Abstract
Key message
Genetic architecture controlling grain lutein content of common wheat was investigated through an integration of genome-wide association study (GWAS) and linkage analysis. Putative candidate genes involved in carotenoid metabolism and regulation were identified, which provide a basis for gene cloning and development of nutrient-enriched wheat varieties through molecular breeding.
Abstract
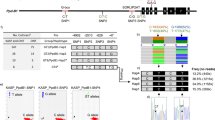
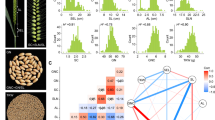
Lutein, known as ‘the eye vitamin’, is an important component of wheat nutritional and end-use quality. However, the genetic manipulation of grain lutein content (LUC) in common wheat has not previously been well studied. Here, quantitative trait loci (QTL) associated with the LUC measured by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) were first identified by integrating a genome-wide association study (GWAS) and linkage mapping. A Chinese wheat mini-core collection (MCC) of 262 accessions and a doubled haploid (DH) population derived from Jinchun 7 and L1219 were genotyped using the 90K SNP array. A total of 124 significant marker-trait associations (MTAs) on all 21 wheat chromosomes except for 1A, 4D, and 5B that formed 58 QTL were detected. Among them, six stable QTL were identified on chromosomes 2AL, 2DS, 3BL, 3DL, 7AL, and 7BS. Meanwhile, three of the ten QTL identified in the DH population, QLuc.5A.1 and QLuc.5A.2 on chromosome 5AL and QLuc.6A.2 on 6AS, were stable and independently explained 5.58–10.86% of the phenotypic variation. The QLuc.6A.2 region colocalized with two MTAs identified by GWAS. Moreover, 71 carotenoid metabolism-related candidate genes were identified, and the allelic effects were analyzed in the MCC panel based on the 90K array. Results revealed that the genes CYP97A3 (Chr. 6B) and CCD1 (Chr. 5A) were significantly associated with LUC. Additionally, the gene PSY3 (QLuc.5A.1) and several candidate genes involved in the methylerythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathways colocalized with stable QTL regions. The present study provides potential targets for future functional gene exploration and molecular breeding in common wheat.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdel-Aal ESM, Young JC, Wood PJ, Rabalski I, Hucl P, Falk D, Fregeau-Reid J (2002) Einkorn: a potential candidate for developing high lutein wheat. Cereal Chem 79:455–457. https://doi.org/10.1094/Cchem.2002.79.3.455
Adom KK, Sorrells ME, Liu RH (2005) Phytochemicals and antioxidant activity of milled fractions of different wheat varieties. J Agric Food Chem 53:2297–2306. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf048456d
Ashokkumar K, Govindaraj M, Karthikeyan A, Shobhana VG, Warkentin TD (2020) Genomics-integrated breeding for carotenoids and folates in staple cereal grains to reduce malnutrition. Front Genet 11:414. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00414
Bates D, Machler M, Bolker BM, Walker SC (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw 67:1–48. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Blanco A, Colasuonno P, Gadaleta A, Mangini G, Schiavulli A, Simeone R, Digesù AM, De Vita P, Mastrangelo AM, Cattivelli L (2011) Quantitative trait loci for yellow pigment concentration and individual carotenoid compounds in durum wheat. J Cereal Sci 54:255–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2011.07.002
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
Chang HY, Cheng TH, Wang AH (2021) Structure, catalysis, and inhibition mechanism of prenyltransferase. IUBMB Life 73:40–63. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.2418
Chen YM, Song WJ, Xie XM, Wang ZH, Guan PF, Peng HR, Jiao YN, Ni ZF, Sun QX, Guo WL (2020) A collinearity-incorporating homology inference strategy for connecting emerging assemblies in the triticeae tribe as a pilot practice in the plant pangenomic era. Mol Plant 13:1694–1708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.09.019
Colasuonno P, Lozito ML, Marcotuli I, Nigro D, Giancaspro A, Mangini G, De Vita P, Mastrangelo AM, Pecchioni N, Houston K, Simeone R, Gadaleta A, Blanco A (2017) The carotenoid biosynthetic and catabolic genes in wheat and their association with yellow pigments. BMC Genom 18(1):122. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-3395-6
Colasuonno P, Marcotuli I, Blanco A, Maccaferri M, Condorelli GE, Tuberosa R, Parada R, de Camargo AC, Schwember AR, Gadaleta A (2019) Carotenoid pigment content in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var durum): an overview of quantitative trait loci and candidate genes. Front Plant Sci 10:1347. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01347
Cunningham FX, Gantt E (1998) Genes and enzymes of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants. Annu Rev Plant Phys 49:557–583. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.49.1.557
