant conditions, we next investigated which factor during pregnancy is responsible for the strong upregulation of Tph1 and Tph2 mRNA. As lactogens have a crucial role in other pregnancy-related changes in islets [2, 3], we analysed the role of PL. We first confirmed that PRLRs are abundantly expressed in both systems, finding in addition that their mRNA levels further increased during pregnancy (ESM Fig. 4a), which is consistent with the literature [29]. Next, we observed that PL increased Tph1 mRNA expression in MIN6 cells in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 3a). Tph2 mRNA expression was also increased by 500 ng/ml PL (Fig. 3b). The induction of TPH1 by PL was further confirmed at the protein level via western blotting (Fig. 3c). Next, we checked that the effect of PL on MIN6 cells was also seen in cultured islets isolated from non-pregnant mice and stimulated for 24 h with 500 ng/ml PL. As seen in Fig. 3d, e, this treatment also induced expression of Tph1 and Tph2 in islets.
Placental lactogens induce Tph1 and Tph2 expression in cultured beta cells. Tph1 mRNA (a) was induced in MIN6 cells by ovine PL (oPL) in a concentration-dependent manner. Effect, in MIN6 cells, of 500 ng/ml oPL (24 h) on Tph2 mRNA (b) and TPH1 protein (c); the immunoblot in c is representative of three independent experiments. Quantitative RT-PCR data are mean ± SEM, n = 3. Effect of 24 h 500 ng/ml oPL on Tph1 mRNA (d) and Tph2 mRNA (e) in islets cultured as monolayers after isolation from non-pregnant mice. MIN6 cells incubated with oPL were treated with specific inhibitors of three signalling pathways, namely tyrphostin AG490 (50 μmol/l) for JAK2–STAT5 (f), MEK1/2-inhibitor-1 (10 μmol/l) for RAS–RAF–MAPK (g) and wortmannin (100 nmol/l) for PI3K (h). Tph1 expression was quantified via quantitative RT-PCR (mean ± SEM, n = 3–4) and TPH1 protein via western blotting (blots are representative of three to four experiments). The JAK2 inhibitor tyrphostin AG490 reduced Tph1 expression in MIN6 cells treated with oPL. For expression of Prlr mRNA in islets during pregnancy, see ESM Fig. 4. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 for difference between non-treated controls and treated conditions, as analysed by Student’s t test (MIN6 cells) and Z test (islets cultured in monolayers)
Placental lactogens activate the JAK2–STAT5 pathway to enhance Tph1 expression
Lactogen-stimulated PRLRs can alter beta cell function via three different signalling pathways: (1) JAK2–STAT5 (2) RAS–RAF–MAPK; and (3) PI3K [4. 5]. To determine whether any of these pathways mediated the strong induction of Tph1 mRNA as observed in vivo and in vitro, we tested the effect of specific pharmacological inhibitors for each of these pathways, using as readouts quantitative RT-PCR for RNA signal and western blotting for protein signal (Fig. 3f–h). Several observations were made. First, only the JAK2–STAT5 pathway was convincingly activated after PL treatment. Second, neither the PI3K inhibitor, wortmannin, nor the MEK1/2-inhibitor-1 significantly downregulated Tph1 expression in PL-treated MIN6 cells (Fig. 3g, h). Finally, the JAK2 inhibitor, tyrphostin AG490, almost completely abolished the influence of PL on Tph1 mRNA and protein levels (Fig. 3f). Next, we overexpressed mRNA encoding the dominant active forms of STAT5A and STAT5B (STAT5A1*6 and STAT5B1*6 respectively) in MIN6 cells. Overproduction of these dominant active forms led to a significant increase in Tph1 mRNA expression (ESM Fig. 4b). Overproduction of a dominant negative STAT5 (STAT5A∆749) counteracted the effect of PL on Tph1 expression (ESM Fig. 4c). Also two putative Stat consensus binding sequences, consistent with the known interferon gamma-activated sequence (consensus, TTCNNNGAA) [30], have been found in Tph1 and Tph2 gene promoters by searching NCBI (accession numbers mus musculus Tph1 and Tph2 genes: U96811 and NC_000076.5 respectively; www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/guide/, accessed 8 July 2010). These data show that during pregnancy, lactogens play an important role in the induction of Tph1 and Tph2 in beta cells via PRLR–JAK2–STAT5 signalling.
