Abstract
Key message
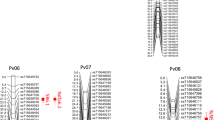
The genetic architecture of symbiotic N fixation and related traits was investigated in the field. QTLs were identified for percent N derived from the atmosphere, shoot [N] and C to N ratio.
Abstract
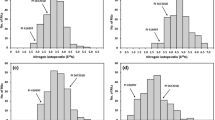
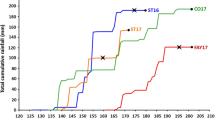
Soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] is cultivated worldwide and is the most abundant source of plant-based protein. Symbiotic N2 fixation (SNF) in legumes such as soybean is of great importance; however, yields may still be limited by N in both high yielding and stressful environments. To better understand the genetic architecture of SNF and facilitate the development of high yielding cultivars and sustainable soybean production in stressful environments, a recombinant inbred line population consisting of 190 lines, developed from a cross between PI 442012A and PI 404199, was evaluated for N derived from the atmosphere (Ndfa), N concentration ([N]), and C to N ratio (C/N) in three environments. Significant genotype, environment and genotype × environment effects were observed for all three traits. A linkage map was constructed containing 3309 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers. QTL analysis was performed for additive effects of QTLs, QTL × environment interactions, and QTL × QTL interactions. Ten unique additive QTLs were identified across all traits and environments. Of these, two QTLs were detected for Ndfa and eight for C/N. Of the eight QTLs for C/N, four were also detected for [N]. Using QTL × environment analysis, six QTLs were detected, of which five were also identified in the additive QTL analysis. The QTL × QTL analysis identified four unique epistatic interactions. The results of this study may be used for genomic selection and introgression of favorable alleles for increased SNF, [N], and C/N via marker-assisted selection.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Ågren GI (2004) The C:N: P stoichiometry of autotrophs - theory and observations. Ecol Lett 7(3):185–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00567.x
Atkins CA (1974) Occurrence and some properties of carbonic anhydrases from legume root nodules. Phytochemistry 13(1):93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(00)91273-1
Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker BM, Walker SC (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Bazzer SK, Kaler AS, Ray JD, Smith JR, Fritschi FB, Purcell LC (2020a) Identification of quantitative trait loci for carbon isotope ratio (δ13C) in a recombinant inbred population of soybean. Theor Appl Genet 133(7):2141–2155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-020-03586-0
Bazzer SK, Ray JD, Smith JR, Fritschi FB, Purcell LC (2020b) Mapping quantitative trait loci (QTL) for plant nitrogen isotope ratio (δ15N) in soybean. Euphytica. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-020-02726-3
Bergersen F, Brockwell J, Gault R, Morthorpe M, Peoples M, Turner G (1989) Effects of available soil nitrogen and rates of inoculation on nitrogen fixation by irrigated soybeans and evaluation of δ15N methods for measurement. Aust J Agric Res 40:763–780
Betts JH, Herridge DF (1987) Isolation of soybean lines capable of nodulation and nitrogen fixation under high levels of nitrate supply. Crop Sci 27(6):1156–1161. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1987.0011183x002700060014x
Bigeleisen J, Mayer MC (1947) Calculation of equilibrium constants for isotopic exchange reactions. J Chem Phys 15(5):261–267
Bulen W, Lecomte J (1966) The nitrogenase system from azotobacter: two-enzyme requirement for N2 reduction, ATP-dependent H2 evolution, and ATP-hydrolysis. Proc Nat Acad Sci 56:979–986
Cafaro La Menza N, Monzon J, Lindquist J, Arkebauer T, Knops J, Unkovich M, Specht J, Grassini P (2020) Insufficient nitrogen supply from symbiotic fixation reduces seasonal crop growth and nitrogen mobilization to seed in highly productive soybean crops. Plant, Cell Environ 43(8):1958–1972. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13804
Carter TE, Todd SM, Gillen AM (2016) Registration of ‘USDA-N8002’ soybean cultivar with high yield and abiotic stress resistance traits. J Plant Registrations 10(3):238–245. https://doi.org/10.3198/jpr2015.09.0057crc
Cassab GI, Varner JE (1988) Cell wall proteins. Annual Rev. Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 39:321–353
Coruzzi GM, Zhou L (2001) Carbon and nitrogen sensing and signaling in plants: emerging “matrix effects.” Curr Opin Plant Biol 4(3):247–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00168-0
D’haeseleer, K., den Herder, G., Laffont, C., Plet, J., Mortier, V., Lelandais-Brière, C., de Bodt, S., de Keyser, A., Crespi, M., Holsters, M., Frugier, F., & Goormachtig, S (2011) Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of a NAC1 transcription factor in Medicago truncatula roots. New Phytol 191(3):647–661. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03719.x
Dhanapal AP, Ray JD, Singh SK, Hoyos-Villegas V, Smith JR, Purcell LC, King CA, Fritschi FB (2015) Genome-wide association analysis of diverse soybean genotypes reveals novel markers for nitrogen traits. The Plant Genome. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2014.11.0086
Diaz del Castillo L, Hunt S, Layzell D (1994) The role of oxygen in the regulation of nitrogenase activity in drought-stressed soybean nodules’. Plant Physiol 106:949–955
DiMario RJ, Clayton H, Mukherjee A, Ludwig M, Moroney JV (2017) Plant carbonic anhydrases: structures, locations, evolution, and physiological roles. Mol Plant 10(1):30–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.09.001
Djekoun A, Planchon C (1991) Water status effect on dinitrogen fixation and photosynthesis in soybean. Agron J 83:316–322
Ebert B, Rautengarten C, Guo X, Xiong G, Stonebloom S, Smith-Moritz AM, Herter T, Chan LJG, Adams PD, Petzold CJ, Pauly M, Willats WGT, Heazlewood JL, Adams PD (2015) Identification and characterization of a golgi-localized UDP-xylose transporter family from arabidopsis. Plant Cell 27(4):1218–1227. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.133827
FAOSTAT. (2021).