Dong C-h, Ma Z-y, Xia X-c, Zhang L-p, He Z-h (2012) Allelic variation at the TaZds-A1 locus on wheat chromosome 2A and development of a functional marker in common wheat. J Integr Agric 11:1067–1074. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2095-3119(12)60099-9
Fraser PD, Bramley PM (2004) The biosynthesis and nutritional uses of carotenoids. Prog Lipid Res 43:228–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2003.10.002
Guan PF, Lu LH, Jia LJ, Kabir MR, Zhang JB, Lan TY, Zhao Y, Xin MM, Hu ZR, Yao YY, Ni ZF, Sun QX, Peng HR (2018) Global QTL analysis identifies genomic regions on chromosomes 4A and 4B harboring stable loci for yield-related traits across different environments in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00529
Hao C, Dong Y, Wang L, You G, Zhang H, Ge H, Jia J, Zhang X (2008) Genetic diversity and construction of core collection in Chinese wheat genetic resources. Chin Sci Bull 53:1518–1526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0212-x
Hao C, Wang Y, Chao S, Li T, Liu H, Wang L, Zhang X (2017) The iSelect 9K SNP analysis revealed polyploidization induced revolutionary changes and intense human selection causing strong haplotype blocks in wheat. Sci Rep 7:41247. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41247
He XY, Zhang YL, He ZH, Wu YP, Xiao YG, Ma CX, Xia XC (2008) Characterization of phytoene synthase 1 gene (Psy1) located on common wheat chromosome 7A and development of a functional marker. Theor Appl Genet 116:213–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-007-0660-8
He Z, Xia X, Liu J, Wen W, Jin H, Zhai S, Li W (2016) Genetic variation of carotenoids in Chinese bread wheat cultivars and the effect of the 1BL.1RS translocation. Front Agric Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.15302/j-fase-2016094
Hentschel V, Kranl K, Hollmann J, Lindhauer MG, Bohm V, Bitsch R (2002) Spectrophotometric determination of yellow pigment content and evaluation of carotenoids by high-performance liquid chromatography in durum wheat grain. J Agric Food Chem 50:6663–6668. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf025701p
Hidalgo A, Brandolini A, Pompei C, Piscozzi R (2006) Carotenoids and tocols of einkorn wheat (Triticum monococcum ssp monococcum L.). J Cereal Sci 44:182–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2006.06.002
Howitt CA, Cavanagh CR, Bowerman AF, Cazzonelli C, Rampling L, Mimica JL, Pogson BJ (2009) Alternative splicing, activation of cryptic exons and amino acid substitutions in carotenoid biosynthetic genes are associated with lutein accumulation in wheat endosperm. Funct Integr Genom 9:363–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-009-0121-3
Hussain A, Larsson H, Kuktaite R, Olsson ME, Johansson E (2015) Carotenoid content in organically produced wheat: relevance for human nutritional health on consumption. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:14068–14083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121114068
International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium (IWGSC), Appels R, Eversole K, Feuillet C et al (2018) Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar7191
Irakli MN, Samanidou VF, Papadoyannis IN (2011) Development and validation of an HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of tocopherols, tocotrienols and carotenoids in cereals after solid-phase extraction. J Sep Sci 34:1375–1382. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201100077
Jittham O, Fu XY, Xu J, Chander S, Li JS, Yang XH (2017) Genetic dissection of carotenoids in maize kernels using high-density single nucleotide polymorphism markers in a recombinant inbred line population. Crop J 5:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2016.06.006
Johnson EJ, Maras JE, Rasmussen HM, Tucker KL (2010) Intake of lutein and Zeaxanthin differ with age, sex, and ethnicity. J Am Diet Assoc 110:1357–1362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2010.06.009
Kuchel H, Langridge P, Mosionek L, Williams K, Jefferies SP (2006) The genetic control of milling yield, dough rheology and baking quality of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 112:1487–1495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0252-z
Landrum JT, Bone RA (2001) Lutein, zeaxanthin, and the macular pigment. Arch Biochem Biophys 385:28–40. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.2000.2171
Li DA, Walker E, Francki MG (2015) Identification of a member of the catalase multigene family on wheat chromosome 7A associated with flour b* colour and biological significance of allelic variation. Mol Genet Genom 290:2313–2324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-1083-x
Lippert C, Listgarten J, Liu Y, Kadie CM, Davidson RI, Heckerman D (2011) FaST linear mixed models for genome-wide association studies. Nat Methods 8:833–835. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1681
