Abstract
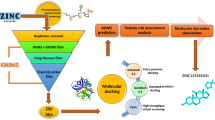
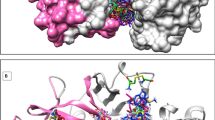
To date, the cause of neurodegeneration is not well understood and diseases that stem from neurodegeneration currently have no known cures. Cathepsin B (CB) enzyme is known to be involved in the production of peptide neurotransmitters and toxic peptides in neurodegenerative diseases. CA-074Me is a membrane-permeable irreversible selective CB inhibitor as confirmed by in vivo studies. Due to the lack of the crystal structure, the binding mode of CA-074Me with the human CB at molecular level has not been previously reported. The main aim of this study is to gain an insight into the binding mode of CB CA-074Me to human CB using various computational tools. Herein, molecular dynamics simulations, binding free energy calculations and per-residue energy decomposition analysis were employed to accomplish the aim of the study. Another objective was to identify novel CB inhibitors based on the structure of CA-074Me using fragment based drug design using scaffold hoping drug design approach. Results showed that two of the designed ligands (hit 1 and hit 2) were found to have better binding affinities than the prototype inhibitor, CA-074Me, by ~2–3 kcal/mol. Per-residue energy decomposition showed that amino acid residues Cys29, Gly196, His197, and Val174 contributed the most toward the binding. The Van der Waals binding forces were found to be the major component of the binding interactions. The findings of this study should assist medicinal chemist toward the design of potential irreversible CB inhibitors.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed SM, Kruger HG, Govender T, Maguire GE, Sayed Y, Ibrahim MA, Naicker P, Soliman ME (2013) Comparison of the molecular dynamics and calculated binding free energies for nine FDA-approved HIV-1 PR drugs against subtype B and C-SA HIV PR. Chem Biol Drug Des 81(2):208–218
Alperin I, Ma B, Wolfson H, Nussinov R (2002) Principles of docking: an overview of search algorithms and a guide to scoring functions. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinform 47:409–443
Andrusier N, Mashiach E, Nussinov R, Wolfson HJ (2008) Principles of flexible protein–protein docking. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinform 73(2):271–289
Asai M, Yagishita S, Iwata N, Saido TC, Ishiura S, Maruyama K (2011) An alternative metabolic pathway of amyloid precursor protein C-terminal fragments via cathepsin B in a human neuroglioma model. FASEB J 25(10):3720–3730
Bajorath J (2002) Integration of virtual and high-throughput screening. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1:882–894
Bellettato CM, Scarpa M (2010) Pathophysiology of neuropathic lysosomal storage disorders. J Inherit Metab Dis 33(4):347–362
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, van Gunsteren WF, DiNola A, Haak JR (1984) Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81:3684–3690
Bostrom J, Berggren K, Elebring T, Greasley PJ, Wilstermann M (2007) Scaffold hopping, synthesis and structure–activity relationships of 5,6-diaryl-pyrazine-2-amide derivatives: a novel series of CB1 receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 15(12):4077–4084
Case DA, Cheatham TE, Darden T, Gohlke H, Luo R, Merz KM, Onufriev A, Simmerling C, Wang B, Woods RJ (2005) The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J Comput Chem 26(16):1668–1688
Chen LY (2008) Nonequilibrium fluctuation-dissipation theorem of Brownian dynamics. J Chem Phys 129(14):144113–144117
Cieplak P, Cornell WD, Bayly C, Kollman PA (1995) Application of the multimolecule and multiconformational RESP methodology to biopolymers—charge derivation for DNA, RNA, and proteins. J Comput Chem 16(11):1357–1377
Ding Y, Cai Y (2013) Conformational dynamics of xylanase a from Streptomyces lividans: implications for TIM-barrel enzyme thermostability. Biopolymers 99(9):594–604
Duan Y, Wu C, Chowdhury S, Lee MC, Xiong GM, Zhang W, Yang R, Cieplak P, Luo R, Lee T, Caldwell J, Wang JM, Kollman P (2003) A point-charge force field for molecular mechanics simulations of proteins based on condensed-phase quantum mechanical calculations. J Comput Chem 24:1999–2012
Eckert H, Bajorath J (2007) Molecular similarity analysis in virtual screening: foundations, limitations and novel approaches. Drug Discov Today 12:225–233
Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowitz ML, Darden T, Lee H, Pedersen LG (1995) A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J Chem Phys 103(19):8577–8593
