Abstract
Key message
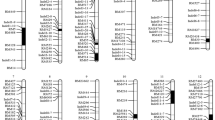
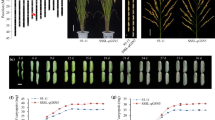
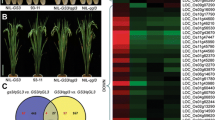
A novel quantitative trait locus qIGL1, which performed a positive function in regulating grain length in rice, was cloned by the map-based cloning approach; further studies revealed that it corresponded to LOC_Os03g30530, and the IGL1 appeared to contribute to lengthening and widening of the cells on the surface of grain hulls.
Abstract
Grain length is a prominent determinant for grain weight and appearance quality of rice. In this study, we conducted quantitative trait locus mapping to determine a genomic interval responsible for a long-grain phenotype observed in a japonica cultivar HD385. This led to the identification of a novel QTL for grain length on chromosome 3, named qIGL1 (for Increased Grain Length 1); the HD385 (Handao 385)-derived allele showed enhancement effects on grain length, and such an allele as well as NIP (Nipponbare)-derived allele was designated qigl1 HD385 and qIGL1NIP, respectively. Genetic analysis revealed that the qigl1HD385 allele displayed semidominant effects on grain length. Fine mapping further narrowed down the qIGL1 to an ~ 70.8-kb region containing 9 open reading frames (ORFs). A comprehensive analysis indicated that LOC_Os03g30530, which corresponded to ORF6 and carried base substitutions and deletions in HD385 relative to NIP, thereby causing changes or losses of amino-acid residues, was the true gene for qIGL1. Comparison of grain traits between a pair of near-isogenic lines (NILs), termed NIL-igl1HD385 and NIL-IGL1NIP, discovered that introduction of the igl1HD385 into the NIP background significantly resulted in the elevations of grain length and 1000-grain weight. Closer inspection of grain surfaces revealed that the cell length and width in the longitudinal direction were significantly longer and greater, respectively, in NIL-igl1HD385 line compared with in NIL-IGL1NIP line. Hence, our studies identified a new semidominant natural allele contributing to the increase of grain length and further shed light on the regulatory mechanisms of grain length.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated during the current study are available in the GenBank repository and can be accessed with the accession number GSE241093 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE241093).
Abbreviations
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
- RIL:
-
Recombinant inbred line
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- NIL:
-
Near-isogenic line
- GS3 :
-
GRAIN SIZE 3
- GL3.1 :
-
GRAIN LENGTH 3.1
- GS2 :
-
GRAIN SIZE ON CHROMOSOME 2
- GL2 :
-
GRAIN LENGTH2
- GLW2 :
-
GRAIN LENGTH AND WIDTH 2
- PT2 :
-
PANICLE TRAITS 2
- OsGRF4 :
-
GROWTH REGULATION FACTOR4
- LGY3 :
-
LONG GRAIN AND HIGH YIELD 3
- GW7 :
-
GRAIN WIDTH 7
- GL7 :
-
GRAIN LENGTH ON CHROMOSOME 7
- SLG7 :
-
SLENDER GRAIN ON CHROMOSOME 7
- GW8 :
-
GRAIN WIDTH 8
- OsSPL16 :
-
SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE 16
- GS9 :
-
GRAIN SIZE 9
- GSK2 :
-
GSK3/SHAGGY-LIKE KINASE 2
- GL10 :
-
GRAIN LENGTH 10
- SMOS1 :
-
SMALL ORGAN SIZE1
- RLA1 :
-
REDUCED LEAF ANGLE 1
- NGR5 :
-
NITROGEN-MEDIATED TILLER GROWTH RESPONSE 5
- DEP1 :
-
DENSE AND ERECT PANICLE 1
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphism
- InDel:
-
Insertion-deletions
- SSR :
-
Simple sequence repeat
- ICIM:
-
The inclusive composite interval map-ping
- LOD:
-
Logarithm of odds score
- DEG:
-
Differentially expressed gene
References
Aya K, Hobo T, Sato-Izawa K, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2014) A novel AP2-type transcription factor, SMALL ORGAN SIZE1, controls organ size downstream of an auxin signaling pathway. Plant Cell Physiol 55:897–912. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcu023
