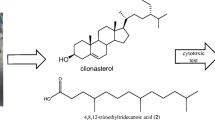
Abstract
Marine sponges have been considered as a gold mine, with respect to the diversity of their secondary metabolites. Many sponge extracts and isolated compounds are potential anticancer agents. In the present study, the antiproliferative activity of Negombata magnifica was investigated as petroleum ether extract (PE), total methanolic extract (ME) and two sub-fractions II and III, isolated pure compounds (palmitic acid and pregnanediol), sponge mesohyl and primmorphs ethyl acetate extract. Palmitic acid was used as a positive control. Cell viability was assessed via MTT assay, and apoptosis was investigated in terms of DNA fragmentation and BCl2 gene expression. Cell cycle analysis was performed via flow cytometry. GLC analysis of PE revealed that it contains 84.46 % hydrocarbons and 15.54 % sterols, whereas the fatty acids contain 38.62 % saturated and 61.38 % unsaturated fatty acids. Results revealed that except for pregnanediol and fraction II, all treatments exhibited cytotoxic activity. Primmorphs ethyl acetate extract and fraction III arrested cells in G0–G1, while fraction II arrested cell cycle in G2/M. PE extract arrested cells in G0–G1 and G2/M. Mesohyl, PE and fraction III could be apoptotic agents as indicated by DNA fragmentation independent on BCL2 expression, while ME and pregnanediol could exhibited pro-apoptotic effect through decreasing BCL2 expression although no DNA ladder was observed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenef B, Arifah K (2012) Cytotoxic effects of conjugated linoleic acids on human breast cancer cells (MCF7). Acad J Cancer Res 5(1):11–16
Agami R, Bernards R (2000) Distinct initiation and maintenance mechanisms cooperate to induce G1 cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage. Cell 102(1):55–66
Artwohl M, Roden M, Waldhäusl W, Freudenthaler A, Baumgartner-Parzer A (2004) Free fatty acids trigger apoptosis and inhibit cell cycle progression in human vascular endothelial cells. FASEB J 18:146–148
Ax P (1996) Multicellular animals. Springer, Berlin, pp 68–76
Belarbi E, Gomez A, Chisti Y, Camacho F, Grima E (2003) Producing drugs from marine sponges. Biotechnol Adv 21:585–598
Blunt W, Stothers B (1977) 13C NMR spectra of steroids—a survey and commentary. Org Magn Reson 9(8):439–464
Borth N, Litsche K, Franke C, Sachse K, Saluz P, Hänel F (2011) Functional interaction between type III-secreted protein IncA of Chlamydophila psittaci and human G3BP1. PLoS One 6(1):e16692
Custodio R, Prokic I, Steffen R, Koziol C, Borojevic R, Brümmer F, Nickel M, Müller W (1998) Primmorphs generated from dissociated cells of the sponge Suberites domuncula: a model system for studies of cell proliferation and cell death. Mech Ageing Dev 105:45–59
Del Gaizo Moore R, Certo M, Love M, Novina D, Letai A (2007) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia requires BCL2 to sequester prodeath BIM, explaining sensitivity to BCL2 antagonist ABT-737. J Clin Invest 117(1):112–121
Deng X (2006) BRCA1: cell cycle checkpoint, genetic instability, DNA damage response and cancer evolution. Nucleic Acids Res 34(5):1416–1426
Dirsch M, Antlsperger S, Hentze H, Vollmar M (2002) Ajoene, an experimental anti-leukemic drug: mechanism of cell death. Leukemia 16:74–83
Dyntar D, Eppenberger-Eberhardt M, Maedler K, Pruschy M, Eppenberger H, Spinas G, Donath M (2001) Glucose and palmitic acid induce degeneration of myofibrils and modulate apoptosis in rat adult cardiomyocytes. Diabetes 50:2105–2113
Essack M, Bajic V, Archer J (2011) Recently confirmed apoptosis-inducing lead compounds isolated from marine sponge of potential relevance in cancer treatment. Mar Drugs 9:1580–1606
Frederick R, Harrison W (1991) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, placozoa, porifera, cnidaria, and ctenophora. Wiley-Liss, New York
Gamet-Payrastre L, Li P, Lumeau S, Cassar G, Dupont A, Chevolleau S, Gasc N, Tulliez J, Terce F (2000) Sulforaphane, a naturally occurring isothiocyanate, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HT29 human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 60:1426–1433
