Abstract
Key message
The common bean locus Co - 4, traditionally referred to as an anthracnose-resistant gene, contains a cluster of predicted receptor-like kinases (COK-4 and CrRLK1-like), and at least two of these kinases are co-regulated with the plant’s basal immunity.
Abstract
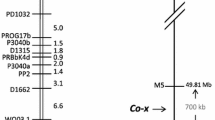
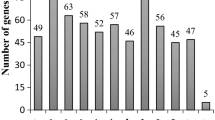
Genetic resistance to anthracnose, caused by the fungus Colletotrichum lindemuthianum (Sacc. and Magnus) Briosi and Cavara, is conferred by major loci throughout the Phaseolus vulgaris genome, named Co. The complex Co-4 locus was previously reported to have several copies of the COK-4 gene that is predicted to code for a receptor-like kinase (RLK). In general, plant RLKs are involved in pathogen perception and signal transduction; however, the molecular function of COK-4 remains elusive. Using newly identified molecular markers (PvTA25 and PvSNPCOK-4), the SAS13 marker, COK-4 sequences and phylogeny, and the recently released bean genome sequence, we determined the most probable boundaries of the Co-4 locus: a 325-Kbp region on chromosome Pv08. Out of the 49 predicted transcripts in that region, 24 encode for putative RLKs (including 18 COK-4 copies) with high similarity to members of the Catharanthus roseus RLK1-like (CrRLK1L) protein family from different plant species, including the well-described FERONIA (FER) and ANXUR. We also determined that two RLK-coding genes in the Co-4 locus (COK-4-3 and FER-like) are transcriptionally regulated when bean plants are challenged with the flg22 peptide, a commonly used elicitor of plant immunity, or the bacterium Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola, the causal agent of halo blight. While COK-4-3 is activated during immune response, FER-like is downregulated suggesting that these genes could play a role in plant responses to biotic stress. These results highlight the importance of dissecting the regulation and molecular function of individual genes within each locus, traditionally referred to as resistance gene based on genetic segregation analysis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awale HE, Kelly JD (2001) Development of SCAR markers linked to Co-4 2 gene in common bean. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 44:119–120
Balardin RS, Kelly JD (1998) Interaction between races of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum and gene pool diversity in Phaseolus vulgaris. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 123:1038–1047
Björklund ÅK, Ekman D, Light S, Frey-Skött J, Elofsson A (2005) Domain rearrangements in protein evolution. J Mol Biol 353(4):911–923. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.08.067
Boller T, Felix G (2009) A renaissance of elicitors: perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60:379–406. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105346
Borges A, Tsai SM, Caldas DGG (2011) Validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR normalization in common bean during biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Rep 5:827–838. doi:10.1007/s00299-011-1204-x
Boycheva S, Daviet L, Wolfender JL, Fitzpatrick TB (2014) The rise of operon-like gene clusters in plants. Trends in Plant Sci 7:447–459. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2014.01.013
Broughton WJ, Hernandez G, Blair M, Beebe S, Gepts P, Vanderleyden J (2003) Beans (Phaseolus spp.)—model food legumes. Plant Soil 252:55–128. doi:10.1023/A:1024146710611
Chinchilla D, Bauer Z, Regenass M, Boller T, Felix G (2006) The Arabidopsis receptor kinase FLS2 binds flg22 and determines the specificity of flagellin perception. Plant Cell 18:465–476. doi:10.1105/tpc.105
Chinchilla D, Zipfel C, Robatzek S, Kemmerling B, Nurnberger T, Jones JDG, Felix G, Boller T (2007) A flagellin-induced complex of the receptor FLS2 and BAK1 initiates plant defence. Nature 448:497-U412. doi:10.1038/nature05999
Dodds PN, Rathjen JP (2010) Plant immunity: towards an integrated view of plant-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Genet 11(8):539–548. doi:10.1038/nrg2812
Ferreira JJ, Campa A, Kelly JD (2013) Organization of genes conferring resistance to anthracnose in common bean. In: Varshney RK, Tuberosa R (eds) Translational genomics for crop breeding, 1st edn. Wiley, Blackwell, pp 151–182
Fouilloux G (1979) New races of bean anthracnose and consequences on our breeding programs. In: Maraitre H, Meyer JA (eds) Disease of tropical food crops. Université Catholique de Louvain la Neuve, Belgium, pp 221–235
Hazen SP, Leroy P, Ward R (2002) AFLP in Triticumaestivum L.: patterns of genetic diversity and genome distribution. Euphytica 125:89–102. doi:10.1023/A:1015760802026
Hou S, Mu R, Ma G, Xu X, Zhang C, Yang Y, Wu D (2011) Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola effector HopF1 inhibits pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity in a RIN4-independent manner in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). FEMS Microbiol Lett 323(1):35–43. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2011.02356.x