Che RH, Tong HN, Shi BH, Liu YQ, Fang SR, Liu DP, Xiao YH, Hu B, Liu LC, Wang HR, Zhao MF, Chu CC (2016) Control of grain size and rice yield by GL2-mediated brassinosteroid responses. Nat Plants 2:15195. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2015.195
Chen WL, Hu XL, Hu L, Hou XY, Xu ZY, Yang FM, Yuan M, Chen FF, Wang YX, Tu B, Li T, Kang LZ, Tang SW, Ma BT, Wang YP, Li SG, Qin P, Yuan H (2022) Wide grain 3, a GRAS protein, interacts with DLT to regulate grain size and brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Rice 15:55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-022-00601-4
Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G, Albers CA, Banks E, DePristo MA, Handsaker RE, Lunter G, Marth GT, Sherry ST, McVean G, Durbin R, Group GPA (2011) The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 27:2156–2158. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr330
Deng W, Li R, Yiwei Xu, Mao R, Chen S, Chen L, Letian Chen YC, Liu Y-G (2019) A lipid transfer protein variant with a mutant eight-cysteine motif causes photoperiod- and thermo-sensitive dwarfism in rice. J Exp Bot 71:1924–1305. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz500
Duan PG, Ni S, Wang JM, Zhang BL, Xu R, Wang YX, Chen HQ, Zhu XD, Li YH (2016) Regulation of OsGRF4 by OsmiR396 controls grain size and yield in rice. Nat Plants 2:15203. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2015.226
Fan C, Xing Y, Mao H, Lu T, Han B, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2006) GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet 112:1164–1171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0218-1
Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J 6:271–282. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1994.6020271.x
Hirano K, Yoshida H, Aya K, Kawamura M, Hayashi M, Hobo T, Sato-Izawa K, Kitano H, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Matsuoka M (2017) SMALL ORGAN SIZE 1 and SMALL ORGAN SIZE 2/DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING form a complex to integrate auxin and brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Mol Plant 10:590–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.12.013
Hu J, Wang YX, Fang YX, Zeng LJ, Xu J, Yu HP, Shi ZY, Pan JJ, Zhang D, Kang SJ, Zhu L, Dong GJ, Guo LB, Zeng DL, Zhang GH, Xie LH, Xiong GS, Li JY, Qian Q (2015) A rare allele of GS2 enhances grain size and grain yield in rice. Mol Plant 8:1455–1465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.07.002
Hu Z, Lu SJ, Wang MJ, He H, Sun L, Wang H, Liu XH, Jiang L, Sun JL, Xin X, Kong W, Chu C, Xue HW, Yang J, Luo X, Liu JX (2018) A novel QTL qTGW3 encodes the GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase OsGSK5/OsSK41 that interacts with OsARF4 to negatively regulate grain size and weight in rice. Mol Plant 11:736–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2018.03.005
Huang XZ, Qian Q, Liu ZB, Sun HY, He SY, Luo D, Xia GM, Chu CC, Li JY, Fu XD (2009) Natural variation at the DEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice. Nat Genet 41:494–497. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.352
Jin Y, Luo Q, Tong H, Wang A, Cheng Z, Tang J, Li D, Zhao X, Li X, Wan J, Jiao Y, Chu C, Zhu L (2011) An AT-hook gene is required for palea formation and floral organ number control in rice. Dev Biol 359:277–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.08.023
Khush GS (2005) What it will take to feed 5.0 billion rice consumers in 2030. Plant Mol Biol 59:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-005-2159-5
Lei M, Huihui Li, Luyan Z, Jiankang W (2015) QTL IciMapping: integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. The Crop J 3:269–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2015.01.001
Li Y, Fan C, Xing Y, Jiang Y, Luo L, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C, Li X, Xiao J, He Y, Zhang Q (2011) Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat Genet 43:1266–1269. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.977