Farrow SC, Facchini PJ (2014) Functional diversity of 2-oxoglutarate/Fe(II)-dependent dioxygenases in plant metabolism. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00524
Fehr WR, Caviness CE, Burmood DT, Pennington JS (1971) Stage of development descriptions for soybeans, Glycine Max (L.) Merrill. Crop Sci 11:929–931
Groth M, Takeda N, Perry J, Uchid H, Dräxl S, Brachmann A, Sato S, Tabata S, Kawaguchi M, Wang TL, Parniskea M (2010) NENA, a Lotus japonicus homolog of Sec13, is required for rhizodermal infection by arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi and rhizobia but dispensable for cortical endosymbiotic development. Plant Cell 22(7):2509–2526. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.069807
Grunvald AK, Torres AR, de Lima L, Passianotto A, Santos MA, Jean M, Belzile F, Hungria M (2018) Identification of QTLs associated with biological nitrogen fixation traits in soybean using a genotyping-by-sequencing approach. Crop Sci 58(6):2523–2532. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2018.01.0031
Guinel F (2015) Ethylene, a hormone at the center-stage of nodulation. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01121
Herridge D, Rose I (2000) Breeding for enhanced nitrogen fixation in crop legumes. Field Crop Res 65:229–248
Herridge D, Atkins C, Pate J, Rainbird R (1978) Allantoin and allantoic acid in the nitrogen economy of the cowpea (Vigna unguiculata [L.] Walp). Plant Physiol 62:495–498
Hoefs, J. (1997). Theoretical and Experiment Principles. In Stable Isotope Geochemistry (Eighth). Springer. http://www.springer.com/series/15201
Hu H, Rappel WJ, Occhipinti R, Ries A, Böhmer M, You L, Xiao C, Engineer CB, Boron WF, Schroeder JI (2015) Distinct cellular locations of carbonic anhydrases mediate carbon dioxide control of stomatal movements. Plant Physiol 169(2):1168–1178. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00646
Huang N-C, Liu K-H, Lo H-J, Tsay Y-F (1999) Cloning and functional characterization of an arabidopsis nitrate transporter gene that encodes a constitutive component of low-affinity uptake. Plant Cell 11:1381–1392
Huang J, Ma Q, Cai Z, Xia Q, Li S, Jia J, Chu L, Lian T, Nian H, Cheng Y (2020) Identification and mapping of stable QTLs for seed oil and protein content in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. J Agric Food Chem 68(23):6448–6460. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01271
Huo X, Li X, Du H, Kong Y, Tian R, Li W, Zhang C (2019) Genetic loci and candidate genes of symbiotic nitrogen fixation–related characteristics revealed by a genome-wide association study in soybean. Mol Breed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-019-1022-3
Hwang S, King CA, Davies MK, Ray JD, Cregan PB, Purcell LC (2013) QTL analysis of shoot ureide and nitrogen concentrations in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. Crop Sci. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2012.11.0641
Hwang S, Ray JD, Cregan PB, Purcell LC (2014) Genetics and mapping of quantitative traits for nodule number, weight, and size in soybean (Glycine max L.[Merr.]). Euphytica 195:419–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-013-1005-0
Karim S, Lundh D, Holmström KO, Mandal A, Pirhonen M (2005) Structural and functional characterization of AtPTR3, a stress-induced peptide transporter of Arabidopsis. J Mol Model 11(3):226–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-005-0257-6
Karim S, Holmström KO, Mandal A, Dahl P, Hohmann S, Brader G, Palva ET, Pirhonen M (2007) AtPTR3, a wound-induced peptide transporter needed for defence against virulent bacterial pathogens in Arabidopsis. Planta 225(6):1431–1445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0451-5
King CA, Purcell LC (2005) Inhibition of N2 fixation in soybean is associated with elevated ureides and amino acids. Plant Physiol 137(4):1389–1396. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.056317
King CA, Purcell LC (2006) Genotypic variation for shoot N concentration and response to water deficits in soybean. Crop Sci 46(6):2396–2402. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2006.03.0165
Kohl DH, Shearer G (1980) Isotopic fractionation associated with symbiotic N2 fixation and uptake of NO2 by plants. Plant Physiol 66(1):51–56
Lerouge P, Roche P, Fauchert C, Maillett F, Truchett G, Prome JC, Denariet J (1990) Symbiotic host-specificity of Rhizobium meliloti is determined by a sulphated and acylated glucosamine oligosaccharide signal. Nature 344:781–784
