Abstract
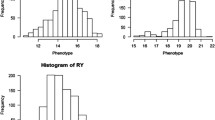
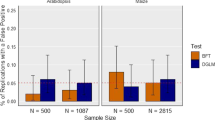
In most quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping studies, phenotypes are assumed to follow normal distributions. Deviations from this assumption may affect the accuracy of QTL detection, leading to detection of false positive QTL. To improve the robustness of QTL mapping methods, we replace the normal distribution assumption for residuals in a multiple QTL model with a Student-t distribution that is able to accommodate residual outliers. A Robust Bayesian mapping strategy is proposed on the basis of the Bayesian shrinkage analysis for QTL effects. The simulations show that Robust Bayesian mapping approach can substantially increase the power of QTL detection when the normality assumption does not hold and applying it to data already normally distributed does not influence the result. The proposed QTL mapping method is applied to mapping QTL for the traits associated with physics–chemical characters and quality in rice. Similarly to the simulation study in the real data case the robust approach was able to detect additional QTLs when compared to the traditional approach. The program to implement the method is available on request from the first or the corresponding author.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews DF, Mallows CL (1974) Scale mixtures of normal distributions. J Roy Stat Soc Ser B 36:99–102
Bao JS, Xia YW (1999) Genetic control of the paste viscosity characteristics in indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 98:1120–1124
Coppieters W, Kvasz A, Farnir F, Arranz JJ, Grisart B, Mackinnon M, Georges M (1998) A rank-based nonparametric method for mapping quantitative trait loci in outbred half-sib pedigrees: application to milk production in a granddaughter design. Genetics 149:1547–1555
Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB (1980) Iteratively reweighted least squares for linear regression when errors are normal/independent distributed. In: Krishnaiah PR (ed) Multivariate analysis. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Diao G, Lin DY (2005) A powerful and robust method for mapping quantitative trait loci in general pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet 77:97–111
Diao G, Lin DY, Zou F (2004) Mapping quantitative trait loci with censored observations. Genetics 168:1689–1698
Elsen JM, Mangin B, Goffinet B, Boichard D, Le RP (1999) Alternative models for QTL detection in livestock I. General introduction. Genet Sel Evol 31:213–224
Feenstra B, Skovgaard IM (2004) A quantitative trait locus mixture model that avoids spurious LOD score peaks. Genetics 167:959–965
Fernandez C, Steel M (1998) On Bayesian modeling of fat tails and skewness. J Am Statist Assoc 93:359–371
Goffinet B, Le RP, Boichard D, Elsen JM, Mangin B (1999) Alternative models for QTL detection in livestock III. Heteroskedastic model and models corresponding to several distributions of the QTL effect. Genet Sel Evol 31:341–350
Hackett CA (1997) Model diagnostics for fitting QTL models to trait and marker data by interval mapping. Heredity 79:319–328
Hastings WK (1970) Monte Carlo sampling methods using Markov chains and their applications. Biometrika 57:97–109
Jamrozik J, Stranden I, Schaeffer LR (2004) Random regression test-day models with residuals following a Student’s-t distribution. J Dairy Sci 87:699–705
Jansen RC (1992) A general mixture model for mapping quantitative trait loci by using molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 85:252–260
Kruglyak L, Lander ES (1995) A nonparametric approach for mapping quantitative trait loci. Genetics 139:1421–1428
Lange K, Sinsheimer JS (1993) Normal/independent distributions and their applications in robust regression. J Am Stat Assoc 2:175–198
Lange KL, Little RJA, Taylor JMG (1989) Robust statistical modelling using the t-distribution. J Am Stat Assoc 84:881–896
Liu C (1996) Robust Bayesian multivariate linear regression with incomplete data. J Am Stat Assoc 435:1219–1227
Mangin B, Goffinet B, Le RP, Boichard D, Elsen JM (1999) Alternative models for QTL detection in livestock II. Likelihood approximations and sire marker genotype estimation. Genet Sel Evol 31:225–237
Metropolis N, Rosenbluth AW, Rosenbluth MN, Teller AH, Teller E (1953) Equations of state calculations by fast computing machines. J Chem Phys 21:1087–1091
Pinheiro JC, Liu CH, Wu YN (2001) Efficient algorithms for robust estimation in linear mixed-effects models using the multivariate t distribution. J Comput Graph Stat 10:249–276
Rebaï A (1997) Comparison of methods for regression interval mapping in QTL analysis with non-normal traits. Genet Res 69:69–74
Ripley B (1987) Stochastic simulation. Wiley, New York
Rogers WH, Tukey JW (1972) Understanding some long-tailed distributions. Stat Neerl 26:211–226
Rohr PV, Hoeschele I (2002) Bayesian QTL mapping using skewed Student-t distributions. Genet Sel Evol 34:1–21
Rosa GJM, Gianola D, Padovani CR (2004) Bayesian longitudinal data analysis with mixed models and thick-tailed distributions using MCMC. J Appl Stat 7:855–873
Rosa GJM, Padovani CR, Gianola D (2003) Robust linear mixed models with normal/independent distributions and Bayesian MCMC implementation. Biom J 5:573–590
Sillanpää MJ, Arjas E (1998) Bayesian mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci from incomplete inbred line cross data. Genetics 148:1373–1388
Sillanpää MJ, Arjas E (1999) Bayesian mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci from incomplete outbred offspring data. Genetics 151:1605–1619
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1995) Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics in biological research. W.H. Freeman, New York
Stranden I, Gianola D (1999) Mixed effects linear models with t-distributions for quantitative genetic analysis: a Bayesian approach. Genet Sel Evol 31:25–42
Symons RC, Daly MJ, Fridlyand J, Speed TP, Cook WD, Gerondakis S, Harris AW, Foote SJ (2002) Multiple genetic loci modify susceptibility to plasmacytoma-related morbidity in Eμ-v-abl transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:11299–11304
Wang H, Zhang YM, Li X, Masinde GL, Mohan S, Baylink DJ, Xu S (2005) Bayesian shrinkage estimation of quantitative trait loci parameters. Genetics 170:465–480
Yang R, Xu S (2007) Bayesian shrinkage analysis of quantitative trait loci for dynamic traits. Genetics 176:1169–1185
Yang R, Yi N, Xu S (2006) Box–Cox transformation for QTL mapping. Genetica 128:133–143
Yi N, Xu S (2000) Bayesian mapping of quantitative trait loci for complex binary traits. Genetics 155:1391–1403
Zhang YM, Xu S (2005) Advanced statistical methods for detecting multiple quantitative trait loci. Recent Res Devel Genet Breed 2:1–23
Zou F, Yandell BS, Fine JP (2003) Rank-based statistical methodologies for quantitative trait locus mapping. Genetics 165:1599–1605
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation Grant 30471236 to RY.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Sillanpää.
Xin Wang and Zhongze Piao contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Piao, Z., Wang, B. et al. Robust Bayesian mapping of quantitative trait loci using Student-t distribution for residual. Theor Appl Genet 118, 609–617 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0924-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0924-y