Huang F, Xu G, Chi Y, Liu H, Xue Q, Zhao T, Gai J, Yu D (2014) A soybean MADS-box protein modulates floral organ numbers, petal identity and sterility. BMC Plant Biol 14(1):89. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-14-89
Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444(7117):323–329. doi:10.1038/nature05286
Katagiri F, Thilmony R, He SY (2002) The Arabidopsis thaliana-Pseudomonas syringae interaction. In: Somerville CR, Meyerowitz EM (eds) The Arabidopsis book. American Society of Plant Biologists, Rockville, pp 1–35. doi:10.1199/tab.0039
Keinath NF, Kierszniowska S, Lorek J, Bourdais G, Kessler SA, Shimosato-Asano H, Panstruga R (2010) PAMP (pathogen-associated molecular pattern)-induced changes in plasma membrane compartmentalization reveal novel components of plant immunity. J Biol Chem 285(50):39140–39149. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.160531
Kelly JD, Vallejo VA (2004) A comprehensive review of the major genes conditioning resistance to anthracnose in common bean. Hortic Sci 39(6):1196–1207
Kessler SA, Shimosato-Asano H, Keinath NF, Wuest SE, Ingram G, Panstruga R, Grossniklaus U (2010) Conserved molecular components for pollen tube reception and fungal invasion. Science 330(6006):968–971. doi:10.1126/science.1195211
Kuć J (1982) Induced immunity to plant disease. Bioscience 32(11):854–860. doi:10.2307/1309008
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(87)90010-3
Lindner H, Müller LM, Boisson-Dernier A, Grossniklaus U (2012) CrRLK1L receptor-like kinases: not just another brick in the wall. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15(6):659–669. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2012.07.003
Liu BH (1998) Statistical genomics: linkage, mapping and QTL analysis. CRC Press, Cleveland 611
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Long M, VanKuren NW, Chen S, Vibranovski MD (2013) New gene evolution: little did we know. Annu Rev Genet 47:307–333. doi:10.1146/annurev-genet-111212-133301
Lopez-Gomez M, Sandal N, Stougaard J, Boller T (2011) Interplay of flg22-induced defence responses and nodulation in Lotus japonicus. J Exp Bot. doi:10.1093/jxb/err1291
Marchler-Bauer A, Zheng C, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, Geer LY, Geer RC, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M, Hurwitz DI, Lanczycki CJ, Lu F, Shennan Lu, Marchler GH, Song JS, Thanki N, Yamashita RA, Zhang D, Bryant SH (2013) CDD: conserved domains and protein three-dimensional structure. Nucleic Acids Res 41(D1):D384-52. doi:10.1093/nar/gks1243
Melotto M, Kelly JD (2001) Fine mapping of the Co-4 locus of common bean reveals a resistance gene candidate, COK-4, that encodes for a protein kinase. Theor Appl Genet 103(4):508–517. doi:10.1007/s001220100609
Melotto M, Balardin RS, Kelly JD (2000) Host-pathogen interaction and variability of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. In: Prusky D, Freeman S, Dickman MB (eds) Colletotrichum host specificity, pathology, and host-pathogen interaction. APS Press, St Paul, pp 346–361
Melotto M, Coelho MF, Pedrosa-Harand A, Kelly JD, Camargo LEA (2004) The anthracnose resistance locus Co-4 of common bean is located on chromosome 3 and contains putative disease resistance-related genes. Theor Appl Genet 109(4):690–699. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1697-6
Michelmore RW, Paran J, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregation populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci 88:9828–9832. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.21.9828
Navarro L, Zipfel C, Rowland O, Keller I, Robatzek S, Boller T, Jones JDG (2004) The transcriptional innate immune response to flg22. Interplay and overlap with Avr gene-dependent defense responses and bacterial pathogenesis. Plant Physiol 135:1113–1128. doi:10.1104/pp.103.036749
O’Connell RJ, Thon MR, Hacquard S et al (2012) Lifestyle transitions in plant pathogenic Colletotrichum fungi deciphered by genome and transcriptome analyses. Nat Genet 44(9):1060–1065. doi:10.1038/ng.2372
Oblessuc PR, Borges A, Chowdhury B, Caldas DGG, Tsai SM, Camargo LEA, Melotto M (2012) Dissecting Phaseolus vulgaris innate immune system against Colletotrichum lindemuthianum infection. PLoS ONE 7(8):e43161. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0043161
Pabón-Mora N, Ambrose BA, Litt A (2012) Poppy APETALA1/FRUITFULL orthologs control flowering time, branching, perianth identity, and fruit development. Plant Physiol 158(4):1685–1704. doi:10.1104/pp.111.192104
Queiroz VT, Sousa CS, Costa MR, Sanglad DA, Arruda KMA, Souza TLPO, Ragagnin VA, Barros EG, Moreira MA (2004) Development of SCAR markers linked to common bean anthracnose resistance genes Co-4 and Co-6. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 47:249–250
Reuter M (2012) Image analysis: dot count. DotCount v1.2. http://reuter.mit.edu/software/dotcount/
Richard MMS, Chen NWG, Thareau V, Pflieger S, Blanchet S, Pedrosa-Harand A, Iwata A, Chavarro C, Jackson SA, Geffroy V (2013) The subtelomerickhipu satellite repeat from Phaseolus vulgaris: lessons learned from the genome analysis of the andean genotype G19833. Front Plant Sci 4:109. doi:10.3389/fpls.2013.00109
