Abstract
Purpose
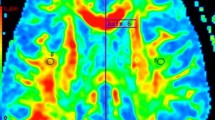
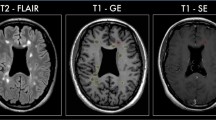
The aim of this study was to determine diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetization transfer (MT) imaging and multivoxel MR spectroscopy findings in plaques, periplaque white matter and normal appearing white matter (NAWM) regions in multiple sclerosis (MS) and to correlate the findings with the expanded disability status scale (EDSS).
Methods
A total of 30 patients with MS and 30 healthy control subjects were studied and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values, MT ratio (MTR), N-acetyl-aspartate/creatine (NAA/Cr) and choline/creatine (Cho/Cr) ratios were measured in plaques, periplaques and NAWM regions and compared with the control subjects.
Results
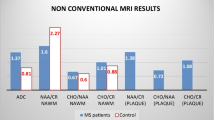
The MTR and NAA/Cr ratio were decreased more in plaques than periplaques and NAWM, in contrast ADC values and Cho/Cr ratios were highest in plaques and higher in periplaques than in NAWM. Decreased MTR and NAA/Cr in NAWM demonstrated moderate inverse correlations (r = − 0.604, p < 0.001 and r = − 0.494, p < 0.001, respectively) while Cho/Cr ratios and ADC of NAWM demonstrated weak linear correlations (r = 0.370, p = 0.004, r = 0.297, p = 0.021 respectively) with EDSS.
Conclusions
The MS, MTR and MR spectroscopy findings were found to be useful for detecting subtle abnormalities in NAWM. Although ADC values were significantly altered in plaque and periplaque regions a significance difference was not found in NAWM.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller DH, Grossman RI, Reingold SC, et al. The role of magnetic resonance techniques in understanding and managing multiple sclerosis. Brain. 1998;121:3–24.
Filippi M, Tortorella C, Rovaris M, et al. Changes in the normal appearing brain tissue and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr. 2000;68:157–61.
Tortorella C, Viti B, Bozzali M, et al. A magnetization transfer histogram study of normal-appearing brain tissue in MS. Neurology. 2000;54:186–93.
Nijeholt GJ, van Walderveen MA, Castelijns JA, et al. Brain and spinal cord abnormalities in multiple sclerosis. Correlation between MRI parameters, clinical subtypes and symptoms. Brain. 1998;121:687–97.
Davie CA, Barker GJ, Thompson AJ, et al. 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy of chronic cerebral white matter lesions and normal appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr. 1997;63:736–42.
Barkhof F, Walderveen M van. Characterization of tissue damage in multiple sclerosis by nuclear magnetic resonance. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999;354:1675–86.
Rovaris M, Comi G, Filippi M. MRI markers of destructive pathology in multiple sclerosis-related cognitive dysfunction. J Neurol Sci. 2006;245:111–6.
Phuttharak W, Galassi W, Laopaiboon V, et al. ADC measurements in various patterns of multiple sclerosis lesions. J Med Assoc Thai. 2006;89:196–204.
Tortorella P, Rocca MA, Mezzapesa DM, et al. MRI quantification of gray and white matter damage in patients with early-onset multiple sclerosis. J Neurol. 2006;253:903–7.
Kappos L, Moeri D, Radue EW, et al. Predictive value of gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for relapse rate and changes in disability or impairment in multiple sclerosis: a meta-analysis. Gadolinium MRI Meta-analysis Group. Lancet. 1999;353:964–9.
Lin X, Tench CR, Morgan PS, Constantinescu CS. Use of combined conventional and quantitative MRI to quantify pathology related to cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79(4):437–41.
Tintoré M, Sastre-Garriga J. New treatment measurements for treatment effects on relapses and progression. J Neurol Sci. 2008;274(1–2):80–3.
Ge Y, Grossman RI, Udupa JK, Babb JS, Mannon LJ, McGowan JC. Magnetization transfer ratio histogram analysis of normal-appearing gray matter and normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2002 Jan-Feb;26(1):62–8.
Zivadinov R, De Masi R, Nasuelli D, Bragadin LM, Ukmar M, Pozzi-Mucelli RS, Grop A, Cazzato G, Zorzon M. MRI techniques and cognitive impairment in the early phase of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Neuroradiology. 2001;43(4):272–8.
Deloire MS, Salort E, Bonnet M, Arimone Y, Boudineau M, Amieva H, Barroso B, Ouallet JC, Pachai C, Galliaud E, Petry KG, Dousset V, Fabrigoule C, Brochet B. Cognitive impairment as marker of diffuse brain abnormalities in early relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr. 2005;76(4):519–26.
Audoin B, Au Duong MV, Ranjeva JP, Ibarrola D, Malikova I, Confort-Gouny S, Soulier E, Viout P, Ali-Chérif A, Pelletier J, Cozzone PJ. Magnetic resonance study of the influence of tissue damage and cortical reorganization on PASAT performance at the earliest stage of multiple sclerosis. Hum Brain Mapp. 2005;24(3):216–28.