Different kinetics of insulin and serotonin release in beta cells
Pregnancy is known to enhance functional beta cell mass [2, 31]. In agreement with this idea, islet insulin content and glucose-induced insulin release increased in pregnant mice (ESM Fig. 5a, b). The time course of insulin content per islet differed from that of islet serotonin content, which declined during the last week of pregnancy and during lactation (Fig. 2c). Next, we investigated whether the stored islet serotonin could be released from islets isolated from P15.5 mice. Insulin and serotonin release were measured after 1 h of incubation in the presence of low (5 mmol/l) and high (20 mmol/l) glucose levels. The basal rate of serotonin release was high compared with that of insulin, making up 16 ± 6% of total islet serotonin content per h vs 1.5 ± 0.7% of total islet insulin content per h (Fig. 4a). A second difference between insulin and serotonin release was found in the degree of glucose stimulation. Thus 20 mmol/l glucose increased insulin release fivefold, but enhanced serotonin release only twofold (Fig. 4a). Similar observations were made with PL-stimulated MIN6 cells (Fig. 4b). Insulin and serotonin content of pregnant islets and MIN6 cells were not influenced by the glucose concentration (ESM Fig. 5c, d). Together, our data indicate that insulin and serotonin release can be at least partially dissociated, both in terms of basal fractional turnover and glucose stimulation. In support of this idea, insulin and serotonin immunostaining did not overlap in PL-treated MIN6 cells (Fig. 4c), suggesting that different granule pools are involved.
Dissociated release of serotonin and insulin from pregnant islets and PL-stimulated MIN6 cells. a Insulin (white bars) and serotonin (black bars) release, expressed as per cent of total content per h from pancreatic islets freshly isolated from P15.5 females, showed a different pattern (for details on content, see ESM Fig. 5c). Release and content were measured after 1 h incubation in 5 or 20 mmol/l glucose. b Similar results were obtained for insulin and serotonin release of ovine PL-treated MIN6 cells incubated for 1 h in 2 or 20 mmol/l glucose (for details on content, see ESM Fig. 5d). The change in insulin content during pregnancy is shown in ESM Fig. 5a; insulin release from islets isolated from non-pregnant vs pregnant mice is shown in ESM Fig. 5b. Values (a, b) are mean ± SEM; n = 4. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 for differences between indicated conditions. c Non-overlapping serotonin and insulin immunostaining in the same MIN6-cell. Two representative microscopic images of MIN6 cells treated for 24 h with 500 ng/ml ovine PL after double immunostaining for serotonin (red) and insulin (green). Cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue)
Serotonin is produced by a subpopulation of beta cells
TPH1 and serotonin could be detected in the same cells, supporting the important role of this isoform in serotonin production of MIN6 cells (Fig. 5a). Interestingly, only a subpopulation of PL-stimulated MIN6 cells had built up a detectable serotonin pool (Fig. 5b). We also observed that with increasing PL concentrations, the number of serotonin-containing cells increased to reach a plateau of approximately 25% at 100 ng/ml (Fig. 5c, ESM Fig. 6). Immunostaining experiments on PL-stimulated islets showed strong beta cell heterogeneity in TPH1 protein and cellular serotonin accumulation (Fig. 5d). No glucagon-positive cells were seen to have accumulated serotonin. This heterogeneity is consistent with and confirms the heterogenic pattern of serotonin staining of pancreatic sections from pregnant mice (Fig. 2f).