Frisch MJ TG, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR MJ, Vreven T, Kudin KN, Burant, JC MJ, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Barone V, Mennucci B,Cossi M, Scalmani G, Rega N, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Hada, M EM, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T HY, Kitao O, Nakai H, Klene M, Li X, Knox, JE HH, Cross JB, Bakken V, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R SR, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C OJ, Ayala PY, Morokuma K, Voth GA, Salvador P DJ, Zakrzewski VG, Dapprich S, Daniels, AD SM, Farkas O, Malick DK, Rabuck AD, Raghavachari, K FJ, Ortiz JV, Cui Q, Baboul AG, Clifford S, Cioslowski J SB, Liu G, Liashenko A, Piskorz P, Komaromi I MR, Fox DJ, Keith T, Al-Laham MA, Peng, CY NA, Challacombe M, Gill PMW, Johnson B, Chen W WM, Gonzalez C, Pople JA (2004) Gaussian Inc, Wallingford, CT
Gan L, Ye SM, Chu A, Anton K, Yi SL, Vincent VA, von Schack D, Chin D, Murray J, Lohr S, Patthy L, Gonzalez-Zulueta M, Nikolich K, Urfer R (2004) Identification of cathepsin B as a mediator of neuronal death induced by Aβ-activated microglial cells using a functional genomics approach. J Biol Chem 279(7):5565–5572
Godschalk F, Genheden S, Soderhjelm P, Ryde U (2013) Comparison of MM/GBSA calculations based on explicit and implicit solvent simulations. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15(20):7731–7739
Hou T, Yu R (2007) Molecular dynamics and free energy studies on the wild-type and double mutant HIV-1 protease complexed with amprenavir and two amprenavir-related inhibitors: mechanism for binding and drug resistance. J Med Chem 50(6):1177–1188
http://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerReport2013.pdf. Accessed June 2013
Jain AN (2004) Virtual screening in lead discovery and optimization. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel 7:396–403
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD, Impey RW, Klein ML (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79:926–935
Karpoormath R, Sayed Y, Govender P, Govender T, Kruger HG, Soliman ME, Maguire GE (2012) Pentacycloundecane derived hydroxy acid peptides: a new class of irreversible non-scissile ether bridged type isoster as potential HIV-1 wild type C-SA protease inhibitors. Bioorg Chem 40(1):19–29
Khurana V, Elson-Schwab I, Fulga TA, Sharp KA, Loewen CA, Mulkearns E, Tyynela J, Scherzer CR, Feany MB (2010) Lysosomal dysfunction promotes cleavage and neurotoxicity of tau in vivo. PLoS Genet 6(7):e1001026–e1001037
Kingham PJ, Pocock JM (2001) Microglial secreted cathepsin B induces neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem 76(5):1475–1484
Kitchen DB, Decornez H, Furr JR, Bajorath J (2004) Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: methods and applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:935–949
Klebe G (2006) Virtual ligand screening: strategies, perspectives and limitations. Drug Discov Today 11:580–594
Koh JY, Choi DW (1987) Quantitative-determination of glutamate mediated cortical neuronal injury in cell-culture by lactate-dehydrogenase efflux assay. J Neurosci Methods 20(1):83–90
Mage MG, Dolan MA, Wang R, Boyd LF, Revilleza MJ, Robinson H, Natarajan K, Myers NB, Hansen TH, Margulies DH (2013) A structural and molecular dynamics approach to understanding the peptide-receptive transition state of MHC-I molecules. Mol Immunol 55(2):123–125
Makatini MM, Petzold K, Arvidsson PI, Honarparvar B, Govender T, Maguire GE, Parboosing R, Sayed Y, Soliman ME, Kruger HG (2012) Synthesis, screening and computational investigation of pentacycloundecane-peptoids as potent CSA-HIV PR inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 57:459–467
Mueller-Steiner S, Zhou Y, Arai H, Roberson ED, Sun B, Chen J, Wang X, Yu G, Esposito L, Mucke L, Gan L (2006) Antiamyloidogenic and neuroprotective functions of cathepsin B: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 51(6):703–714
Murata M, Miyashita S, Yokoo C, Tamai M, Hanada K, Hatayama K, Towatari T, Nikawa T, Katunuma N (1991) Novel epoxysuccinyl peptides—selective inhibitors of cathepsin-b, invitro. FEBS Lett 280(2):307–310
Naicker P, Achilonu I, Fanucchi S, Fernandes M, Ibrahim MA, Dirr HW, Soliman ME, Sayed Y (2012) Structural insights into the South African HIV-1 subtype C protease: impact of hinge region dynamics and flap flexibility in drug resistance. J Biomol Struct Dyn 31(12):1370–1380
Ode H, Matsuyama S, Hata M, Hoshino T, Kakizawa J, Sugiura W (2007) Mechanism of drug resistance due to N88S in CRF01_AE HIV-1 protease, analyzed by molecular dynamics simulations. J Med Chem 50(8):1768–1777
Onufriev A, Bashford D, Case DA (2000) Modification of the generalized Born model suitable for macromolecules. J Phys Chem B 104(15):3712–3720
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25(13):1605–1612
Renko M, Pozgan U, Majera D, Turk D (2010) Stefin A displaces the occluding loop of cathepsin B only by as much as required to bind to the active site cleft. FEBS J 277(20):4338–4345
