Purpose:
To unravel biological mechanisms potentially resulting in the obliteration process after radiosurgery (RS) of human cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) by investigating molecular signatures on the transcriptomic level in peripheral blood of patients.
Patients and Methods:
Venous blood samples were obtained at definite points of time before and after RS. The samples were tested for radiation-induced changes regarding biological markers (mRNA) using cDNA and oligo-microarray technology. The corresponding expression profiles were correlated with clinical data and obliteration signs in radiologic imaging.
Results:
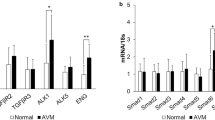
The proof of principle that RS outcome can be successfully correlated with transcriptomics of cellular blood components as disease parameter was demonstrated. The authors identified 76 differentially regulated genes (p < 0.001) after RS. Interestingly, in particular genes with known roles in antiangiogenic and procoagulative pathways were identified as potentially relevant. In particularly, the authors found a significant downregulation of neuropilin-2, protein C inhibitor and cyclin-dependent kinase 6. They also found that low pretreatment blood mRNA levels of TLR4 (toll-like receptor 4) and STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) correlated with fast obliteration of AVMs.
Conclusion:
The authors report on a novel technique for molecular biological analysis of blood from patients with cerebral AVM treated with RS. Differential regulation of genes in peripheral blood was successfully correlated with RS and time to obliteration of AVMs. The identified genes indicate a potential new methodology to monitor RS, which may result in an individualized therapy and optimized follow-up.
Ziel:
Untersucht wurden die molekularen Mechanismen der Wirkung ionisierender Strahlung auf das pathologische Gefäßkonvolut bei zerebralen arteriovenösen Malformationen (AVM) im peripheren Blut von Patienten nach Radiochirurgie (RS).
Patienten und Methodik:
Bei Patienten mit zerebraler AVM wurde zu definierten Zeitpunkten vor und nach RS eine venöse Blutprobe gewonnen und mittels cDNA- und Oligo-Microarray-Technologie auf strahleninduzierte Veränderungen hinsichtlich biologischer Marker (mRNA) getestet. Die entsprechenden Expressionsprofile wurden mit dem Obliterationsverlauf in der radiologischen Bildgebung verglichen.
Ergebnisse:
Erstmals konnte gezeigt werden, dass eine Korrelation zwischen klinischen Parametern nach RS zerebraler AVM und Genaktivität von peripheren Blutbestandteilen möglich ist. Es konnten 76 Gene als signifikant (p < 0,001) reguliert identifiziert werden. Insbesondere wurden antiangiogene Mechanismen der Strahlenwirkung sowie prokoagulatorische Effekte als funktionell relevant identifiziert. Beispielsweise zeigte sich eine signifikant verminderte Expression von Neuropilin-2 (NRP-2), Protein-C-Inhibitor (PCI) und „cyclin-dependent kinase 6“ (CDK6). Darüber hinaus konnten eine positive Korrelation zwischen niedrigen prätherapeutischen mRNA-Werten von TLR4 („toll-like receptor 4“) und STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) im Blut der Patienten und schneller Obliteration der AVM nachgewiesen werden.
Schlussfolgerung:
Durch genomweite Untersuchungen an Blutproben von Patienten mit zerebraler AVM vor und nach RS konnten erstmals molekulare Signaturen im peripheren Blut identifiziert werden. Diese erlauben möglicherweise ein biologisches Therapiemonitoring. Die unterschiedliche Genregulation im peripheren Blut nach RS konnte erfolgreich mit der Zeit bis zur Obliteration der AVM korreliert werden. Weiterführende Untersuchungen der identifizierten Gene und Proteine sollen in Zukunft eine optimierte Verlaufskontrolle nach Radiotherapie und eine individuell optimierte Behandlung ermöglichen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdollahi A, Schwager C, Kleeff J, et al. Transcriptional network governing the angiogenic switch in human pancreatic carcinoma. PNAS 2007;104:12890–5.
Abiatari I, DeOliveira T, Kerkadze V, et al. Consensus transcriptome signature of perineural invasion in pancreatic carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 2009;8:1494–504.
Almog N, Ma L, Raychowdhury R, et al. Transcriptional switch of dormant tumors to fast-growing angiogenic phenotype. Cancer Res 2009;69:836–44.
Bromberg J, Darnell Jr JE. The role of STATs in transcriptional control and their impact on cellular function. Oncogene 2000;19:2468–73.
Capalbo G, Rödel C, Stauber RH, et al. The role of survivin for radiation therapy. Prognostic and predictive factor and therapeutic target [Review]. Strahlenther Onkol 2007;183:593–9.
Domhan S, Muschal S, Schwager C, et al. Molecular mechanisms of the antiangiogenic and antitumor effects of mycophenolic acid. Mol Cancer Ther 2008;7:1656–68.
Favier B, Alam A, Barron P, et al. Neuropilin-2 interacts with VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 and promotes human endothelial cell survival and migration. Blood 2006;108:1243–50.
