Abstract
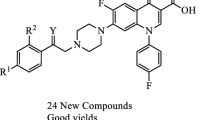
A series of twenty new N-substituted amino methyl-[1,2,3] triazolyl derivatives at C-7 position of fluoroquinolones were designed and synthesized through multistep synthesis. The synthesized compounds were characterized by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, ESI–MS, and IR. The antibacterial activities of these new fluoroquinolones were evaluated using a standard broth micro dilution technique. Out of the twenty derivatives, aryl substituted amino derivatives (6m to 6q) exhibited very good potency in inhibiting the growth of Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE faecalis) (MIC: 0.25–4.00 μg/mL) as compared to the marketed drugs Linezolid and Ciprofloxacin.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bryskier A, Chantot JF (1995) Classification and structure-activity relationships of fluoroquinolones. Drugs 49(suppl 2):16–28
De Souza MVN (2005) New fluoroquinolones: a class of potent antibiotics. Mini-Rev Med Chem 5:1009–1017
Domagala JM (1994) Structure-activity and structure-side-effect relationships for the quinolone antibacterials. J Antimicrob Chemother 33:685–706
Dubar F, Anquetin G, Pradines B, Dive D, Khalife J, Biot C (2009) Enhancement of the antimalarial activity of ciprofloxacin using a double prodrug/bioorganometallic approach. J Med Chem 52:7954–7957
Hooper David C (2001) Mechanisms of action of antimicrobials: focus on fluoroquinolones. Clin Infect Dis 32:S9–S15
Koga H, Itoh A, Murayama S, Suzue S (1980) Structure-activity relationships of antibacterial 6,7- and 7,8-disubstituted 1-alkyl-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acids. J Med Chem 23(12):1358–1363
Ledoussal B, Bouzard D, Coroneos E (1992) Potent non-6-fluoro-substituted quinolone antibacterials: synthesis and biological activity. J Med Chem 35(1):198–200
Mitscher LA (2005) Bacterial topoisomerase inhibitors: quinolone and pyridone antibacterial agents. Chem Rev 105:559–592
Patpi SR, Pulipati L, Yogeeswari P, Sriram D, Jain N, Sridhar B, Murthy R, Anjana Devi T, Kalivendi SV, Kantevari S (2012) Design, synthesis, and structure-activity correlations of novel dibenzo[b,d]furan, dibenzo[b,d]thiophene, and N-methylcarbazole clubbed [1,2,3] triazoles as potent inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Med Chem 55(8):3911–3922
Piddock LJV, Marshall AJ, Jin YF (1994) Activity of Bay y3118 against quinolone-susceptible and -resistant gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38:422–427
Selvakumar Natesan, Rajulu Gavara Govinda, Pazhanimuthu annamalia, ganesh sambasivam (2011) Histone deacetylase inhibitors, WO2011/021209 A1
Shanmugavelan P, Nagarajan S, Sathishkumar M, Ponnuswamy A, Yogeeswari P, Sriram D (2011) Efficient synthesis and in vitro antitubercular activity of [1,2,3] triazoles as inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21(24):7273–7276
Sumangala V, Poojary B, Chidananda N, Fernandes J, Kumari NS (2010) Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of [1,2,3] triazoles containing quinoline moiety. Arch Pharm Res 33(12):1911–1918
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Anthem biosciences management, Anthem biosciences, Bangalore, India, for their invaluable support and allocation of resources for this work. We would like thank Analytical chemistry team, Department of analytical chemistry, Anthem biosciences, Bangalore, India, for having carried out all the analytical work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Govinda Rajulu, G., Bhojya Naik, H.S., Viswanathan, A. et al. Design and synthesis of new N-substituted amino methyl-[1,2,3] triazolyl moieties of fluoroquinolones as antibacterial agents. Med Chem Res 22, 3843–3856 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0394-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0394-2