Abstract
Key message
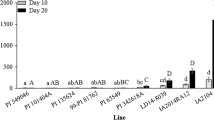
Five soybean plant introductions expressed antibiosis resistance to multiple soybean aphid biotypes. Two introductions had resistance genes located in the Rag1, Rag2, and Rag3 regions; one introduction had resistance genes located in the Rag1, Rag2, and rag4 regions; one introduction had resistance genes located in the Rag1 and Rag2 regions; and one introduction had a resistance gene located in the Rag2 region.
Abstract
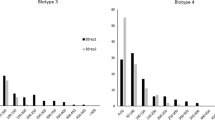
Soybean aphid (Aphis glycines Matsumura) is the most important soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] insect pest in the USA. The objectives of this study were to characterize the resistance expressed in five plant introductions (PIs) to four soybean aphid biotypes, determine the mode of resistance inheritance, and identify markers associated with genes controlling resistance in these accessions. Five soybean PIs, from an initial set of 3000 PIs, were tested for resistance against soybean aphid biotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4 in choice and no-choice tests. Of these five PIs, PI 587663, PI 587677, and PI 587685 expressed antibiosis against all four biotypes, while PI 587972 and PI 594592 expressed antibiosis against biotypes 1, 2, and 3. F2 populations derived from PI 587663 and PI 587972 were evaluated for resistance against soybean aphid biotype 1, and populations derived from PIs 587677, 587685, and 594592 were tested against biotype 3. In addition, F2:3 plants were tested against biotypes 2 and 3. Genomic DNA from F2 plants was screened with markers linked to Rag1, Rag2, Rag3, and rag4 soybean aphid-resistance genes. Results showed that PI 587663 and PI 594592 each had three genes with variable gene action located in the Rag1, Rag2, and Rag3 regions. PI 587677 had three genes with variable gene action located in the Rag1, Rag2 and rag4 regions. PI 587685 had one dominant gene located in the Rag1 region and an additive gene in the Rag2 region. PI 587972 had one dominant gene located in the Rag2 region controlling antixenosis- or antibiosis-type resistance to soybean aphid biotypes 1, 2, or 3. PIs 587663, 587677, and 587685 also showed antibiosis-type resistance against biotype 4. Information on multi-biotype aphid resistance and resistance gene markers will be useful for improving soybean aphid resistance in commercial soybean cultivars.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
References
Ajayi-Oyetunde OO, Diers BW, Lagos-Kutz DM, Hill CB, Hartman GL, Reuter-Carlson U, Bradley CA (2016) Differential reactions of soybean isolines with combinations of aphid resistance genes Rag1, Rag2, and Rag3 to four soybean aphid biotypes. J Econ Entomol 109:1431–1437
Alt J, Ryan-Mahmutagic M (2013) Soybean aphid biotype 4 identified. Crop Sci 53:1491–1495
Bales C, Zhang G, Liu M, Mensah C, Gu C, Song Q, Hyten D, Cregan P, Wang D (2013) Mapping soybean aphid resistance genes in PI 567598B. Theor Appl Genet 126:2081–2091
Bansal R, Mian M, Michel AP (2013) Identification of novel sources of host plant resistance to known soybean aphid biotypes. J Econ Entomol 106:1479–1485
Beckendorf EA, Catangui MA, Riedell WE (2008) Soybean aphid feeding injury and soybean yield, yield components, and seed composition. Agron J 100:237–246
Bhusal SJ, Jiang G-L, Tilmon KJ, Hesler LS (2013) Identification of soybean aphid resistance in early maturing genotypes of soybean. Crop Sci 53:491–499
Bhusal SJ, Jiang G-L, Hesler LS, Orf JH (2014) Soybean aphid resistance in soybean germplasm accessions of maturity group I. Crop Sci 54:2093–2098
Chen Y, Mensah C, DiFonzo C, Wang D (2006) Identification of QTLs underlying soybean aphid resistance in PI 567541B. The ASA-CSSA-SSSA International Annual Meetings
Chirumamilla A, Hill CB, Hartman GL (2014) Stability of soybean aphid resistance in soybean across different temperatures. Crop Sci 54:2557–2563
Cregan P, Quigley C (1997) Simple sequence repeat DNA marker analysis. In: Caetano-Anolles G, Gresshoff P (eds) DNA markers: protocols, applications and overview. Wiley, New York, pp 173–185