Frendeus B, Wachtler C, Hedlund M, et al. Escherichia coli P fimbriae utilize the toll-like receptor 4 pathway for cell activation. Mol Microbiol 2001;40:37–51.
Gabryś D, Dörfler A, Yaromina A, et al. Effects of lovastatin alone or combined with irradiation on tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Strahlenther Onkol 2008;184:48–53.
Germeyer A, Hamilton AE, Laughlin LS, et al. Cellular expression and hormonal regulation of neuropilin-1 and -2 messenger ribonucleic acid in the human and rhesus macaque endometrium. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:1783–90.
Gluzman-Poltorak Z, Cohen T, Herzog Y, et al. Neuropilin-2 is a receptor for the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) forms VEGF-145 and VEGF-165 [Erratum in: J Biol Chem 2000;275:29922]. J Biol Chem 2000;275:18040–5.
Grossel MJ, Hinds PW. From cell cycle to differentiation: an expanding role for cdk6. Cell Cycle 2006;5:266–70.
Hashimoto T, Lam T, Boudreau NJ, et al. Abnormal balance in the angiopoietin-tie2 system in human brain arteriovenous malformations. Circ Res 2001;89:111–3.
Kader A, Goodrich JT, Sonstein WJ, et al. Recurrent cerebral arteriovenous malformations after negative postoperative angiograms. J Neurosurg 1996;85:14–8.
Kolodkin AL, Levengood DV, Rowe EG, et al. Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell 1997;90:753–62.
Lanza V, Pretazzoli V, Olivieri G, et al. Transcriptional response of human umbilical vein endothelial cells to low doses of ionizing radiation. J Radiat Res (Tokyo) 2005;46:265–76.
Milker-Zabel S, Bois AZ, Ranai G, et al. SU11657 enhances radiosensitivity of human meningioma cells. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008;70:1213–8.
Moretti S, Procopio A, Boemi M, et al. Neuronal semaphorins regulate a primary immune response. Curr Neurovasc Res 2006;3:295–305.
Niyazi M, Marini P, Daniel PT, et al. Efficacy of a triple treatment with irradiation, agonistic TRAIL receptor antibodies and EGFR blockade. Strahlenther Onkol 2009;185:8–18.
Pollock BE, Flickinger JC. A proposed radiosurgery-based grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 2002;96:79–85.
Pollock BE, Gorman DA, Coffey RJ. Patient outcomes after arteriovenous malformation radiosurgical management: results based on a 5- to 14-year follow-up study. Neurosurgery 2003;52:1291–7.
Rades D, Golke H, Schild SE, et al. Impact of VEGF and VEGF receptor 1 (FLT1) expression on the prognosis of stage III esophageal cancer patients after radiochemotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol 2008;184:416–20.
Rödel C, Sauer R. Integration of novel agents into combined-modality treatment for rectal cancer patients [Review]. Strahlenther Onkol 2007;183:227–35.
Saltzman A, Stone M, Franks C, et al. Cloning and characterization of human Jak-2 kinase: high mRNA expression in immune cells and muscle tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998;246:627–33.
Schutze C, Dorfler A, Eicheler W, et al. Combination of EGFR/HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibition by BIBW 2992 and BIBW 2669 with irradiation in FaDu human squamous cell carcinoma. Strahlenther Onkol 2007;183:256–64.
Schwager C, Wirkner U, Abdollahi A, et al. TableButler - a Windows based tool for processing large data tables generated with high-throughput methods. BMC Bioinformatics 2009;10:235.
Seki E, De Minicis S, Österreicher CH, et al. TLR4 enhances TGF-β signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med 2007;13:1324–32.
Spetzler RF, Martin NA. A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 1986;65:476–83.
Steiner L, Lindquist C, Adler JR, et al. Clinical outcome of radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 1992;77:1–8.
Sulpice E, Plouet J, Berge M, et al. Neuropilin-1 and neuropilin-2 act as coreceptors, potentiating proangiogenic activity. Blood 2008;111:2036–45.
Takashima S, Kitakaze M, Asakura M, et al. Targeting of both mouse neuropilin-1 and neuropilin-2 genes severely impairs developmental yolk sac and embryonic angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002;99:3657–62.
Watanabe R, Wada H, Sakakura M, et al. Plasma levels of activated protein C-protein C inhibitor complex in patients with hypercoagulable states. Am J Hematol 2000;65:35–40.
Zabel A, Milker-Zabel S, Huber P, et al. Treatment outcome after linac-based radiosurgery in cerebral arteriovenous malformations: retrospective analysis of factors affecting obliteration. Radiother Oncol 2005;77:105–10.
Zabel-du Bois A, Ackermann B, Hauswald H, et al. Influence of i.v. contrast agent on dose calculation in 3-D treatment planning for radiosurgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Strahlenther Oncol 2009;185:318–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zabel-du Bois, A., Wagner-Ecker, M., Milker-Zabel, S. et al. Gene Expression Signatures in the Peripheral Blood After Radiosurgery of Human Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Strahlenther Onkol 186, 91–98 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-010-2034-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-010-2034-4