Abstract
Key message
A leaflet trait on different canopy layers may have different QTLs; leaflet trait QTLs may cluster to form joint QTL segments; all canopy layer QTLs form a complete QTL system for a leaflet trait.
Abstract
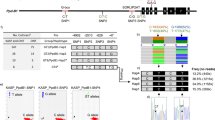
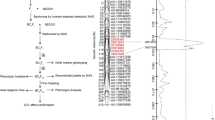
As the main part of the plant canopy structure, leaf/leaflet size and shape affect the plant architecture and yield. To explore the leaflet trait QTL system, a population composed of 199 recombinant inbred lines derived from Changling (annual wild, narrow leaflet) and Yiqianli (landrace, broad leaflet) with their parents was tested for leaflet length (LL), width (LW) and length to width (LLW). The population was genotyped with specific-locus amplified fragment sequencing (SLAF-seq) and applied for linkage mapping of the leaflet traits. The results showed that the leaflet traits varied greatly even within a plant, which supported a stratified leaflet sampling strategy to evaluate these traits at top, middle and bottom canopy layers. Altogether, 13 LL, 10 LW and 9 LLW in a total of 32 plus 3 duplicated QTLs were identified, in which, 17 QTLs were new ones, and 48.6%, 28.6% and 22.8% of QTLs were from the top, middle and bottom layers, respectively, indicating the genetic importance of the top layer leaves. Since a leaflet trait may have layer-specific QTLs, all layer QTLs form a complete QTL system. Five QTL clusters each with their QTL supporting intervals overlapped were designated as joint QTL segments (JQSs). In JQS-16, with its linkage map further validated using PCR markers, two QTLs, qLW-16-1 and qLLW-16-1 of the top layer leaflet, were identified six QTL·times. Six candidate genes were predicted, with Glyma.16G127900 as the most potential one for LW and LLW. Three PCR markers, Gm16PAV0653, BARCSOYSSR_16_0796 and YC-16-3, were suggested for marker-assisted selection for LW and LLW in JQS-16.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Anten NPR, Vermeulen PJ (2016) Tragedies and crops: understanding natural selection to improve cropping systems. Trends Ecol Evol 31(6):429–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2016.02.010
Bao XY, Li ZG, Yao XD (2021) Changes in photosynthetic traits and their responses to increasing fertilization rates in soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr) during decades of genetic improvement. J Sci Food Agric 101(11):4715–4723. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.11117
Dai N, Wang W, Patterson SE, Bleecker AB (2013) The TMK subfamily of receptor-like kinases in Arabidopsis display an essential role in growth and a reduced sensitivity to auxin. PLoS ONE 8(4):e60990. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060990
Donald CM (1968) The breeding of crop ideotypes. Euphytica 17:385–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00056241
Fang C, Ma YM, Wu SW et al (2017) Genome-wide association studies dissect the genetic networks underlying agronomical traits in soybean. Genome Biol 18:161. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-017-1289-9
Fehr WR, Caviness CE, Burmood DT, Pennington JS (1971) Stages of development descriptions for soybeans, Glycine max (L.) Merrill. Crop Sci 11(6):929–931. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1971.0011183X001100060051x
Gao SQ, Qiu HM, Hou YL et al (2017) Correlation analysis between symbiotic nitrogen fixation efficiency and root traits at soybean flower stage based on RIL population. Soybean Sci Technol 3:13–17
Guo W, Chen L, Luis HE et al (2020) Altering plant architecture to improve performance and resistance. Trends Plant Sci 25(11):1154–1170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2020.05.009
Hartwig EE, Edwards CJ (1970) Effects of morphological characteristics upon seed yield in soybeans. Agron J 62:64–65. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1970.00021962006200010021x
Jeong N, Moon JK, Kim HS et al (2011) Fine genetic mapping of the genomic region controlling leaflet shape and number of seeds per pod in the soybean. Theor Appl Genet 122(5):865–874. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1492-5
Jeong N, Suh SJ, Kim MH et al (2012) Ln is a key regulator of leaflet shape and number of seeds per pod in soybean. Plant Cell 24(12):4807–4818. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.104968
Jun TH, Freewalt K, Michel AP et al (2014) Identification of novel QTL for leaf traits in soybean. Plant Breed 133:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12107
Kim HK, Kang ST, Suh DY (2005) Analysis of quantitative trait loci associated with leaflet types in two recombinant inbred lines of soybean. Plant Breed 124(6):582–589. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2005.01152.x
Li M, Cheng LL, Zeng J et al (2020) Identification of additive–epistatic QTLs conferring seed traits in soybean using recombinant inbred lines. Front Plant Sci 11:566056. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.566056
Li YL, Cheng QS, Wu XX et al (2016) QTL mapping and epistatic interaction analysis of canopy parameters in soybean. Mol Plant Breed 14(12):3414–3429. https://doi.org/10.13271/j.mpb.014.003414
Lopez-Maestre H, Brinza L, Marchet C et al (2016) SNP calling from RNA-seq data without a reference genome: identification, quantification, differential analysis and impact on the protein sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 44(19):e148. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw655
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15(12):550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8(19):4321–4325. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/8.19.4321
Orf JH, Chase K, Jarvik T et al (1999) Genetics of soybean agronomic traits: I. Comparison of three related recombinant inbred populations. Crop Sci 39(6):1642–1651. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1999.3961642x