A subpopulation of PL-stimulated beta cells was induced to produce serotonin. a Confocal microscopy of MIN6 cells treated for 24 h with 500 ng/ml ovine PL (oPL). Double immunostaining for TPH1 (green) and serotonin (red). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Immunoreactive TPH1 and serotonin are present in the same cell. b Presence of serotonin (red) in a subset of PL-stimulated insulin-containing MIN6 cells (insulin, green). c Per cent of serotonin-positive MIN6 cells after treatment with different concentrations of oPL for 24 h; values mean ± SEM, n = 3 except for 100 ng/ml where n = 2; counting done blind by three independent persons. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 for difference between non-treated controls and treated conditions. d Confocal microscopy of islets treated for 24 h with 500 ng/ml oPL, showing overlays of immunoreactivity for TPH1 (green) and serotonin (red), insulin (green) and serotonin (red), and glucagon (green) and serotonin (red). Data indicate that a subpopulation of primary islet beta cells contains serotonin after stimulation with PL
Low serotonin receptor expression in islets of pregnant and non-pregnant mice
A local effect of serotonin on beta cell function (insulin production, release, beta cell replication) is expected to depend on expression of one of the 14 serotonin receptors in islets. However, as illustrated in ESM Fig. 7, we were unable to detect a real signal for these receptors in islets, either with MOE430_2.0 arrays (ESM Fig. 7a) or with MoGene_1.0_ST arrays (ESM Fig. 7b–o), whereas brain tissue gave clear signals for several receptors. Furthermore, none of the serotonin receptors increased significantly (p < 0.001, fold change ≥1.5) during pregnancy. We next performed quantitative RT-PCR analysis for Htr1d and Htr2b; however, expression of these was below the detection limit (data not shown). Together, we observed that the very low receptor expression did not parallel the strong induction of the serotonin biosynthetic pathway.
Discussion
In this paper we provide evidence for a strong upregulation of serotonin production in a subpopulation of mouse beta cells during pregnancy, an upregulation which is dependent on lactogens. In this physiogical condition, Tph1 in particular was dramatically induced, resulting in an accumulation of serotonin in beta cells and subsequent rapid secretion of the synthesised serotonin. During in vitro release experiments, we showed that the fractional turnover time of newly synthesised and stored serotonin is in the range of a few hours, i.e. ten times smaller than that of insulin [32, 33].
It is widely agreed today that the serotonin system in mammals is subdivided into cell types that synthesise serotonin via TPH1 (non-neuronal cells) or TPH2 (neuronal cells) [8, 9, 16–18]. Beta cells do not follow this subdivision, as we observed induction of both genes, Tph1 and Tph2. This duality is intriguing because on the one hand pancreatic beta cells and enterochromaffin cells seem to be derived from a common developmental precursor cell in the endoderm [34], and on the other hand adult differentiated beta cells share many phenotypic traits with neurons, a fact explained by the common avoidance of repressor element 1-silencing transcription factor production [35, 36]. One aspect of this “neuron-like” behaviour is that adult beta cells produce several enzymes for neurotransmitter synthesis, e.g. tyrosine hydroxylase [37], dopa decarboxylase [19] and glutamate decarboxylase [38]. Beta cells, moreover, store and secrete γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and possibly other amines via synaptic-like microvesicles [39]. The current observations extend this neuronal phenotype by showing that beta cells express Tph2 and store serotonin in a compartment that does not overlap with insulin. The stronger correlation between islet serotonin content and Tph1 mRNA expression vs islet serotonin and Tph2 mRNA expression may, however, indicate that, of the two isoenzymes, Tph1 contributes most to serotonin biosynthesis in islets. This idea is supported by immunohistochemistry of pancreatic sections of pregnant Tph1-KO, as no serotonin staining was detected in the islets (Fig. 2f).