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3(6):1101–1108. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Schmutz J, McClean PE, Mamidi S et al (2014) A reference genome for common bean and genome-wide analysis of dual domestications. Nat Genet 46:707–713. doi:10.1038/ng.3008
Sessa G, Martin GB (2000) Signal recognition and transduction mediated by the tomato Pto kinase: a paradigm of innate immunity in plants. Microb Infec 2(13):1591–1597
Shiu SH, Bleecker AB (2001) Plant receptor-like kinase gene family: diversity, function, and signaling. Sci STKE 113:re22. doi:10.1126/stke.2001.113.re22
Silverio L, Vidigal MC, Vidigal Filho PS, Barelli MAA, Thomazella C, Nunes WMC (2002) Genetic resistance to Colletotrichum lindemuthianum race 2047 in G2333. Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop 45:74–75
Singh SP, Schwartz HF (2010) Breeding common bean for resistance to diseases: a review. Crop Sci 50(6):2199. doi:10.2135/cropsci2009.03.0163
Song WY, Wang GL, Chen L, Kim HS, Pi LY, Gardner J, Wang B, Holsten T, Zhai WX, Zhu LH, Fauquet C, Ronald PC (1995) A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene Xa21. Science 270:1804–1806. doi:10.1126/science.270.5243.1804
Spoel SH, Dong X (2012) How do plants achieve immunity? Defence without specialized immune cells. Nat Rev Immunol 12(2):89–100. doi:10.1038/nri3141
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tatusova TA, Madden TL (1999) BLAST 2 sequences, a new tool for comparing protein and nucleotide sequences. FEMS Microbiol Lett 174:247–250. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13575.x
Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genom Res 11:1441–1452. doi:10.1101/gr.184001 PMID:11483586
Thomma BPHJ, Nürnberger T, Joosten MHAJ (2011) Of PAMPs and effectors: the blurred PTI-ETI dichotomy. Plant Cell 23(1):4–15. doi:10.1105/tpc.110.082602
Vanhouten W, MacKenzie S (1999) Construction and characterization of a common bean bacterial artificial chromosome library. Plant Mol Biol 40(6):977–983. doi:10.1023/A:1006234823105
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78. doi:10.1093/jhered/93.1.77
Wolf S, Hématy K, Höfte H (2012) Growth control and cell wall signaling in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63:381–407. doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-042811-105449
Young RA, Kelly JD (1996) Characterization of genetic resistance to Colletotrichum lindemuthianum in common bean differential cultivars. Plant Dis 80(6):650–654. doi:10.1590/S1516-89132008000500002
Young RA, Melotto M, Nodari RO, Kelly JD (1998) Marker assisted dissection of the oligogenic anthracnose resistance in common bean cultivar G2333. Theor Appl Genet 96:87–94. doi:10.1007/s001220050713
Zipfel C, Robatzek S, Navarro L, Oakeley EJ, Jones JD, Felix G, Boller T (2004) Bacterial disease resistance in Arabidopsis through flagellin perception. Nature 428:764–767. doi:10.1038/nature02485
Zmasek CM, Godzik A (2011) Strong functional patterns in the evolution of eukaryotic genomes revealed by the reconstruction of ancestral protein domain repertoires. Genom Biol 12(1):R4. doi:10.1186/gb-2011-12-1-r4
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. L.E.A. Camargo for hosting CF and MM in his lab during the screening process for AFLP markers; Dr. J.D. Kelly for common bean seeds and the Colletotrichum lindemuthianum isolate; Dr. David Guttman for the Pseudomonas phaseolicola strain. The authors also thank CAPES/Science Without Borders for the post-doctoral fellowship awarded to PRO (award #9773-13-4), and FAPESP for the Undergraduate Research Assistantship to CF (award #01/11218-0). This study was funded by FAPESP—Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Brazil (Grant #00/09049-2) to MM.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical standards
All experiments described in this manuscript comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. E. Mather.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
122_2015_2500_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
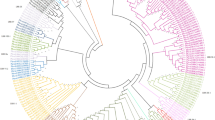
Fig. S1 Phylogenetic analysis of the top 100 protein kinases with the highest similarity to the predicted COK-4_SEL1308 protein. The top 100 hits were obtained from BLASTP analysis (threshold E-value ≤ 1 x 10−20 and identity > 30 %) using COK-4_SEL1308 as query against the common bean proteome database available at Phytozome. The phylogenetic tree was obtained with the maximum parsimony method using the MEGA 5.05 software (Tamura et al. 2011). Bootstrap support values are adjacent to the tree nodes. Co-4 locus-associated kinases formed a single cluster (red box), and kinase/malectin proteins formed another sub-cluster (blue box). (PDF 34 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oblessuc, P.R., Francisco, C. & Melotto, M. The Co-4 locus on chromosome Pv08 contains a unique cluster of 18 COK-4 genes and is regulated by immune response in common bean. Theor Appl Genet 128, 1193–1208 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2500-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2500-6