Reyes FC, Buono RA, Roschzttardtz H et al (2014) A novel endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) component in Arabidopsis thaliana controls cell expansion and development. J Biol Chem 289(8):4980–4988. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.529685
Richter R, Behringer C, Müller IK, Schwechheimer C (2010) The GATA-type transcription factors GNC and GNL/CGA1 repress gibberellin signaling downstream from DELLA proteins and phytochrome-interacting factors. Genes Dev 24(18):2093–2104. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.594910
Rogier O, Chateigner A, Amanzougarene S et al (2018) Accuracy of RNAseq based SNP discovery and genotyping in Populusnigra. BMC Genom 19:909. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-5239-z
Sayama T, Tanabata T, Saruta M et al (2017) Confirmation of the pleiotropic control of leaflet shape and number of seeds per pod by the Ln gene in induced soybean mutants. Breed Sci 67(4):363–369. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.16201
Sheng C, Song S, Zhou R et al (2021) QTL-Seq and transcriptome analysis disclose major QTL and candidate genes controlling leaf size in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Front Plant Sci 12:580846. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.580846
Song QJ, Jia GF, Zhu YL et al (2010) Abundance of SSR motifs and development of candidate polymorphic SSR markers (BARCSOYSSR_1.0) in soybean. Crop Sci 50(5):1950–1960. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2009.10.0607
Takahashi N (1934) Linkage relation between the genes for the form of leaves and the number of seeds per pod of soybeans. Jpn J Genet 9:208–225. https://doi.org/10.1266/jjg.9.208
Thompson JA, Nelson RL, Schweitzer LE (1995) Relationships among specific leaf weight, photosynthetic rate, and seed yield in soybean. Crop Sci 35(6):1575–1581. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1995.0011183X003500060010x
Togashi A, Oikawa S (2021) Leaf productivity and persistence have been improved during soybean (Glycine max) domestication and evolution. J Plant Res 134:223–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-021-01263-x
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T et al (2012) Primer3-new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 40(15):e115. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks596
Van Ooijen J (2006) Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Wageningen, Kyazma BV
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/93.1.77
Wang YF, Lu JJ, Chen SY et al (2014) Exploration of presence/absence variation and corresponding polymorphic markers in soybean genome. J Integr Plant Biol 56(10):1009–1019. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12208
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm
Wang L, Cheng YB, Ma QB et al (2019) QTL fine-mapping of soybean (Glycine max L.) leaf type associated traits in two RILs populations. BMC Genom 20:260. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5610-8
Wei J, Chen YY, Wang WM (2019) A high-density genetic linkage map and QTL mapping for sex and growth-related traits of large-scale loach (Paramisgurnus dabryanus). Front Genet 10:1023. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.01023
Wen ZX, Tan RJ, Zhang SC et al (2018) Integrating GWAS and gene expression data for functional characterization of resistance to white mould in soya bean. Plant Biotechnol J 16(11):1825–1835. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12918
Yamanaka N, Ninomiya S, Hoshi M et al (2001) An informative linkage map of soybean reveals QTLs for flowering time, leaflet morphology and regions of segregation distortion. DNA Res 8(2):61–72. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/8.2.61
Yan XF, Zhao HK, Liu XD et al (2013) Phenotypic traits and diversity of different leaf shape accessions of the wild soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. et Zucc.) in China. Can J Plant Sci 94(2):397–404. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjps2013-097
Yu KY, Wang JS, Sun CY et al (2020) High-density QTL mapping of leaf-related traits and chlorophyll content in three soybean RIL populations. BMC Plant Biol 20:470. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02684-x
Zeng J, Xu XC, Xu YF et al (2021) Utilization of dynamic transcriptomics analysis for candidate gene mining of 100-seed weight in soybean. Acta Agron Sin 47(11):2121–2133. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1006.2021.04249
Zhang QQ, Yuan ZK, Zhao HH et al (2019) Development of InDel markers between rice cultivars based on transcriptome sequencing. Mol Plant Breed 17(16):5334–5341. https://doi.org/10.13271/j.mpb.017.005334
Zhao J, Chen L, Zhao TJ et al (2017) Chicken toes-like leaf and petalody flower (CTP) is a novel regulator that controls leaf and flower development in soybean. J Exp Bot 68(20):5565–5581. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx358
Acknowledgements
The bioinformatics analysis of present work was supported by the high-performance computing platform of Bioinformatics Center, Nanjing Agricultural University.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFF1001204, 2021YFD1201604), the Natural Science Foundation of China (31571694), MOE 111 Project (B08025), MOA CARS-04 Program, Jiangsu Higher Education PAPD Program, and Jiangsu JCICMCP Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ, ML and GX designed the experiment, YW, HQ and GX prepared the materials, ML, BF, YX, MR and XX carried out the field experiment. JZ conduct bioinformatics analysis. ML, JZ and FK performed PCR marker analysis. JZ, ML and GX drafted the manuscript, GX and JG revised and finalized the manuscript. All authors approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Henry T. Nguyen.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, J., Li, M., Qiu, H. et al. Identification of QTLs and joint QTL segments of leaflet traits at different canopy layers in an interspecific RIL population of soybean. Theor Appl Genet 135, 4261–4275 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-022-04216-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-022-04216-7