A parallel finding between this study and previous analysis of GABA synthesis and release [40] is that the fractional release rates of GABA and serotonin largely exceed those of insulin by one order of magnitude. At one level, this difference could be explained by the fact that release rates of GABA [40] and serotonin depend on enzymatic biosynthetic flux, which is governed by levels of flux-controlling enzymes, whereas insulin release is primarily controlled at the level of exocytosis. At another level, the explanation could be the existence of non-overlapping storage pools of insulin and serotonin, suggesting that serotonin is not stored in dense-core granules, but rather in synaptic-like microvesicles, as proposed for GABA [39]. However, when serotonin or its precursor 5-hydroxytryptophan are added to the medium, it is stored together with insulin in dense-core granules [41]. In contrast to GABA production, the synthesis and storage of serotonin only occurs at detectable rates during pregnancy, a process which seems to be critically dependent on PL-stimulation of PRLRs and activation of the JAK2–STAT5 pathway. According to our observations, this process is also restricted to a subset of the beta cell population. Rodent beta cells are known to be functionally heterogeneous in glucose-induced insulin biosynthesis and release [42–44]. Precisely why Tph1 is strongly induced in a subpopulation of beta cells needs to be further studied. One explanation is that this induction only occurs in newly divided beta cells or in cells that are preparing for replication. Alternatively, serotonin biosynthesis may be restricted anatomically to sites in the islet that sustain increased islet function, considering the fact that serotonin is a powerful vasoconstrictor.
What could be the function of the pregnancy-induced serotonin production that we observed? Although it has been known for decades that islets of some species are serotonin-rich in the non-pregnant condition [45] and pancreatic beta cells can take up exogenous serotonin [46], the role of this amine in beta cell physiology remains poorly understood.
Paulman et al. recently described receptor-independent serotonylation of Rab proteins in beta cells [22], indicating that serotonin generates an autocrine signal for enhanced beta cell function. However, we were unable to detect any serotonylation via ELISA when MIN6 cells were treated with PL for 24 h (data not shown; see also, ESM Methods).
A second role of serotonin might be the stimulation of beta cell proliferation. TPH1-dependent serotonin production sustains replication of hepatocytes in the regenerating liver [14] and regulates bone mass [13]. One argument against a triggering role of pregnancy-induced serotonin in the control of beta cell proliferation is the time course. In the accompanying manuscript in this issue of Diabetologia [47], we show that the peak of cell cycle gene expression occurs at P9.5, which cannot be explained by Tph1 expression and serotonin production. But perhaps serotonin could have a permissive role at a later regulatory step? Not consistent with this idea is the fact that we found no difference in the amount of proliferating beta cells between wild-type and Tph1-KO mice during pregnancy, although no serotonin could be detected in the KO mice (ESM Fig. 8, ESM Methods). Therefore, it seems unlikely that Tph1 induction in islets of pregnant mice plays a major role in beta cell proliferation during pregnancy.
A third possibility is that the secreted serotonin plays a systemic role. Our inability to detect islet serotonin receptor mRNA expression above background signal and failure to measure an upregulation of any of these receptors during pregnancy (ESM Fig. 7) may support this possibility. Studies with Tph1-KO mice have shown that maternal serotonin production is important for normal brain and heart development of the fetus [17, 28, 48]. The induction of Tph1 in beta cells during the 2nd week of pregnancy and the decline of its expression after P15.5 is compatible with a time window in which fetal cells are receptive to serotonin but cannot yet produce the monoamine themselves. A broader link between serotonin and mammalian female reproduction has already been established. Thus serotonin biosynthesis is upregulated in mammary glands during pregnancy and plays a local negative feedback on milk synthesis [11, 49, 50]. To check this third possibility, further investigations are required.
Finally, serotonin can be converted to melatonin via a two-step pathway [15]. However, arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase, the enzyme of the first step, is not induced in islets during pregnancy and expression of it is also very low in non-pregnant islets (data not shown). Taken together with the fact that there is a natural melatonin ‘knockdown’ in C57BL6/J mice [51] we propose that serotonin is not metabolised to melatonin in islets during pregnancy.