Crossley MS, Hogg DB (2015) Rag virulence among soybean aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in Wisconsin. J Econ Entomol 108:326–338
Crute IR, Pink D (1996) Genetics and utilization of pathogen resistance in plants. The Plant Cell 8:1747
Djian-Caporalino C, Palloix A, Fazari A, Marteu N, Barbary A, Abad P, Sage-Palloix A-M, Mateille T, Risso S, Lanza R (2014) Pyramiding, alternating or mixing: comparative performances of deployment strategies of nematode resistance genes to promote plant resistance efficiency and durability. BMC Plant Biol 14:53. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2229/14/53
Fehr WR, Caviness CE, Burmood DT, Pennington JS (1971) Stage of development descriptions for soybeans, Glycine max (L.) Merrill. Crop Sci 11:929–931
Fernandez-Cornejo J, Nehring R, Osteen C, Wechsler S, Martin A, Vialou A (2014) Pesticide Use in US Agriculture: 21 Selected Crops, 1960–2008. United States Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service
Fox CM, Kim K-S, Cregan PB, Hill CB, Hartman GL, Diers BW (2014) Inheritance of soybean aphid resistance in 21 soybean plant introductions. Theor Appl Genet 127:43–50
Hartman GL, Domier LL, Wax LM, Helm CG, Onstad DW, Shaw JT, Solter LF, Voegtlin DJ, D’Arcy CJ, Gray ME, Steffey KL, Isard SA, Orwick PL (2001) Occurrence and distribution of Aphis glycines on soybeans in Illinois in 2000 and its potential control. Online Plant Health Progress doi:101094/PHP-2001-0205-01-HN. Plant Health Progress
Hesler LS, Prischmann DA, Dashiell KE (2012) Field and laboratory evaluations of soybean lines against soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 105:608–615
Hesler LS, Chiozza MV, O’Neal ME, MacIntosh GC, Tilmon KJ, Chandrasena DI, Tinsley NA, Cianzio SR, Costamagna AC, Cullen EM (2013) Performance and prospects of Rag genes for management of soybean aphid. Entomol Exp Appl 147:201–216
Hill JH, Alleman R, Hogg DB, Grau CR (2001) First report of transmission of Soybean mosaic virus and Alfalfa mosaic virus by Aphis glycines in the New World. Plant Dis 85:561
Hill CB, Li Y, Hartman GL (2004) Resistance to the soybean aphid in soybean germplasm. Crop Sci 44:98–106
Hill CB, Li Y, Hartman GL (2006a) A single dominant gene for resistance to the soybean aphid in the soybean cultivar Dowling. Crop Sci 46:1601–1605
Hill CB, Li Y, Hartman GL (2006b) Soybean aphid resistance in soybean Jackson is controlled by a single dominant gene. Crop Sci 46:1606–1608
Hill CB, Kim K-S, Crull L, Diers BW, Hartman GL (2009) Inheritance of resistance to the soybean aphid in soybean PI 200538. Crop Sci 49:1193–1200
Hill CB, Crull L, Herman TK, Voegtlin DJ, Hartman GL (2010) A new soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) biotype identified. J Econ Entomol 103:509–515
Hill C, Chirumamilla A, Hartman G (2012) Resistance and virulence in the soybean-Aphis glycines interaction. Euphytica 186:635–646
Hyten DL, Song Q, Choi I-Y, Yoon M-S, Specht JE, Matukumalli LK, Nelson RL, Shoemaker RC, Young ND, Cregan PB (2008) High-throughput genotyping with the GoldenGate assay in the complex genome of soybean. Theor Appl Genet 116:945–952
Hyten DL, Choi I-Y, Song Q, Specht JE, Carter TE, Shoemaker RC, Hwang E-Y, Matukumalli LK, Cregan PB (2010) A high density integrated genetic linkage map of soybean and the development of a 1536 universal soy linkage panel for quantitative trait locus mapping. Crop Sci 50:960–968
Jun T-H, Mian MR, Michel AP (2012) Genetic mapping revealed two loci for soybean aphid resistance in PI 567301B. Theor Appl Genet 124:13–22
Kaczorowski KA, Kim K-S, Diers BW, Hudson ME (2008) Microarray-based genetic mapping using soybean near-isogenic lines and generation of SNP markers in the Rag1 aphid-resistance interval. Plant Gen 1:89–98
Keim P, Shoemaker RC (1988) Construction of a random recombinant DNA library that is primarily single copy sequence. Soybean Genet Newsl 15:147–148
Kim C, Schaible G, Garrett L, Lubowski R, Lee D (2008a) Economic impacts of the US soybean aphid infestation: a multi-regional competitive dynamic analysis. Agr Resource Econ Rev 37:227–242
Kim K, Hill CB, Hartman GL, Diers BW (2008b) Discovery of soybean aphid biotypes. Crop Sci 48:923–928