Roux B, Nina M, Pomes R, Smith JC (1996) Thermodynamic stability of water molecules in the bacteriorhodopsin proton channel: a molecular dynamics free energy perturbation study. Biophys J 71(2):670–681
Ryckaert JP, Ciccotti G, Berendsen HJC (1977) Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J Comput Phys 23:327–341
San Sebastian W, Samaranch L, Kells AP, Forsayeth J, Bankiewicz KS (2013) Gene therapy for misfolding protein diseases of the central nervous system. Neurotherapeutics 10(3):498–510
Schuffenhauer A (2012) Computational methods for scaffold hopping. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Mol Sci 2(6):842–867
Shachar T, Lo Bianco C, Recchia A, Wiessner C, Raas-Rothschild A, Futerman AH (2011) Lysosomal storage disorders and Parkinson’s disease: Gaucher disease and beyond. Mov Disord 26(9):1593–1604
Shoichet BK (2004) Virtual screening of chemical libraries. Nature 432:862–865
Sitkoff D, Sharp KA, Honig B (1994) Accurate calculation of hydration free-energies using macroscopic solvent models. J Phys Chem 98(7):1978–1988
Skovronsky DM, Lee VMY, Trojanowskiz JQ (2006) Neurodegenerative diseases: new concepts of pathogenesis and their therapeutic implications. Annu Rev Pathol Mech Dis 1:151–170
Srinivasan J, Cheatham TE, Cieplak P, Kollman PA, Case DA (1998) Continuum solvent studies of the stability of DNA, RNA, and phosphoramidate—DNA helices. J Am Chem Soc 120(37):9401–9409
Stahura FL, Bajorath J (2005) New methodologies for ligand-based virtual screening. Curr Pharm Des 11:1189–1202
Steverding D (2001) The cathepsin B-selective inhibitors CA-074 and CA-074Me inactivate cathepsin L under reducing conditions. Open Enzym Inhib J 4:11–16
Takalo M, Haapasalo A, Natunen T, Viswanathan J, Kurkinen KM, Tanzi RE, Soininen H, Hiltunen M (2013) Targeting ubiquilin-1 in Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets 17(7):795–810
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) Software news and update AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31(2):455–461
Tsuchiya K, Kohda Y, Yoshida M, Zhao L, Ueno T, Yamashita J, Yoshioka T, Kominami E, Yamashima T (1999) Postictal blockade of ischemic hippocampal neuronal death in primates using selective cathepsin inhibitors. Exp Neurol 155(2):187–194
Tsui V, Case DA (2001) Theory and applications of the generalized Born solvation model in macromolecular simulations. Biopolymers 56(4):275–291
van Leuven F (2000) Single and multiple transgenic mice as models for Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 61(3):305–312
Vogt M, Bajorath J (2009) Data mining approaches for compound selection and iterative screening. In: Balakin KV (ed) Pharmaceutical data mining: approaches and applications for drug discovery. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, pp 115–143
Wang J-C, Lin J-H (2013) Scoring functions for prediction of protein–ligand interactions. Curr Pharm Des 19(12):2174–2182
Wang Y, Qin ZH (2010) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of excitotoxic neuronal death. Apoptosis 15(11):1382–1402
Wang W, Donini O, Reyes CM, Kollman PA (2001) Biomolecular simulations: recent developments in force fields, simulations of enzyme catalysis, protein–ligand, protein–protein, and protein–nucleic acid noncovalent interactions. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 30:211–243
Wang J, Wolf RM, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA, Case DA (2004) Development and testing of a general amber force field. J Comput Chem 25:1157–1174
Watanabe D, Yamamoto A, Tomoo K, Matsumoto K, Murata M, Kitamura K, Ishida T (2006) Quantitative evaluation of each catalytic subsite of cathepsin B for inhibitory activity based on inhibitory activity–binding mode relationship of epoxysuccinyl inhibitors by X-ray crystal structure analyses of complexes. J Mol Biol 362(5):979–993
Willett P (2006) Similarity-based virtual screening using 2D fingerprints. Drug Discov Today 11:1046–1053
Xie Y, Liao C, Zhou J (2013) Effects of external electric fields on lysozyme adsorption by molecular dynamics simulations. Biophys Chem 179:26–34
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Center of High Performance Computing (CHPC, Cape Town) for the use of their computational facility, the School of Health Sciences, UKZN, for their financial support, and S. Bharat for his assistance with compound library generation and useful discussions relating to methods and results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mashamba-Thompson, T., Soliman, M.E.S. Insight into the binding theme of CA-074Me to cathepsin B: molecular dynamics simulations and scaffold hopping to identify potential analogues as anti-neurodegenerative diseases. Med Chem Res 24, 701–713 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-014-1145-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-014-1145-3