In summary, we have shown that a spectacular rise of serotonin production occurs in islets during pregnancy and that this process occurs via PL stimulation of the JAK2–STAT5 pathway in a subpopulation of beta cells. The functional role of this newly identified source of serotonin constitutes an important issue to be studied in further detail.
Abbreviations
- GABA:
-
Gamma aminobutyric acid
- JAK2:
-
Janus kinase 2
- KO:
-
Knockout
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MEK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase
- P:
-
Pregnancy day
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PL:
-
Placental lactogen
- PRLR:
-
Prolactin receptor
- STAT5:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5
- TPH:
-
Tryptophan hydroxylase
References
Herrera E (2000) Metabolic adaptations in pregnancy and their implications for the availability of substrates to the fetus. Eur J Clin Nutr 54(Suppl 1):S47–S51
Parsons JA, Brelje TC, Sorenson RL (1992) Adaptation of islets of Langerhans to pregnancy: increased islet cell proliferation and insulin secretion correlates with the onset of placental lactogen secretion. Endocrinology 130:1459–1466
Sorenson RL, Brelje TC (1997) Adaptation of islets of Langerhans to pregnancy: beta-cell growth, enhanced insulin secretion and the role of lactogenic hormones. Horm Metab Res 29:301–307
Brelje TC, Svensson AM, Stout LE, Bhagroo NV, Sorenson RL (2002) An immunohistochemical approach to monitor the prolactin-induced activation of the JAK2/STAT5 pathway in pancreatic islets of Langerhans. J Histochem Cytochem 50:365–383
Huang C, Snider F, Cross JC (2009) Prolactin receptor is required for normal glucose homeostasis and modulation of beta-cell mass during pregnancy. Endocrinology 150:1618–1626
Amaral ME, Ueno M, Carvalheira JB et al (2003) Prolactin-signal transduction in neonatal rat pancreatic islets and interaction with the insulin-signaling pathway. Horm Metab Res 35:282–289
Rieck S, White P, Schug J et al (2009) The transcriptional response of the islet to pregnancy in mice. Mol Endocrinol 23:1702–1712
Hornung JP (2003) The human raphe nuclei and the serotonergic system. J Chem Neuroanat 26:331–343
Gershon MD, Tack J (2007) The serotonin signaling system: from basic understanding to drug development for functional GI disorders. Gastroenterology 132:397–414
Fanburg BL, Lee SL (1997) A new role for an old molecule: serotonin as a mitogen. Am J Physiol 272:L795–L806
Matsuda M, Imaoka T, Vomachka AJ et al (2004) Serotonin regulates mammary gland development via an autocrine-paracrine loop. Dev Cell 6:193–203
Vitalis T, Parnavelas JG (2003) The role of serotonin in early cortical development. Dev Neurosci 25:245–256
Yadav VK, Oury F, Suda N et al (2009) A serotonin-dependent mechanism explains the leptin regulation of bone mass, appetite, and energy expenditure. Cell 138:976–989
Lesurtel M, Graf R, Aleil B et al (2006) Platelet-derived serotonin mediates liver regeneration. Science 312:104–107
Tyce GM (1990) Origin and metabolism of serotonin. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 16(Suppl 3):S1–S7
Walther DJ, Peter JU, Bashammakh S et al (2003) Synthesis of serotonin by a second tryptophan hydroxylase isoform. Science 299:76
Côté F, Thevenot E, Fligny C et al (2003) Disruption of the nonneuronal tph1 gene demonstrates the importance of peripheral serotonin in cardiac function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:13525–13530
Sakowski SA, Geddes TJ, THomas DM, Levi E, Hatfield JS, Kuhn DM (2006) Differential tissue distribution of tryptophan hydroxylase isoforms 1 and 2 as revealed with monospecific antibodies. Brain Res 1085:11–18
Ahren B, Lundquist I (1985) Effects of L-dopa-induced dopamine accumulation on 45Ca2+ efflux and insulin secretion in isolated rat islets. Pharmacology 30:71–82