Li SC, Gao FY, Xie KL, Zeng XH, Cao Y, Zeng J, He ZS, Ren Y, Li WB, Deng QM, Wang SQ, Zheng AP, Zhu J, Liu HN, Wang LX, Li P (2016) The OsmiR396c-OsGRF4-OsGIF1 regulatory module determines grain size and yield in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 14:2134–2146. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12569
Li N, Xu R, Li Y (2019) Molecular networks of seed size control in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 70:435–463. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050718-095851
Liu J, Chen J, Zheng X, Wu F, Lin Q, Heng Y, Tian P, Cheng Z, Yu X, Zhou K, Zhang X, Guo X, Wang J, Wang H, Wan J (2017) GW5 acts in the brassinosteroid signalling pathway to regulate grain width and weight in rice. Nat Plants 3:17043. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2017.43
Liu Q, Han RX, Wu K, Zhang JQ, Ye YF, Wang SS, Chen JF, Pan YJ, Li Q, Xu XP, Zhou JW, Tao DY, Wu YJ, Fu XD (2018) G-protein beta gamma subunits determine grain size through interaction with MADS-domain transcription factors in rice. Nat Commun 9:852. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03047-9
Mao H, Sun S, Yao J, Wang C, Yu S, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2010) Linking differential domain functions of the GS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:19579–19584. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1014419107
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Khush GS, Coffman WR, Tanksley SD (1988) Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 76:815–829. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00273666
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PI, Daly MJ, Sham PC (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575. https://doi.org/10.1086/519795
Qi P, Lin YS, Song XJ, Shen JB, Huang W, Shan JX, Zhu MZ, Jiang L, Gao JP, Lin HX (2012) The novel quantitative trait locus GL3.1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating Cyclin-T1;3. Cell Res 22:1666–16680. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2012.151
Qian Q, Zhu L (2020) Gain-of-function mutations: key tools for modifying or designing novel proteins in plant molecular engineering. J Exp Bot 71:1203–1205. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz519
Qiao SL, Sun SY, Wang LL, Wu ZH, Li CX, Li XM, Wang T, Leng LN, Tian WS, Lu TG, Wang XL (2017) The RLA1/SMOS1 transcription factor functions with OsBZR1 to regulate brassinosteroid signaling and rice architecture. Plant Cell 29:292–309. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00611
Qiao JY, Jiang HZ, Lin YQ, Shang LG, Wang M, Li DM, Fu XD, Geisler M, Qi YH, Gao ZY, Qian Q (2021) A novel miR167a-OsARF6-OsAUX3 module regulates grain length and weight in rice. Mol Plant 14:1683–1698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2021.06.023
Qiong G, Ning Z, Wei-Qing W, Shao-Yan S, Chen B, Xian-Jun S (2021) The ubiquitin-interacting motif-type ubiquitin receptor HDR3 interacts with and stabilizes the histone acetyltransferase GW6a to control the grain size in rice. Plant Cell 33:3331–3347. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koab194
Ruan BP, Shang LG, Zhang B, Hu J, Wang YX, Lin H, Zhang AP, Liu CL, Peng YL, Zhu L, Ren DY, Shen L, Dong GJ, Zhang GH, Zeng DL, Guo LB, Qian Q, Gao ZY (2020) Natural variation in the promoter of TGW2 determines grain width and weight in rice. New Phytol 227:629–640. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16540
Sakamoto T, Matsuoka M (2008) Identifying and exploiting grain yield genes in rice. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2008.01.009
Shi CL, Dong NQ, Guo T, Ye WW, Shan JX, Lin HX (2020) A quantitative trait locus GW6 controls rice grain size and yield through the gibberellin pathway. Plant J 103:1174–1188. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14793
Song XJ, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Lin HX (2007) A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet 39:623–630. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng2014