Lu S, Li L (2008) Carotenoid metabolism: biosynthesis, regulation, and beyond. J Integr Plant Biol 50:778–785. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00708.x
Masisi K, Diehl-Jones WL, Gordon J, Chapman D, Moghadasian MH, Beta T (2015) Carotenoids of aleurone, germ, and endosperm fractions of barley, corn and wheat differentially inhibit oxidative stress. J Agric Food Chem 63:2715–2724. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5058606
Meng L, Li HH, Zhang LY, Wang JK (2015) QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J 3:269–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2015.01.001
Nisar N, Li L, Lu S, Khin NC, Pogson BJ (2015) Carotenoid metabolism in plants. Mol Plant 8:68–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.007
Niu GQ, Guo Q, Wang J, Zhao S, He YK, Liu L (2020) Structural basis for plant lutein biosynthesis from alpha-carotene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117:14150–14157. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2001806117
Pang YL, Liu CX, Wang DF, St Amand P, Bernardo A, Li WH, He F, Li LZ, Wang LM, Yuan XF, Dong L, Su Y, Zhang HR, Zhao M, Liang YL, Jia HZ, Shen XT, Lu Y, Jiang HM, Wu YY, Li AF, Wang HG, Kong LR, Bai GH, Liu SB (2020) High-resolution genome-wide association study identifies genomic regions and candidate genes for important agronomic traits in wheat. Mol Plant 13:1311–1327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.07.008
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D (2006) Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 38:904–909. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1847
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/155.2.945
Qin X, Zhang W, Dubcovsky J, Tian L (2012) Cloning and comparative analysis of carotenoid β-hydroxylase genes provides new insights into carotenoid metabolism in tetraploid (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum) and hexaploid (Triticum aestivum) wheat grains. Plant Mol Biol 80:631–646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-012-9972-4
Qin X, Fischer K, Yu S, Dubcovsky J, Tian L (2016a) Distinct expression and function of carotenoid metabolic genes and homoeologs in developing wheat grains. BMC Plant Biol 16:155. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0848-7
Qin XQ, Fischer K, Dubcovsky J, Tian L (2016b) Endosperm carotenoid concentrations in wheat are better correlated with PSY1 transcript levels than enzyme activities. Crop Sci 56:3173–3184. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2016.06.0520
Ramachandran A, Pozniak CJ, Clarke JM, Singh AK (2010) Carotenoid accumulation during grain development in durum wheat. J Cereal Sci 52:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2010.02.014
Ramirez-Gonzalez RH, Borrill P, Lang D, Harrington SA, Brinton J, Venturini L, Davey M, Jacobs J, van Ex F, Pasha A, Khedikar Y, Robinson SJ, Cory AT, Florio T, Concia L, Juery C, Schoonbeek H, Steuernagel B, Xiang D, Ridout CJ, Chalhoub B, Mayer KFX, Benhamed M, Latrasse D, Bendahmane A, Wulff BBH, Appels R, Tiwari V, Datla R, Choulet F, Pozniak CJ, Provart NJ, Sharpe AG, Paux E, Spannagl M, Brautigam A, Uauy C, Sequencing IWG (2018) The transcriptional landscape of polyploid wheat. Science 361(6403):eaar6089. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar6089
Reimer S, Pozniak CJ, Clarke FR, Clarke JM, Somers DJ, Knox RE, Singh AK (2008) Association mapping of yellow pigment in an elite collection of durum wheat cultivars and breeding lines. Genome 51:1016–1025. https://doi.org/10.1139/G08-083
Ribaya-Mereado JD, Blumberg JB (2004) Lutein and zeaxanthin and their potential roles in disease prevention. J Am Coll Nutr 23:567s–587s. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2004.10719427
Rodriguez PL (1998) Protein phosphatase 2C (PP2C) function in higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 38:919–927. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1006054607850
Rosello M, Royo C, Alvaro F, Villegas D, Nazco R, Soriano JM (2018) Pasta-making quality qtlome from mediterranean durum wheat landraces. Front Plant Sci 9:1512. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01512
Ruiz-Sola MA, Rodriguez-Concepcion M (2012) Carotenoid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis: a colorful pathway. Arabidopsis Book 10:e0158. https://doi.org/10.1199/tab.0158
Stanley L, Yuan YW (2019) Transcriptional regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants: so many regulators, so little consensus. Front Plant Sci 10:1017. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01017
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) MEGA11 molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38:3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
Trono D (2019) Carotenoids in cereal food crops: composition and retention throughout grain storage and food processing. Plants (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8120551