Hoyer D, Hannon JP, Martin GR (2002) Molecular, pharmacological and functional diversity of 5-HT receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:533–554
Walther DJ, Peter JU, Winter S et al (2003) Serotonylation of small GTPases is a signal transduction pathway that triggers platelet alpha-granule release. Cell 115:851–862
Paulmann N, Grohmann M, Voigt JP et al (2009) Intracellular serotonin modulates insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cells by protein serotonylation. PLoS Biol 7:e1000229
Lemaire K, Ravier MA, Schraenen A et al (2009) Insulin crystallization depends on zinc transporter ZnT8 expression, but is not required for normal glucose homeostasis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:14872–14877
Schoonjans L, Kreemers V, Danloy S, Moreadith RW, Laroche Y, Collen D (2003) Improved generation of germline-competent embryonic stem cell lines from inbred mouse strains. Stem Cells 21:90–97
Quoix N, Cheng-Xue R, Guiot Y, Herrera PL, Henquin JC, Gilon P (2007) The GluCre-ROSA26EYFP mouse: a new model for easy identification of living pancreatic alpha-cells. FEBS Lett 581:4235–4240
Bonanno JA, Srinivas SP (1997) Cyclic AMP activates anion channels in cultured bovine corneal endothelial cells. Exp Eye Res 64:953–962
Thorrez L, Van Deun K, Tranchevent LC et al (2008) Using ribosomal protein genes as reference: a tale of caution. PLoS One 3:e1854
Côté F, Fligny C, Bayard E et al (2007) Maternal serotonin is crucial for murine embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:329–334
Moldrup A, Petersen ED, Nielsen JH (1993) Effects of sex and pregnancy hormones on growth hormone and prolactin receptor gene expression in insulin-producing cells. Endocrinology 133:1165–1172
Heim MH (1996) The Jak-STAT pathway: specific signal transduction from the cell membrane to the nucleus. Eur J Clin Invest 26:1–12
Van Assche FA, Aerts L, De Prins F (1978) A morphological study of the endocrine pancreas in human pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 85:818–820
Henquin JC, Nenquin M, Stiernet P, Ahren B (2006) In vivo and in vitro glucose-induced biphasic insulin secretion in the mouse: pattern and role of cytoplasmic Ca2+ and amplification signals in beta-cells. Diabetes 55:441–451
Ling Z, Pipeleers DG (1996) Prolonged exposure of human beta cells to elevated glucose levels results in sustained cellular activation leading to a loss of glucose regulation. J Clin Invest 98:2805–2812
Oliver-Krasinski JM, Stoffers DA (2008) On the origin of the beta cell. Genes Dev 22:1998–2021
Atouf F, Czernichow P, Scharfmann R (1997) Expression of neuronal traits in pancreatic beta cells. Implication of neuron-restrictive silencing factor/repressor element silencing transcription factor, a neuron-restrictive silencer. J Biol Chem 272:1929–1934
Thiel G, Schuit F (2008) No REST for healthy beta cells. Diabetologia 51:1343–1346
Iturriza FC, Thibault J (1993) Immunohistochemical investigation of tyrosine-hydroxylase in the islets of Langerhans of adult mice, rats and guinea pigs. Neuroendocrinology 57:476–480
Vincent SR, Hokfelt T, Wu JY, Elde RP, Morgan LM, Kimmel JR (1983) Immunohistochemical studies of the GABA system in the pancreas. Neuroendocrinology 36:197–204
Reetz A, Solimena M, Matteoli M, Folli F, Takei K, De Camilli P (1991) GABA and pancreatic beta-cells: colocalization of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and GABA with synaptic-like microvesicles suggests their role in GABA storage and secretion. EMBO J 10:1275–1284
Smismans A, Schuit F, Pipeleers D (1997) Nutrient regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid release from islet beta cells. Diabetologia 40:1411–1415
Ekholm R, Ericson LE, Lundquist I (1971) Monoamines in the pancreatic islets of the mouse. Subcellular localization of 5-hydroxytryptamine by electron microscopic autoradiography. Diabetologia 7:339–348