Sun P, Zhang W, Wang Y, He Q, Shu F, Liu H, Wang J, Yuan L, Deng H (2016) OsGRF4 controls grain shape, panicle length and seed shattering in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 58:836–847. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12473
Sun S, Wang L, Mao H, Shao L, Li X, Xiao J, Ouyang Y, Zhang Q (2018) A G-protein pathway determines grain size in rice. Nat Commun 9:851. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03141-y
Tang QY, Zhang CX (2013) Data processing system (DPS) software with experimental design, statistical analysis and data mining developed for use in entomological research. Insect Sci 20:254–260. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7917.2012.01519.x
Tong HN, Liu LC, Jin Y, Du L, Yin YH, Qian Q, Zhu LH, Chu CC (2012) DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase to mediate brassinosteroid responses in rice. Plant Cell 24:2562–2577. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.097394
Wang S, Wu K, Yuan Q, Liu X, Liu Z, Lin X, Zeng R, Zhu H, Dong G, Qian Q, Zhang G, Fu X (2012) Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet 44:950–954. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2327
Wang SK, Li S, Liu Q, Wu K, Zhang JP, Wang SS, Wang Y, Chen XB, Zhang Y, Gao CX, Wang F, Huang HX, FU XD (2015a) The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality. Nat Genet 47:949–954. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3352
Wang Y, Xiong G, Hu J, Jiang L, Yu H, Xu J, Fang Y, Zeng L, Xu E, Ye W, Meng X, Liu R, Chen H, Jing Y, Zhu X, Li J, Qian Q (2015b) Copy number variation at the GL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice. Nat Genet 47:944–948. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3346
Wang AH, Hou QQ, Si LZ, Huang XH, Luo JH, Lu DF, Zhu JJ, Shangguan YY, Miao JS, Xie YF, Wang YC, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhou CC, Li Y, Fan DL, Lu YQ, Tian QL, Wang ZX, Han B (2019) The PLATZ transcription factor GL6 affects grain length and number in rice. Plant Physiol 180:2077–2090. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.01574
Wang CC, Yu H, Huang J, Wang WS, Faruquee M, Zhang F, Zhao XQ, Fu BY, Chen K, Zhang HL, Tai SS, Wei C, McNally KL, Alexandrov N, Gao XY, Li J, Li ZK, Xu JL, Zheng TQ (2020) Towards a deeper haplotype mining of complex traits in rice with RFGB v2.0. Plant Biotechnol J 18:14–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13215
Wing RA, Purugganan MD, Zhang Q (2018) The rice genome revolution: from an ancient grain to green super rice. Nat Rev Genet 19:505–517. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-018-0024-z
Wu K, Wang S, Song W, Zhang J, Wang Y, Liu Q, Yu J, Ye Y, Li S, Chen J, Zhao Y, Wang J, Wu X, Wang M, Zhang Y, Liu B, Wu Y, Harberd NP, Fu X (2020) Enhanced sustainable green revolution yield via nitrogen-responsive chromatin modulation in rice. Science 367:eaaz2046. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaz2046
Wu Y, Zhao Y, Yu J, Wu C, Wang Q, Liu X, Gao X, Wu K, Fu X, Liu Q (2023) Heterotrimeric G protein γ subunit DEP1 synergistically regulates grain quality and yield by modulating the TTP (TON1-TRM-PP2A) complex in rice. J Genet Genom 50:528–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2023.02.009
Xie W, Wang G, Yuan M, Yao W, Lyu K, Zhao H, Yang M, Li P, Zhang X, Yuan J, Wang Q, Liu F, Dong H, Zhang L, Li X, Meng X, Zhang W, Xiong L, He Y, Wang S, Yu S, Xu C, Luo J, Li X, Xiao J, Lian X, Zhang Q (2015) Breeding signatures of rice improvement revealed by a genomic variation map from a large germplasm collection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:E5411-5419. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1515919112
Xing Y, Zhang Q (2010) Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:421–442. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112209