Vallabhaneni R, Wurtzel ET (2009) Timing and biosynthetic potential for carotenoid accumulation in genetically diverse germplasm of maize. Plant Physiol 150:562–572. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.137042
Van Ooijen J (2006) JoinMap 4: Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Kyazma BV, Wageningen
Villanueva RAM, Chen ZJ (2019) ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis, 2nd edition. Meas-Interdiscip Res 17:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1080/15366367.2019.1565254
Wang S, Wong D, Forrest K, Allen A, Chao S, Huang BE, Maccaferri M, Salvi S, Milner SG, Cattivelli L (2014) Characterization of polyploid wheat genomic diversity using a high-density 90 000 single nucleotide polymorphism array. Plant Biotechnol J 12:787–796. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12183
Wang S, Basten C, Zeng Z (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC. http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm
Zhai SN, Xia XC, He ZH (2016) Carotenoids in staple cereals: metabolism, regulation, and genetic manipulation. Front Plant Sci 7:1197. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01197
Zhai SN, Liu JD, Xu DG, Wen WE, Yan J, Zhang PZ, Wan YX, Cao SH, Hao YF, Xia XC, Ma WJ, He Z (2018) A genome-wide association study reveals a rich genetic architecture of flour color-related traits in bread wheat. Front Plant Sci 9:1136. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01136
Zhang KP, Chen GF, Zhao L, Liu B, Xu XB, Tian JC (2009) Molecular genetic analysis of flour color using a doubled haploid population in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 165:471–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9756-8
Zhang C, Dong SS, Xu JY, He WM, Yang TL (2019) PopLDdecay: a fast and effective tool for linkage disequilibrium decay analysis based on variant call format files. Bioinformatics 35:1786–1788. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty875
Zhao J, Zheng X, Qiao L, Ge C, Wu B, Zhang S, Qiao L, Feng Z, Zheng J (2020) Effects of HMW-GSs on quality related traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under different water regimes. PLoS ONE 15:e0237711. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0237711
Zhu Q, Wang B, Tan J, Liu T, Li L, Liu YG (2020) Plant synthetic metabolic engineering for enhancing crop nutritional quality. Plant Commun 1:100017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xplc.2019.100017
Zhu T, Wang L, Rimbert H, Rodriguez JC, Deal KR, De Oliveira R, Choulet F, Keeble-Gagnere G, Tibbits J, Rogers J, Eversole K, Appels R, Gu YQ, Mascher M, Dvorak J, Luo MC (2021) Optical maps refine the bread wheat Triticum aestivum cv. Chinese Spring genome assembly. The Plant J 107:303–314. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15289
Ziegler JU, Wahl S, Wurschum T, Longin CFH, Carle R, Schweiggert RM (2015) Lutein and lutein esters in whole grain flours made from 75 genotypes of 5 triticum species grown at multiple sites. J Agric Food Chem 63:5061–5071
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M670701), the Agricultural Science Research of Shanxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences (YZGC013), Fund from Shanxi Key Laboratory of Crop Genetics and Molecular Improvement (KFJJ2019-02), and Fund from State Key Laboratory of Sustainable Dryland Agriculture, Shanxi Agricultural University (YJHZKF2103).
Funding
This study was funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M670701), the Agricultural Science Research of Shanxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences (YZGC013), Fund from Shanxi Key Laboratory of Crop Genetics and Molecular Improvement (KFJJ2019-02), Fund from State Key Laboratory of Sustainable Dryland Agriculture, Shanxi Agricultural University (YJHZKF2103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CH and XZ conceived the project; PG, LZ, and XL carried out experiments; JJZ and LQ participated in field experiments; JZ, BW, and JH contributed to data analyses; PG analyzed experimental results; PG, XL, and JZ wrote the manuscript; XZ, CH, and JZ provided extensive revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Susanne Dreisigacker.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure S1
The grain lutein content (LUC) profile after saponification of the extract in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis.
Supplementary file2 (TIF 490 kb)
Figure S2
Phenotypic comparison between the 1RS.1BL wheat-rye translocation lines and non-translocation lines in the MCC panel.
Supplementary file3 (TIF 623 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, P., Li, X., Zhuang, L. et al. Genetic dissection of lutein content in common wheat via association and linkage mapping. Theor Appl Genet 135, 3127–3141 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-022-04175-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-022-04175-z