Portaccio E, Stromillo ML, Goretti B, Zipoli V, Siracusa G, Battaglini M, Giorgio A, Bartolozzi ML, Guidi L, Sorbi S, Federico A, Amato MP, De Stefano N. Neuropsychological and MRI measures predict short-term evolution in benign multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2009;73(7):498–503.
Filippi M, Rocca MA, Benedict RH, DeLuca J, Geurts JJ, Rombouts SA, Ron M, Comi G. The contribution of MRI in assessing cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2010;75(23):2121–8.
Grossman RI. Magnetization transfer in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1994;36(Suppl):97–9.
Larsson HB, Thomsen C, Frederiksen J, et al. In vivo magnetic resonance diffusion measurement in the brain of patients with multiple sclerosis. Magn Reson Imaging. 1992;10:7–12.
Horsfield MA, Lai M, Webb SL, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficients in benign and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis by nuclear magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med. 1996;36:393–400.
Simone IL, Tortorella C, Federico F, et al. Axonal damage in multiple sclerosis plaques: a combined magnetic resonance imaging and 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J Neurol Sci. 2001;182:143–50.
De Stefano N, Matthews PM, Fu L, et al. Axonal damage correlates with disability in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Results of a longitudinal magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Brain. 1998;121:1469–77.
De Stefano N, Matthews PM, Antel JP, et al. Chemical pathology of acute demyelinating lesions and its correlation with disability. Ann Neurol. 1995;38:901–9.
McDonald WI, Compston A, Edan G, Goodkin D, Hartung HP, Lublin FD, McFarland HF, Paty DW, Polman CH, Reingold SC, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Sibley W, Thompson A, Van Den Noort S, Weinshenker BY, Wolinsky JS. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the international panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2001;50:121–7.
Truyen L, van Waesberghe JH, van Walderveen MA, et al. Accumulation of hypointense lesions (“black holes”) on T1 spin-echo MRI correlates with disease progression in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1996;47:1469–76.
Walderveen MA van,Lycklama A, Nijeholt GJ, et al. Hypointense lesions on T1-weighted spin-echo magnetic resonance imaging: relation to clinical characteristics in subgroups of patients with multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 2001;58:76–81.
Miller DH, Thompson AJ, Filippi M. Magnetic resonance studies of abnormalities in the normal appearing white matter and grey matter in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol. 2003;250:1407–19.
Castriota Scanderbeg A, Tomaiuolo F, Sabatini U, et al. Demyelinating plaques in relapsing-remitting and secondary-progressive multiple sclerosis: assessment with diffusion MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000;21:862–8.
Rocca MA, Mastronardo G, Rodegher M, et al. Long-term changes of magnetization transfer – derived measures from patients with relapsing-remitting and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999;20:821–7.
Rovaris M, Filippi M, Minicucci L, et al. Cortical/subcortical disease burden and cognitive impairment in patients with multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000;21:402–8.
Fu L, Matthews PM, De Stefano N, et al. Imaging axonal damage of normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Brain. 1998;121:103–13.
Le Bihan D, Turner R, Douek P, et al. Diffusion MR imaging: clinical applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992;159:591–9.
Garaci FG, Colangelo V, Ludovici A, et al. A diffusion longitudinal MR imaging study in normal-appearing white matter in untreated relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28:475–8.
Anik Y, Kural Z, Demirci A, et al. Magnetization transfer ratio in neuro-Behçet disease. Neuroradiology. 2005;47:108–13.
Filippi M, Campi A, Dousset V, et al. A magnetization transfer imaging study of normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1995;45:478–82.
Chen JT, Collins DL, Freedman MS, et al. The Canadian MS/BMT Study Group. Local magnetization transfer ratio signal inhomogeneity is related to subsequent change in MTR in lesions and normal-appearing white-matter of multiple sclerosis patients. Neuroimage. 2005;25:1272–8.
Barkhof F, Bruck W, De Groot CJ, et al. Remyelinated lesions in multiple sclerosis: magnetic resonance image appearance. Arch Neurol. 2003;60:1073–81.
Santos AC, Narayanan S, de Stefano N, et al. Magnetization transfer can predict clinical evolution in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol. 2002;249:662–8.
Davie CA, Hawkins CP, Barker GJ, et al. Serial proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in acute multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain. 1994;117:49–58.
Yaldizli O, Atefy R, Gass A, et al. Corpus callosum index and long-term disability in multiple sclerosis patients. J Neurol. 2010;257:1256–64.
Audoin B, Zaaraoui W, Reuter F, et al. Atrophy mainly affects the limbic system and the deep grey matter at the first stage of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr. 2010;81:690–5.
Prakhova LN, Il’ves AG, Petrov AM, et al. Brain atrophy and neurological impairment in patients with multiple sclerosis. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2009;109(7 Suppl 2):32–7.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anik, Y., Demirci, A., Efendi, H. et al. Evaluation of Normal Appearing White Matter in Multiple Sclerosis. Clin Neuroradiol 21, 207–215 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-011-0091-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-011-0091-4