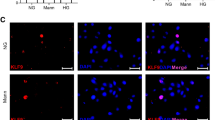
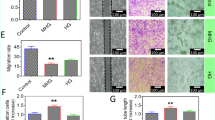
Abstract
In diabetic retinopathy (DR), visual deterioration is related with retinal neovascularization and vascular hyperpermeability. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) agents are currently utilized to suppress retinal neovascularization and macular edema (ME); however, there are still concerns on the widespread use of them because VEGF is a trophic factor for neuronal and endothelial cells in the retina. As an alternative treatment strategy for DR, it is logical to address hypoxia-related molecules to treat DR because the retina is in relative hypoxia as DR progresses. In this study, we demonstrate that destabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) by SH-1242 and SH-1280, novel heat shock protein 90 (hsp90) inhibitors, leads to suppression of hypoxia-mediated retinal neovascularization and vascular leakage in diabetic retina. In vitro experiments showed that these inhibitors inhibited hypoxia-induced upregulation of target genes of HIF-1α and further secretion of VEGF. Furthermore, these inhibitors effectively suppressed expression of target genes of HIF-1α including vegfa in the retina of oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) mice. Interestingly, despite hsp90 inhibition, these inhibitors do not induce definite toxicity at the level of gene expression, cellular viability, and histologic integrity. We suggest that SH-1242 and SH-1280 can be utilized in the treatment of DR, as an alternative treatment of direct VEGF inhibition.
Key message
-
SH-1242 and SH-1280 are novel hsp90 inhibitors similar to deguelin.
-
HIF-1α destabilization by hsp90 inhibition leads to anti-angiogenic effects.
-
Despite hsp90 inhibition, both inhibitors do not induce definite toxicity.
-
HIF-1α modulation can be a safer therapeutic option than direct VEGF inhibition.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonetti DA, Klein R, Gardner TW (2012) Diabetic retinopathy. N Engl J Med 366:1227–1239
Jo DH, Kim JH, Kim JH (2010) How to overcome retinal neuropathy: the fight against angiogenesis-related blindness. Arch Pharm Res 33:1557–1565
Jo DH, Kim JH, Kim JH (2012) How to overcome diabetic retinopathy: focusing on blood-retinal barrier. Immunol Endocr Metab Agents Med Chem 12:110–117
Nguyen QD, Brown DM, Marcus DM, Boyer DS, Patel S, Feiner L, Gibson A, Sy J, Rundle AC, Hopkins JJ et al (2012) Ranibizumab for diabetic macular edema: results from 2 phase III randomized trials: RISE and RIDE. Ophthalmology 119:789–801
Heo JW, Kim JH, Cho CS, Jun HO, Kim DH, Yu YS, Kim JH (2012) Inhibitory activity of bevacizumab to differentiation of retinoblastoma cells. PLoS One 7:e33456
Saint-Geniez M, Maharaj AS, Walshe TE, Tucker BA, Sekiyama E, Kurihara T, Darland DC, Young MJ, D’Amore PA (2008) Endogenous VEGF is required for visual function: evidence for a survival role on muller cells and photoreceptors. PLoS One 3:e3554
Kurihara T, Westenskow PD, Bravo S, Aguilar E, Friedlander M (2012) Targeted deletion of Vegfa in adult mice induces vision loss. J Clin Invest 122:4213–4217
Ditzel J (1976) Oxygen transport impairment in diabetes. Diabetes 25:832–838
Kim JH, Kim JH, Yu YS, Shin JY, Lee HY, Kim KW (2008) Deguelin inhibits retinal neovascularization by down-regulation of HIF-1alpha in oxygen-induced retinopathy. J Cell Mol Med 12:2407–2415
DeNiro M, Al-Halafi A, Al-Mohanna FH, Alsmadi O, Al-Mohanna FA (2010) Pleiotropic effects of YC-1 selectively inhibit pathological retinal neovascularization and promote physiological revascularization in a mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy. Mol Pharmacol 77:348–367
Yoshida T, Zhang H, Iwase T, Shen J, Semenza GL, Campochiaro PA (2010) Digoxin inhibits retinal ischemia-induced HIF-1alpha expression and ocular neovascularization. FASEB J 24:1759–1767
Neckers L, Ivy SP (2003) Heat shock protein 90. Curr Opin Oncol 15:419–424
Chang DJ, An H, Kim KS, Kim HH, Jung J, Lee JM, Kim NJ, Han YT, Yun H, Lee S et al (2012) Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel deguelin-based heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) inhibitors targeting proliferation and angiogenesis. J Med Chem 55:10863–10884
