Abstract
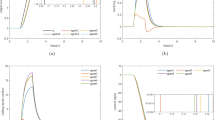
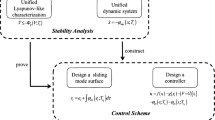
In this paper, the finite-time control of nonlinear impulsive switched positive systems (ISPSs) is studied, where the impulses and bounded disturbance are both fully considered. By designing a novel event-triggered strategy, we present LMI-based conditions for the existence of a controller that guarantees finite-time boundedness (FTB) of the resulting closed-loop systems based on the average dwell time (ADT) method. Further, the finite-time weighted \(L_2\)-gain performance of the considered systems is analyzed. Also, a lower bound of the minimum inter-event interval is obtained to preclude the Zeno behavior. Finally, a numerical example is given to compare the differences between different controllers and to verify the effectiveness of the presented conclusions.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
A. Adaldo, F. Alderisio, D. Liuzza, G. Shi, D.V. Dimarogonas, M.D. Bernardo, K.H. Johansson, Event-triggered pinning control of switching networks. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2(2), 204–213 (2015)
F. Amato, M. Ariola, P. Dorato, Finite-time control of linear systems subject to parameteric uncertainties and disturbances. Automatica 37, 1459–1463 (2001)
C. Briat, Dwell-time stability and stabilization conditions for linear positive impulsive and switched systems. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst 24, 198–226 (2017)
G. Chen, Y. Yang, New necessary and sufficient conditions for finite-time stability of impulsive switched linear time-varying systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 12(1), 140–148 (2018)
X. Chen, H. Liu et al., Adaptive neural preassigned-time ccontrol for macro-micro composite positioning stage with displacement constraints. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2023.3254602
X. Chen, F. Zhao et al., Reduced-order observer-Based preassigned finite-time control of nonlinear systems and its applications. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber. Syst. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2023.3241365
M. Donkers, W. Heemels, Output-based event-triggered control with guaranteed \(L_{\infty }\)-gain and improved and decentralised event-triggering. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 57(6), 1362–1367 (2012)
R. Dorf, M. Farren, C. Phillips, Adaptive sampling frequency for sampled-data control systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 7(1), 38–47 (1962)
L. Farina, S. Rinaldi, Positive linear systems: theory and applications (Wiley, New Jersey, 2011)
J. P. Hespanha, A. S. Morse, Stability of switched systems with average dwell-time, In: Proceedings of the 38th IEEE conference on decision and control, 3, 2655-2660 (1999)
S. Hu, X. Chen, J. Qiu et al., Dynamic event-triggered bipartite consensus of multiagent systems with estimator and cooperative-competitive interactions. IEEE Trans. Circuits-II Express Briefs 69(7), 3309–3313 (2022)
L. Jiao, Y. Yang, D. Yang, H. Li, Stabilization for impulsive switched positive systems under asynchronous switching. In: textit 2018 Chinese control and decision conference (CCDC) pp. 766-771 (2018)
J. Lam, Y. Chen, X. Liu et al., Positive systems theory and applications, Part of the Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences Book Series (Springer, Switzerland, 2019), p.480
S. Li, Z. Xiang, Exponential stability analysis and \(L_2\)-gain control synthesis for positive switched T-S fuzzy systems. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst 27, 77–91 (2018)
X. Lin, Y. Zou, S. Li, H. Du, Finite-time stability and finite-time weighted \(L_2\)-gain analysis for switched systems with time-varying delay. IET Control Theory Appl. 7(7), 1058–1069 (2013)
S. Liu, Z. Xiang, Exponential \(L_1\) output tracking control for positive switched linear systems with time-varying delays. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst 11, 118–128 (2014)
T. Liu, B. Wu, L. Liu, Y. Wang, Asynchronously finite-time control of discrete impulsive switched positive time-delay systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 352(10), 4503–4514 (2015)
Z. Liu, X. Zhang, X. Lu, T. Hou, Exponential stability of impulsive positive switched systems with discrete and distributed time-varying delays. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear 29(10), 3125–3138 (2019)
X. Lu, H. Li, C. Wang, X. Zhang, Stability analysis of positive switched impulsive systems with delay on time scales. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear 30(16), 6879–6890 (2020)
P. Nam, H. Trinh, P. Pathirana, V. Phat, Stability analysis of nonlinear time-delay systems using a novel piecewise positive systems method. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 63(1), 291–297 (2017)
S. Pan, Y. Shao, A Novel Approach to Input-to-State Stability of Impulsive Switched Nonlinear Systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process 41, 3739–3754 (2022)
S. Pan, Y. Shao, Exponential stability of totally positive switched linear systems with both stable and unstable subsystems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear 32(14), 8073–8085 (2022)
C. Wang, X. Chen, J. Cao et al., Neural network-based distributed adaptive pre-assigned finite-time consensus of multiple TCP/AQM networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits-I Regular Papers 99, 1–9 (2020)
J. Wang, J. Liang, C. Zhang, D. Fan, Robust dissipative filtering for impulsive switched positive systems described by the fornasini-marchesini second model. J. Frankl. Inst. 359, 123–144 (2022)
Q. Xi, X. Liu, Mode-dependent impulsive control of positive switched systems: stability and \(l_1\)-gain analysis. Chaos Solitons Fract. 140, 110276 (2020)
D. Xie, H. Zhang, H. Zhang, B. Wang, Exponential stability of switched systems with unstable subsystems: a mode-dependent average dwell time approach. Circuits Syst. Signal Process 32, 3093–3105 (2013)
Y. Yin, Z. Lin, Y. Liu, K.L. Teo, Event-triggered constrained control of positive systems with input saturation. Int J. Robust Nonlin. 28(11), 3532–3542 (2018)
J. Zhang, E. Fridman, Dynamic event-triggered control of networked stochastic systems with scheduling protocols. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 99, 1–1 (2021)
J. Zhang, S. Li, Z. Xiang, Adaptive fuzzy finite-time fault-tolerant control for switched nonlinear large-scale systems with actuator and sensor faults. J. Frankl. Inst. 357(16), 11629–11644 (2020)
J. Zhang, L. Liu, S. Li, X. Deng, Event-triggered \(l_1\)-gain control of nonlinear positive switched systems. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 34(3), 873–398 (2021)
X. Zhao, X. Liu, S. Yin, H. Li, Improved results on stability of continuous-time switched positive linear systems. Automatica 50(2), 614–621 (2014)
Q. Zheng, S. Xu, B. Du, Asynchronous nonfragile guaranteed cost control for impulsive switched fuzzy systems with quantizations and its applications. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 30(10), 4471–4483 (2022)
C. Zhu, X. Li, J. Cao, Finite-time \(H_\infty \) dynamic output feedback control for nonlinear impulsive switched systems Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 39, 100975 (2021)
G. Zong, H. Ren, L. Hou, Finite-time stability of inter-connected impulsive switched systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 10(6), 648–654 (2016)
W. Zou, S. Peng, Z. Xiang, S. Yan, Finite-time consensus of second-order switched nonlinear multi-agent systems IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. 31(5), 1757–1762 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 11861027 and Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province under Grant LY22F030008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, S., Huang, S. & Shao, Y. Finite-Time Control of Nonlinear Impulsive Switched Positive Systems Based on an Event-Triggered Controller. Circuits Syst Signal Process 43, 729–749 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02501-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02501-4
Keywords
- Impulsive switched positive systems
- Finite-time control
- Finite-time weighted \(L_2\)-gain
- Event-triggered controller
- Average dwell time