Libault M, Farmer A, Brechenmacher L, Drnevich J, Langley RJ, Bilgin DD, Radwan O, Neece DJ, Clough SJ, May GD, Stacey G (2010) Complete transcriptome of the soybean root hair cell, a single-cell model, and its alteration in response to Bradyrhizobium japonicum infection. Plant Physiol 152(2):541–552. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.148379
Lumactud RA, Dollete D, Liyanage DK, Szczyglowski K, Hill B, Thilakarathna MS (2022) The effect of drought stress on nodulation, plant growth, and nitrogen fixation in soybean during early plant growth. J Agron Crop Sci. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12627
MacKay TFC, Stone EA, Ayroles JF (2009) The genetics of quantitative traits: challenges and prospects. Nat Rev Genet 10(8):565–577. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2612
Manjarrez-Sandoval P, Chen P, Mozzoni L, Florez-Palacios L, Orazaly M, Wu C, Sinclair TR, Carter TE, Purcell LC, King CA (2020) Registration of soybean germplasm lines R10–2436 and R10–2710 with drought tolerance traits and high yield under moderate water stress. J Plant Regist 14(2):189–196. https://doi.org/10.1002/plr2.20048
Mariotti A (1983) Atmospheric nitrogen is a reliable standard for 15N abundance measurements. Nature 303(23):685–687
Maurino VG, Engqvist MKM (2015) 2-Hydroxy acids in plant metabolism. The Arabidopsis Book 13:e0182. https://doi.org/10.1199/tab.0182
Medic J, Atkinson C, Hurburgh CR (2014) Current knowledge in soybean composition. J Am Oil Chem Soc 91(3):363–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-013-2407-9
Meng L, Li H, Zhang L, Wang J (2015) QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J 3(3):269–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2015.01.001
Mylona P, Pawlowski K, Bisseling T (1995) Symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Plant Cell 7:869–885
Oldroyd GED, Downie JA (2008) Coordinating nodule morphogenesis with rhizobial infection in legumes. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:519–546. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092839
Ooki Y, Banba M, Yano K, Maruya J, Sato S, Tabata S, Saeki K, Hayashi M, Kawaguchi M, Izui K, Hata S (2005) Characterization of the Lotus japonicus symbiotic mutant lot1 that shows a reduced nodule number and distorted trichomes. Plant Physiol 137(4):1261–1271. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.056630
Pate JS, Atkins CA, White ST, Rainbird RM, Woo KC (1980) Nitrogen nutrition and xylem transport of nitrogen in ureide-producing grain legumes. Plant Physiol 65:961–965
Penmetsa RV, Cook DR (1997) A legume ethylene-insensitive mutant hyperinfected by its rhizobial symbiont. Science 275(5299):527–530
Piepho HP, Möhring J (2007) Computing heritability and selection response from unbalanced plant breeding trials. Genetics 177(3):1881–1888. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.107.074229
Ray JD, Dhanapal AP, Singh SK, Hoyos-Villegas V, Smith JR, Purcell LC, King CA, Boykin D, Cregan PB, Song Q, Fritschi FB (2015) Genome-wide association study of ureide concentration in diverse maturity group IV soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] accessions. G3 Genes, Genom, Genet 5(11):2391–2403. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.115.021774
Roy S, Liu W, Nandety RS, Crook A, Mysore KS, Pislariu CI, Frugoli J, Dickstein R, Udvardi MK (2020) Celebrating 20 years of genetic discoveries in legume nodulation and symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Plant Cell 32(1):15–41. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00279
Sall K, Sinclair TR (1991) Soybean genotypic differences in sensitivity of symbiotic nitrogen fixation to soil dehydration. Plant Soil 133:31–37
Salvagiotti F, Cassman KG, Specht JE, Walters DT, Weiss A, Dobermann A (2008) Nitrogen uptake, fixation and response to fertilizer N in soybeans: a review. Field Crop Res 108(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2008.03.001
Santachiara G, Borrás L, Salvagiotti F, Gerde JA, Rotundo JL (2017) Relative importance of biological nitrogen fixation and mineral uptake in high yielding soybean cultivars. Plant Soil 418(1–2):191–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3279-9
Serraj R, Sinclair TR, Purcell LC (1999) Symbiotic N 2 fixation response to drought. J Exp Botany 50(331):143–155
Serraj R, Vadez V, Sinclair TR (2001) Feedback regulation of symbiotic N 2 fixation under drought stress. Agronomie 21:621–626
Shapiro SS, Wilk MB (1965) An Analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 52(3):591–611
Shearer G, Kohl DH (1986) N2-Fixation in field settings: estimations based on natural 15N abundance. Rev Aust J Plant Physiol 13:699–756