Schuit FC, In't Veld PA, Pipeleers DG (1988) Glucose stimulates proinsulin biosynthesis by a dose-dependent recruitment of pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 85:3865–3869
Van Schravendijk CF, Kiekens R, Pipeleers DG (1992) Pancreatic beta cell heterogeneity in glucose-induced insulin secretion. J Biol Chem 267:21344–21348
Salomon D, Meda P (1986) Heterogeneity and contact-dependent regulation of hormone secretion by individual B cells. Exp Cell Res 162:507–520
Bird JL, Wright EE, Feldman JM (1980) Pancreatic islets: a tissue rich in serotonin. Diabetes 29:304–308
Lundquist I, Ekholm R, Ericson LE (1971) Monoamines in the pancreatic islets of the mouse. 5-hydroxytryptamine as an intracellular modifier of insulin secretion, and the hypoglycaemic action of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Diabetologia 7:414–422
Schraenen A, de Faudeur G, Thorrez L et al (2010) mRNA expression analysis of cell cycle genes in islets of pregnant mice. Diabetologia doi:10.1007/s00125-010-1912-8
Fligny C, Fromes Y, Bonnin P et al (2008) Maternal serotonin influences cardiac function in adult offspring. FASEB J 22:2340–2349
Horseman ND (1999) Prolactin and mammary gland development. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 4:79–88
Marshall AM, Nommsen-Rivers LA, Hernandez LL et al (2010) Serotonin transport and metabolism in the mammary gland modulates secretory activation and involution. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:837–846
Roseboom PH, Namboodiri MA, Zimonjic DB et al (1998) Natural melatonin 'knockdown' in C57BL/6J mice: rare mechanism truncates serotonin N-acetyltransferase. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 63:189–197
Acknowledgements
We thank the Cell Imaging Core of the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven for confocal microscopy. MIN6 cells were kindly donated by E. Yamato (Division of Stem Cell Regulation Research, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka, Japan) and STAT5 plasmids by F. Gouilleux (GICC, Faculté de Médecine, Université François Rabelais, Tours, France). This study was supported by research grants from the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (GOA 2004/11), the Belgian Ministry of Science Policy (IUAP P6/40), the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation (JDRF 1-2010-393) the Research Foundation–Flanders (FWO) and the European Union (EURODIA FP6-518153).
Duality of interest
The authors declare that there is no duality of interest associated with the manuscript.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A. Schraenen and K. Lemaire contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM Methods
(PDF 36 kb)
ESM Table 1
(PDF 31 kb)
ESM Table 2
(PDF 33 kb)
ESM Fig. 1
mRNA expression tissue profiling of enzymes involved in the serotonin biosynthetic pathway. (a) Scheme of serotonin biosynthesis from tryptophan. mRNA expression analysis (MOE430_2.0) of Tph1 (b), Tph2 (c) and Ddc (d) in various mouse tissues including islets from pregnant and non-pregnant mice. Values are mean ± SD, n = 3–5; ***p < 0.001 Student’s t test (PDF 230 kb)
ESM Fig. 2
Time course of Tph1 mRNA expression in indicated tissues during pregnancy(a), and mRNA expression of Ddc during pregnancy (b) (NP, non-pregnant). a Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Tph1 gene expression of non-pregnant (NP) mice, pregnant mice as indicated and mice at 10 days postpartum (10 dpp) mean ± SEM, n = 3–7. Tph1 mRNA was strongly increased during pregnancy in islets, whereas variation in Tph1 mRNA expression in intestine was small. b Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Ddc mRNA expression as indicated, mean ± SEM of three to seven independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 for difference between non-pregnant and pregnant conditions (PDF 203 kb)
ESM Fig. 3