Kim K-S, Chirumamilla A, Hill CB, Hartman GL, Diers BW (2014) Identification and molecular mapping of two soybean aphid resistance genes in soybean PI 587732. Theor Appl Genet 127:1251–1259
Lehman A, O’Rourke N, Hatcher L, Stepanski E (2013) JMP for basic univariate and multivariate statistics: methods for researchers and social scientists. SAS Institute
Li Y, Hill CB, Carlson SR, Diers BW, Hartman GL (2007) Soybean aphid resistance in the soybean cultivars Dowling and Jackson map to linkage group M. Mol Breed 19:25–34
Liang X, Biao W, Tianlong W (2013) Identification of Two Soybean Aphid Biotypes. Crops 4:033
Little TM, Hills FJ (1978) Agricultural Experimentation: Design and Analysis. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Liu G, Xing H, Diao Y, Yang X, Sun D, Wang Q, Qi N, Lin H (2014) Identification of resistance to soybean aphids in early germplasm. Crop Sci 54:2707–2712
Macedo TB, Bastos CS, Higley LG, Ostlie KR, Madhavan S (2003) Photosynthetic responses of soybean to soybean aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) injury. J Econ Entomol 96:188–193
McCarville MT, O’Neal ME, Potter B, Tilmon KJ, Cullen EM, McCornack BP, Tooker JF, Prischmann-Voldseth D (2014) One gene versus two: a regional study on the efficacy of single gene versus pyramided resistance for soybean aphid management. J Econ Entomol 107:1680–1687
Mensah C, DiFonzo C, Nelson RL, Wang D (2005) Resistance to soybean aphid in early maturing soybean germplasm. Crop Sci 45:2228–2233
Mian MAR, Kang ST, Beil SE, Hammond RB (2008) Genetic linkage mapping of the soybean aphid resistance gene in PI 243540. Theor Appl Genet 117:955–962
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli R (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci 88:9828–9832
Mundt C (1991) Probability of mutation of multiple virulence and durability of resistance gene pyramids: Further comments. Phytopathology 81:240–242
NASS (2015) National Agricultural Statistics Service. United States
Pawlowski M, Hill CB, Voegtlin DJ, Hartman GL (2014) Soybean aphid intrabiotype variability based on colonization of specific soybean genotypes. Insect Sci. doi:10.1111/1744-7917.12169
Ragsdale DW, Landis DA, Brodeur J, Heimpel GE, Desneux N (2011) Ecology and management of the soybean aphid in North America. Annnu Rev Entomol 56:375–399
Riedell W, Catangui M (2006) Greenhouse studies of soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) effects on plant growth, seed yield and composition. J Agric Urban Entomol 23:225–235
Tilmon K, Hodgson E, O’Neal M, Ragsdale D (2011) Biology of the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in the United States. JIPM 2:A1–A7
Wang D, Shi J, Carlson SR, Cregan PB, Ward RW, Diers BW (2003) A low-cost, high-throughput polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis system for genotyping with microsatellite DNA markers. Crop Sci 43:1828–1832
Wiarda SL, Fehr WR, O’Neal ME (2012) Soybean aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) development on soybean with Rag1 alone, Rag2 alone, and both genes combined. J Econ Entomol 105:252–258
Zhang G, Gu C, Wang D (2009) Molecular mapping of soybean aphid resistance genes in PI 567541B. Theor Appl Genet 118:473–482
Zhang G, Gu C, Wang D (2010) A novel locus for soybean aphid resistance. Theor Appl Genet 120:1183–1191
Zhong YP, Xiao L, Wang B, Jiang YN, Yan JH, Cheng LJ, Wu TL (2014) Biotypic variation among soybean aphid isolates from four provinces in China. Crop Sci 54:2023–2029
Acknowledgements
We thank the United Soybean Board for partial funding for this research. We also thank Brian Diers for critically reviewing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The authors state that the experiments comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed (USA).
Additional information
Communicated by Henry T. Nguyen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hill, C.B., Shiao, D., Fox, C.M. et al. Characterization and genetics of multiple soybean aphid biotype resistance in five soybean plant introductions. Theor Appl Genet 130, 1335–1348 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2891-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2891-7