Shearer G, Kohl DH, Chien S (1978) The Nitrogen-15 abundance in a wide variety of soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42(6):899–902. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1978.03615995004200060013x
Sinclair TR, De Wit CT (1975) Photosynthate and nitrogen requirements for seed production by various crops. Science 189(4202):565–567
Sinclair TR, Serraj R (1995) Legume nitrogen fixation and drought. Nature 378:344–344
Song Q, Hyten DL, Jia G, Quigley CV, Fickus EW, Nelson RL, Cregan PB (2013) Development and evaluation of SoySNP50K, a High-density genotyping array for soybean. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054985
Song Q, Yan L, Quigley C, Jordan BD, Fickus E, Schroeder S, Song B, Charles An Y, Hyten D, Nelson R, Rainey K, Beavis WD, Specht J, Diers B, Cregan P (2017) Genetic characterization of the soybean nested association mapping population. The Plant Genome. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2016.10.0109
Steketee CJ, Sinclair TR, Riar MK, Schapaugh WT, Li Z (2019) Unraveling the genetic architecture for carbon and nitrogen related traits and leaf hydraulic conductance in soybean using genome-wide association analyses. BMC Genom. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-6170-7
Tanya P, Srinivies P, Toojinda T, Vanavichit A, Lee S (2005) Identification of SSR markers associated with N-2-fixation components in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. Korean J Genet 27:351–359
Unkovich, Murray., & Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research (2008) Measuring plant-associated nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Australian Centre Int Agric Res. https://doi.org/10.5555/20093005327
Vadez V, Sinclair TR (2001) Leaf ureide degradation and N2 fixation tolerance to water deficit in soybean. J Exp Bot 52(354):153–159
van de Sande K, Pawlowski K, Czaja I, Wieneke U, Schell J, Schmidt J, Walden R, Matvienko M, Wellink J, van Kammen A, Franssen H, Bisseling T (1996) Modification of Phytohormone response by a peptide encoded by ENOD40 of legumes and a nonlegume. Science 273:370–373
Wanek W, Arndt SK (2002) Difference in d15N signatures between nodulated roots and shoots of soybean is indicative of the contribution of symbiotic N 2 fixation to plant N. J Exp Bot 53(371):1109–1118
Xie Q, Frugis G, Colgan D, Chua NH (2000) Arabidopsis NAC1 transduces auxin signal downstream of TIR1 to promote lateral root development. Genes Dev 14(23):3024–3036. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.852200
Yan W, Zhong Y, Shangguan Z (2015) The relationships and sensibility of wheat C:N: P stoichiometry and water use efficiency under nitrogen fertilization. Plant, Soil Environ 61(5):201–207. https://doi.org/10.17221/28/2015-PSE
Zhang L, Yu Z, Xu Y, Yu M, Ren Y, Zhang S, Yang G, Huang J, Yan K, Zheng C, Wu C (2021) Regulation of the stability and ABA import activity of NRT1.2/NPF4.6 by CEPR2-mediated phosphorylation in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 14(4):633–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2021.01.009
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge partial funding of this research by the United Soybean Board (Project #1820-172-0118-A). This research was supported in part by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. We gratefully acknowledge the technical field assistance of Mr. Philip Handly, Mr. Hans Hinrichsen, and Mr. Matt Kersh in Stoneville. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the US Department of Agriculture. The findings and conclusions in this publication are those of the authors and should not be construed to represent any official USDA or U.S. Government determination or policy. USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge partial funding of this research by the United Soybean Board (Project #1820–172-0118-A). This research was supported in part by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JRS and AP led the development of the genetic material. All authors contributed to performance of field experiments. CBK, MA, and JDR analyzed the data. CBK wrote manuscript with editing by FBF, JDR, and JRS. FBF, JDR, and JRS designed the experiment. FBF coordinated the project. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by Istvan Rajcan.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Krueger, C.B., Ray, J.D., Smith, J.R. et al. Identification of QTLs for symbiotic nitrogen fixation and related traits in a soybean recombinant inbred line population. Theor Appl Genet 137, 89 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-024-04591-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-024-04591-3