Gross A, McDonnell M, Korsmeyer J (1999) Bcl-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:1899–1911
Harada H, Yamashita U, Kurihara H, Fukushi E, Kawabata J, Kamei Y (2002) Antitumor activity of palmitic acid found as a selective cytotoxic substance in a marine red alga. Anticancer Res 22(5):2587–2590
Hashem F, El-Souda S, Selim A, Shaker K, Maamoun A, Aboutabl E (2014) Composition of lipoidal matter and evaluation of hepatoprotective, cytotoxic, and antioxidant activities of Khaya grandifoliola CDC. Growing in Egypt. Egypt Pharm J 13(1):13–18
Hayashi Y, Nishikawa Y, Mori H, Tamura H, Matsushita Y, Matsu T (1998) Antitumor activity of (10E, 12Z)-9-hydroxy-10, 12-octadecadienoic acid from rice bran. J Ferment Bioeng 86(2):149–153
Joshi H, Joshi B, Sati H, Gururaja MP, Shetty R, Subrahmanyam E, Satyanaryana D (2009) Fatty acids from memecylon umbellatum (Burm.). Asian J Res Chem 2(2):178–180
Liu J, Hu W, He L, Ye M, Li Y (2004) Effects of lycorine on HL-60 cells via arresting cell cycle and inducing apoptosis. FEBS Lett 578:245–250
McClintock B, Baker J (2010) Marine chemical ecology. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, pp 1–624
Mittal S, El-Serag B (2013) Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: consider the population. J Clin Gastroenterol 47:S2–S6
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Müller W (2003) The origin of metazoan complexity: porifera as integrated animals. Integr Comp Biol 43:3–10
Müller W, Böhm M, Batel R, De Rosa S, Tommonaro G, Müller M, Schröder C (2000) Application of cell culture for the production of bioactive compounds from sponges: synthesis of avarol by primmorphs from Dysidea avara. J Nat Prod 63:1077–1081
Osinga R, Tramper J, Wijffels H (1999) Cultivation of marine sponges. Mar Biotechnol 1:509–532
Rady H (2014) Sponge mesohyl induces anti-proliferation activity and cell cycle arrest in colon cancer in-vitro. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci 5(6):1070–1074
Sheppard J, Iverson L (1975) Esterification of fatty acids for gas-liquid chromatographic analysis. J Chromatogr Sci 13:448–452
Trimborn M, Lwig M, Glanz D, Gruner M, Glaesser D (2000) Linoleic acid cytotoxicity to bovine lens epithelial cells: influence of albumin on linoleic acid uptake and cytotoxicity. Ophthalmic Res 32:87–93
Tsuda K, Sakai K, Tanbe K, Kishidi Y (1960) Isolation of 22-dehydrocholesterol from Hypnea japonica. J Am Chem Soc 82:1442–1447
Uriz J, Turon X, Becerro MA, Galera J (1996) Feeding deterrence in sponges. The role of toxicity, physical defenses, energetic contents, and life-history stage. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 205:187–204
Weissenfels N, Stniegler B (1979) Bau und Funktion des Süsswasser schwammes Ephydatiafluviatilis L. (Ponifera). VI. Das Individualitätsproblem Zoomorphol 92:49
Xue X, Qu XJ, Gao ZH, Sun CC, Liu HP, Zhao CR, Cheng YN, Lou HX (2012) Riccardin D, a novel macrocyclic bisbibenzyl, induces apoptosis of human leukemia cells by targeting DNA topoisomerase II. Invest New Drugs 30(1):212–222
Yang X, Chan C (2009) Repression of PKR mediates palmitate-induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells through regulation of Bcl-2. Cell Res 19:469–486
Zea S, Fernando P, Martinez A, Duque C (1999) Production of bioactive furanoseesterterpen teronic acids as possible internal chemical defense mechanism in the sponge Ircinia felix (Porifera: demospongiae). Mem Queensl Mus 44:687–696
Zhang W, Zhang X, Cao X, Xu J, Zhao Q, Yu X, Jin M, Deng M (2003) Optimizing the formation of in vitro sponge primmorphs from the Chinese sponge Stylotellaagminata (Ridley). J Biotechnol 100:161–168
Zhao Q, Zhang W, Jin M, Yu X, Deng M (2008) Formulation of a basal medium for primary cell culture of the marine sponge Hymeniacidon perleve. Biotechnol Prog 21(3):1008–1012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rady, H.M., Hassan, A.Z., Salem, S.M. et al. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by Negombata magnifica sponge in hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Chem Res 25, 456–465 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-015-1491-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-015-1491-9