Smith LE, Wesolowski E, McLellan A, Kostyk SK, D’Amato R, Sullivan R, D’Amore PA (1994) Oxygen-induced retinopathy in the mouse. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 35:101–111
Lemmen C, Lengauer T, Klebe G (1998) FLEXS: a method for fast flexible ligand superposition. J Med Chem 41:4502–4520
Kim JH, Kim JH, Yu YS, Kim DH, Kim CJ, Kim KW (2007) Establishment and characterization of a novel, spontaneously immortalized retinoblastoma cell line with adherent growth. Int J Oncol 31:585–592
Kim JH, Kim C, Kim JH, Lee BJ, Yu YS, Park KH, Kim KW (2008) Absence of intravitreal bevacizumab-induced neuronal toxicity in the retina. Neurotoxicology 29:1131–1135
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT et al (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet 25:25–29
Edgar R, Domrachev M, Lash AE (2002) Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res 30:207–210
Oh SH, Woo JK, Jin Q, Kang HJ, Jeon JW, Kim KW, Hong WK, Lee HY (2008) Identification of novel antiangiogenic anticancer activities of deguelin targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha. Int J Cancer 122:5–14
Kim CK, Choi YK, Lee H, Ha KS, Won MH, Kwon YG, Kim YM (2010) The farnesyltransferase inhibitor LB42708 suppresses vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis by inhibiting ras-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signal pathways. Mol Pharmacol 78:142–150
Kim JH, Kim JH, Yu YS, Cho CS, Kim KW (2009) Blockade of angiotensin II attenuates VEGF-mediated blood-retinal barrier breakdown in diabetic retinopathy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:621–628
Gerhauser C, Lee SK, Kosmeder JW, Moriarty RM, Hamel E, Mehta RG, Moon RC, Pezzuto JM (1997) Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase induction by deguelin, a natural product cancer chemopreventive agent. Cancer Res 57:3429–3435
Kim WY, Chang DJ, Hennessy B, Kang HJ, Yoo J, Han SH, Kim YS, Park HJ, Seo SY, Mills G et al (2008) A novel derivative of the natural agent deguelin for cancer chemoprevention and therapy. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 1:577–587
Caboni P, Sherer TB, Zhang N, Taylor G, Na HM, Greenamyre JT, Casida JE (2004) Rotenone, deguelin, their metabolites, and the rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Chem Res Toxicol 17:1540–1548
Chun KH, Kosmeder JW 2nd, Sun S, Pezzuto JM, Lotan R, Hong WK, Lee HY (2003) Effects of deguelin on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway and apoptosis in premalignant human bronchial epithelial cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:291–302
Oh SH, Woo JK, Yazici YD, Myer JN, Kim WY, Jin Q, Hong SS, Park HJ, Suh YG, Kim KW et al (2007) Structural basis for depletion of heat shock protein 90 client proteins by deguelin. J Natl Cancer Inst 99:949–961
Forsythe JA, Jiang BH, Iyer NV, Agani F, Leung SW, Koos RD, Semenza GL (1996) Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Mol Cell Biol 16:4604–4613
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9:669–676
Semenza GL (2000) HIF-1: mediator of physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 88:1474–1480
Potente M, Gerhardt H, Carmeliet P (2011) Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell 146:873–887
Teng Y, Cui H, Yang M, Song H, Zhang Q, Su Y, Zheng J (2009) Protective effect of puerarin on diabetic retinopathy in rats. Mol Biol Rep 36:1129–1133
Yang W, Yu X, Zhang Q, Lu Q, Wang J, Cui W, Zheng Y, Wang X, Luo D (2013) Attenuation of streptozotocin-induced diabetic retinopathy with low molecular weight fucoidan via inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor. Exp Eye Res 115C:96–105
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (2012-0006019), the Bio-Signal Analysis Technology Inno-vation Program (2009-0090895), the Global Research Laboratory Program (2011-0021874), the Pioneer Research Program (2012-0009544) of NRF/MEST, and the Seoul National University Research Fund (800-20130338).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 670 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jo, D.H., An, H., Chang, DJ. et al. Hypoxia-mediated retinal neovascularization and vascular leakage in diabetic retina is suppressed by HIF-1α destabilization by SH-1242 and SH-1280, novel hsp90 inhibitors. J Mol Med 92, 1083–1092 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1168-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1168-8