Abstract
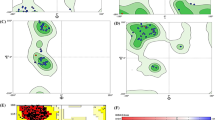
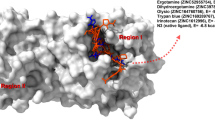
β-Arrestins are well-known negative regulators of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) signaling. The present study is aimed to build human β-arrestins 3D structures by homology modeling followed by identification and characterization of binding sites and there by assessing druggability of the proteins. Based upon BLAST results, bovine β-arrestin (PDB ID:1G4M) was considered as a template for homology modeling. Homology models were constructed using MODELLER program, refined and validated using PROCHECK in which >97 % of residues present in the favored regions of the Ramachandran plots. Since there are no co-ordinates of ligands available in the template, we used various binding site prediction algorithms to predict different binding pockets on the modeled proteins. To examine the response of proteins toward various apoptosis inducers, molecular docking study was carried out. The identification of 3D structures, binding sites for various signaling molecules will guide us designing molecular tools for therapeutic intervention that may prove useful in numerous disorders associated with β-arrestin-GPCRs signaling.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway PG, Howard L, Dolph PJ (2000) The formation of stable rhodopsin–arrestin complexes induces apoptosis and photoreceptor cell degeneration. Neuron 28:129–138
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSIBLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Attramadal H, Arriza JL, Aoki C, Dawson TM, Codina J, Kwatra MM, Snyder SH, Caron MG, Lefkowitz (1992) RJ Beta-arrestin2, a novel member of the arrestin/beta-arrestin gene family. J Biol Chem 267:17882–17890
Bohn LM, Lefkowitz RJ, Gainetdinov RR, Peppel K, Caron MG, Lin FT (1999) Enhanced morphine analgesia in mice lacking beta-arrestin 2. Science 286:2495–2498
Conner DA, Mathier MA, Mortensen RM, Christe M, Vatner SF, Seidman CE, Seidman JG (1997) β-Arrestin1 knockout mice appear normal but demonstrate altered cardiac responses to beta-adrenergic stimulation. Circ Res 81:1021–1026
DeWire SM, Ahn S, Lefkowitz RJ, Shenoy SK (2007) β-Arrestins and cell signaling. Annu Rev Physiol 69:483–510
Elbegdorj O, Westkaemper RB, Zhang Y (2013) A homology modeling study toward the understanding of three-dimensional structure and putative pharmacological profile of the G-protein coupled receptor GPR55. J Mol Graph Model 39:50–60
Gasteiger J, Marsili M (1980) Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 36:3219–3228
Han M, Gurevich VV, Vishnivetskiy SA, Sigler PB, Schubert C (2001) Crystal structure of β-arrestin at 1.9 Å: possible mechanism of receptor binding and membrane translocation. Structure 9:869–880
Jain AN (1996) Scoring noncovalent protein-ligand interactions: a continuous differentiable function tuned to compute binding affinities. J Comput-Aided Mol Des 10:427–440
Kingston DG, Newman DJ (2007) Taxoids: cancer-fighting compounds from nature. Curr Opin Drug Discov Dev 10:130–144
Kiselev A, Socolich M, Vinós J, Hardy RW, Zuker CS, Ranganathan RA (2000) Molecular pathway for light-dependent photorecptor apoptosis in Drosophila. Neuron 28:139–152
Kuhn H (1978) Light-regulated binding of rhodopsin kinase and other proteins to cattle photoreceptor membranes. Biochemistry 17:4389–4395
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Crystallogr 26:283–291
Laurie A, Jackson R (2005) Q-SiteFinder: an energy-based method for the prediction of protein–ligand binding sites. Bioinformatics 21:1908–1916
Lefkowitz RJ, Whalen EJ (2004) β-Arrestins: traffic cops of cell signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16:162–168
Luttrell LM, Ferguson SS, Daaka Y, Miller WE, Maudsley S, Rocca GJD, Lin F, Kawakatsu H, Owada K, Luttrell DK, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ (1999) β-Arrestin-dependent formation of beta2 adrenergic receptor-Src protein kinase complexes. Science 283:655–661
Milano SK, Pace HC, Kim YM, Brenner C, Benovic JL (2002) Scaffolding functions of arrestin-2 revealed by crystal structure and mutagenesis. Biochemistry 41:3321–3328
Reiter E, Lefkowitz RJ (2006) GRKs and β-arrestins: roles in receptor silencing, trafficking and signaling. Trends Endocrinol Metab 17:159–165
Roman G, He J, Davis RL (2000) Kurtz, a novel nonvisual arrestin, is an essential neural gene in Drosophila. Genetics 155:1281–1295
Sanchez R, Sali A (1997) Evaluation of comparative protein structure modeling by MODELLER-3. Proteins Struct Funct Genet 1:50–58
Schaffer AA, Wolf YI, Ponting CP, Koonin EV, Aravind L, Altschul SF (1999) IMPALA: matching a protein sequence against a collection of PSI-BLAST-constructed position-specific score matrices. Bioinformatics 15:1000–1011
Shenoy SK, Lefkowitz RJ (2005) Receptor regulation: β-arrestin moves up a notch. Nat Cell Biol 7:1159–1161
Singh UC, Weiner PK, Caldwell JK, Kollman PA (1986) AMBER version 3.0. University of California at San Francisco, San Francisco
Sun X, Zhang Y, Wang J, Wei L, Li H, Hanley G, Zhao M, Li Y, Yin D (2010) β-Arrestin 2 modulates resveratrol-induced apoptosis and regulation of Akt/GSK3ß pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta 1800:912–918
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Varmus H (2006) The new era in cancer research. Science 312:1162–1165
Vyas VK, Ukawala RD, Ghate M, Chintha C (2012) Homology modeling a fast tool for drug discovery: current perspectives. Indian J Pharm Sci 74:1–17
Vyas VK, Chintha C, Pandya MR (2013) Biology and medicinal chemistry approaches towards various apoptosis inducers. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem 13:433–455
Zhang Z, Hao J, Zhao Z, Ben P, Fang F, Shi L, Gao Y, Liu J, Wen C, Luo L, Yin Z (2009) β-Arrestins facilitate ubiquitin-dependent degradation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) and attenuate H2O2-induced apoptosis. Cell Signal 21:1195–1206
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Nirma University, Ahmedabad, India for providing necessary facilities to carry out this work, and Dr. R.S. Rathore, Application Scientist, Schrodinger GmbH, Bangalore, India for providing Schrödinger 12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chintha, C., Gupta, N., Ghate, M. et al. Homology modeling, binding site identification, and docking study of human β-arrestin: an adaptor protein involved in apoptosis. Med Chem Res 23, 1189–1201 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0725-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0725-y