Effect of pregnancy on serotonin content in intestine. Serotonin content was measured in duodenum, jejunum and colon. No significant difference in serotonin content of the intestine was seen between non-pregnant (NP) and P15.5 mice (mean ± SEM, n = 5) (PDF 152 kb)
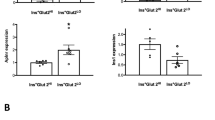
ESM Fig. 4
Prlr mRNA expression in islets during pregnancy and overproduction of STAT5. a Quantitative RT-PCR of Prlr mRNA expression of islets isolated from non-pregnant (NP) mice, pregnant mice as indicated and mice at 10 days postpartum (10 dpp). Data are mean ± SEM, n = 2–7. b Overproduction of constitutively active STAT5A and STAT5B, referred to as STAT5A1*6 and STAT5B1*6, in MIN6 cells. Tph1 mRNA expression of transfected cells was determined by quantitative RT-PCR, mean ± SEM, n = 5. cTph1 mRNA expression of MIN6 cells cultured with or without 500 ng/ml ovine PL (oPL) after overproduction of the dominant negative form called STAT5AΔ749; values mean ± SEM, n = 5. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 for difference between non-pregnant and pregnant or postpartum condition, and between indicated conditions (PDF 218 kb)
ESM Fig. 5
Content and release of insulin and serotonin from islets isolated from non-pregnant and pregnant mice. a Insulin content rose during pregnancy, mean ± SEM, n = 2–11. b Insulin release of islets from P15.5 mice (black bars), adjusted for insulin content, was enhanced as compared with non-pregnant (NP) islets (white bars) in glucose stimulated conditions. Release and content were measured after 1 h incubation in 5, 10 or 20 mmol/l glucose, mean ± SEM, n = 5–7. c Insulin (white bars) and serotonin (black bars) content were measured for islets after 1 h incubation in 5 or 20 mmol/l glucose, mean ± SEM, n = 4. d As described for c for MIN6 cells after 1 h in 2 or 20 mmol/l glucose, mean ± SEM, n = 4. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 for differences between non-pregnant and pregnant conditions (PDF 200 kb)
ESM Fig. 6
Serotonin immunoreactivity in MIN6 cells incubated with different concentrations of ovine PL (oPL), see also Fig. 5c. MIN6 cells were treated with different concentrations of oPL for 24 h and immunostained for serotonin. The amount of cells positive for serotonin (red) increased with oPL concentration. Cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue) (PDF 1143 kb)
ESM Fig. 7
Expression profiles of serotonin receptors in islets of Langerhans during pregnancy. mRNA expression of serotonin receptors was analysed via microarray using two different microarray platforms. a Profile determined by Affymetrix MOE430_2.0 arrays of islets from non-pregnant mice (NP, black bars), P15.5 mice (red bars), brain cortex (white bars) and brainstem (grey bars). b–o Profiles determined by MoGene_1.0_ST arrays of islets in conditions and at times indicated. NP, non-pregnant; 10 dpp, 10 days postpartum. Values are mean ± SD, n ≥ 3. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 for differences between non-pregnant and pregnant conditions, as determined by Student’s t test. Note: none of the receptors reached the criteria of p < 0.001 and fold-change ≥1.5, which were used to search for differentially expressed genes (PDF 430 kb)
ESM Fig. 8
Beta cell proliferation in Tph1-KO mice during pregnancy was estimated via Mki67 and insulin immunostaining, expressed as per cent of insulin-positive cells. Values mean ± SEM, animals 10 to 11 weeks old, n = 2 for KO, n = 3 for wild-type. Although serotonin staining was absent in P12.5 Tph1-KO mice, a similar amount of beta cell proliferation was detected in these compared with wild-type mice (PDF 148 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Schraenen, A., Lemaire, K., de Faudeur, G. et al. Placental lactogens induce serotonin biosynthesis in a subset of mouse beta cells during pregnancy. Diabetologia 53, 2589–2599 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-010-1913-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-010-1913-7