Ying JZ, Ma M, Bai C, Huang XH, Liu JL, Fan YY, Song XJ (2018) TGW3, a Major QTL that negatively modulates grain length and weight in rice. Mol Plant 11:750–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2018.03.007
Yu J, Miao J, Zhang Z, Xiong H, Zhu X, Sun X, Pan Y, Liang Y, Zhang Q, Abdul Rehman RM, Li J, Zhang H, Li Z (2018) Alternative splicing of OsLG3b controls grain length and yield in japonica rice. Plant Biotechnol J 16:1667–1678. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12903
Zhan PL, Ma SP, Xiao ZL, Li FP, Wei X, Lin SJ, Wang XL, Ji Z, Fu Y, Pan JH, Zhou M, Liu Y, Chang ZY, Li L, Bu SH, Liu ZP, Zhu HT, Liu GF, Zhang GQ, Wang SK (2022) Natural variations in grain length 10 (GL10) regulate rice grain size. J Genet Genom 49:405–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2022.01.008
Zhang XJ, Wang JF, Huang J, Lan HX, Wang CL, Yin CF, Wu YY, Tang HJ, Qian Q, Li JY, Zhang HS (2012) Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:21534–21539. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1219776110
Zhang ZY, Li JJ, Tang ZS, Sun XM, Zhang HL, Yu JP, Yao GX, Li GL, Guo HF, Li JL, Wu HM, Huang HG, Xu YW, Yin ZG, Qi YH, Huang RF, Yang WC, Li ZC (2018) Gnp4/LAX2, a RAWUL protein, interferes with the OsIAA3-OsARF25 interaction to regulate grain length via the auxin signaling pathway in rice. J Exp Bot 69:4723–4737. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery256
Zhao TJ, Zhao SY, Chen HM, Zhao QZ, Hu ZM, Hou BK, Xia GM (2006) Transgenic wheat progeny resistant to powdery mildew generated by Agrobacterium inoculum to the basal portion of wheat seedling. Plant Cell Rep 25:1199–1204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-006-0184-8
Zhao DS, Li QF, Zhang CQ, Zhang C, Yang QQ, Pan LX, Ren XY, Lu J, Gu MH, Liu QQ (2018) GS9 acts as a transcriptional activator to regulate rice grain shape and appearance quality. Nat Commun 9:1240. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03616-y
Zhao H, Li J, Yang L, Qin G, Xia C, Xu X, Su Y, Liu Y, Ming L, Chen LL, Xiong L, Xie W (2021) An inferred functional impact map of genetic variants in rice. Mol Plant 14:1584–1599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2021.06.025
Zhou Y, Miao J, Gu H, Peng X, Leburu M, Yuan F, Gu H, Gao Y, Tao Y, Zhu J, Gong Z, Yi C, Gu M, Yang Z, Liang G (2015) Natural variations in SLG7 regulate grain shape in rice. Genetics 201:1591–1599. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.115.181115
Zuo J, Li J (2014) Molecular genetic dissection of quantitative trait loci regulating rice grain size. Annu Rev Genet 48:99–118. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-120213-092138
Acknowledgements
Data analysis was supported by the high-performance computing platform of Bioinformatics Center, Nanjing Agricultural University.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20211211) to H. Chen, and by Jiangsu Agriculture Science and Technology Innovation Fund (JASTIF) [CX(22)3156] to H. La and by Open Research Fund Program of Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Rice Genetics and Breeding (SDKF-2023–04) to Q. Wang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JN and HL conceived the experiments; JN, HC, and HL wrote the manuscript. JN, FW, CY, QY, TH and JH performed the laboratorial experiments. QW, PZ, YZ, LS and DA conducted part of field experiments. JD performed haplotype analysis. YL, ZZ, JG and JJ undertook the other data analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The authors declare that the study complies with the current laws of China.
Additional information
Communicated by Matthias Wissuwa.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, J., Wang, F., Yang, C. et al. Identification of Increased Grain Length 1 (IGL1), a novel gene encoded by a major QTL for modulating grain length in rice. Theor Appl Genet 137, 24 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-023-04531-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-023-04531-7