Abstract
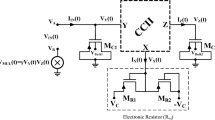
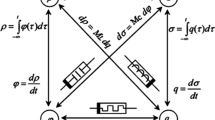
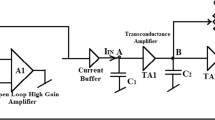
Memcapacitor is a type of capacitor but exhibits nonlinear behavior, and its capacitance depends on the past capacitance value. Researchers focused on the memcapacitors and meminductors upon postulation of memristor which is the forth passive fundamental circuit element. Memcapacitor emulator circuits have continuously been designed by researchers since it cannot be found as discrete circuit elements. A number of memcapacitor emulators have been offered in the literature to investigate its usability in CMOS designs. However, the offered designs have some insufficiencies such as grounded restriction, being composed of complex structure, etc. In this study, we designed a simple multioutput operational transconductance amplifier (MO-OTA)-based fully floating and electronically controllable memcapacitor emulator circuit. The circuit is composed of only two MO-OTAs, two analog multipliers, two grounded passive elements, and four transistors. This proposed circuit can also be implemented in VLSI and on breadboard using discrete circuit elements. Performance analyses were completed via using TSMC 0.18 μm parameters. Finally, the obtained results of the proposed fully floating emulator circuit are consistent with the expected memcapacitors behavior. This makes the circuit suitable for ideal memcapacitor emulator.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable
References
A. Ascoli, R. Tetzlaff, F. Corinto, M. Mirchev, M. Gilli, Memristor-based filtering applications, in LATW 2013—14th IEEE Latin-American Test Workshop (2013), pp. 1–6
Y. Babacan, An operational transconductance amplifier-based memcapacitor and meminductor. Istanb. Univ. J. Electric. Electron. Eng. 18, 36–38 (2018)
D. Biolek, Z. Biolek, V. Biolková, Behavioral modeling of memcapacitor. Radioengineering 20, 228–233 (2011)
D. Biolek, V. Biolková, Z. Kolka, Mutators simulating memcapacitors and meminductors, in IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems, Proceedings, APCCAS (2010), pp. 800–803
L.O. Chua, Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18, 507–519 (1971)
F. Corinto, A. Ascoli, M. Gilli, Nonlinear dynamics of memristor oscillators. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 58, 1323–1336 (2011)
E. Demir, A. Yesil, Y. Babacan, T. Karacali, Operational transconductance amplifier based electronically controllable memcapacitor and meminductor emulators. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 30, 21502224 (2021)
M. Di Ventra, Y.V. Pershin, L.O. Chua, Circuit elements with memory: memristors, memcapacitors, and meminductors. Proc. IEEE 97, 1717–1724 (2009)
M.E. Fouda, A.G. Radwan, Fractional-order memristor response under DC and periodic signals. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 34, 961–970 (2015)
S. Hamdioui, H. Aziza, G.C. Sirakoulis, Memristor based memories: technology, design and test, in Proceedings—2014 9th IEEE International Conference on Design and Technology of Integrated Systems in Nanoscale Era, DTIS 2014 (2014), pp. 1–7
Y. Ho, G.M. Huang, P. Li, Dynamical properties and design analysis for nonvolatile memristor memories. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 58, 724–736 (2011)
M. Itoh, L.O. Chua, Memristor oscillators. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 18, 3183–3206 (2008)
H. Kim, M.P. Sah, C. Yang, L.O. Chua, Memristor-based multilevel memory, in 2010 12th International Workshop on Cellular Nanoscale Networks and Their Applications, CNNA 2010 (2010), pp. 1–6
H. Kim, M.P. Sah, C. Yang, S. Cho, L.O. Chua, Memristor emulator for memristor circuit applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 59, 2422–2431 (2012)
M. Krems, Y.V. Pershin, M. Di Ventra, Ionic memcapacitive effects in nanopores. Nano Lett 10, 2674–2678 (2010)
S. Kvatinsky, A. Kolodny, U.C. Weiser, and E. G. Friedman, in Memristor-based IMPLY logic design procedure, in Proceedings—IEEE International Conference on Computer Design: VLSI in Computers and Processors (2011), pp. 142–147
C. Li, D. Belkin, Y. Li, P. Yan, M. Hu, N. Ge, H. Jiang, E. Montgomery, P. Lin, Z. Wang, W. Song, J.P. Strachan, M. Barnell, Q. Wu, R.S. Williams, J.J. Yang, Q. Xia, Efficient and self-adaptive in-situ learning in multilayer memristor neural networks. Nat. Commun. 9, 1–8 (2018)
C. Li, M. Hu, Y. Li, H. Jiang, N. Ge, E. Montgomery, J. Zhang, W. Song, N. Dávila, C.E. Graves, Z. Li, J.P. Strachan, P. Lin, Z. Wang, M. Barnell, Q. Wu, R.S. Williams, J.J. Yang, Q. Xia, Analogue signal and image processing with large memristor crossbars. Nat. Electron. 1, 52–59 (2018)
J. Martinez-Rincon, M. Di Ventra, Y.V. Pershin, Solid-state memcapacitive system with negative and diverging capacitance. Phys. Rev. B Condens Matter Mater. Phys. 81, 195430 (2010)
B. Muthuswamy, Implementing memristor based chaotic circuits. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 20, 1335–1350 (2010)
K. Orman, Temperature profile tracking control with memristor based PI controller in the heat flow system. Int. J. Mod. Res. Eng. Technol. 4, 12–15 (2019)
K. Orman, Memristor based PD controller design and application on a ball and beam control system, in Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering Technologies ICENTE (2020), pp. 143–146
K. Orman, Memristor based 2 dof PID controller design and speed control test in DC motor, in Global—Conference on Engineering Research (GLOBCER'21) (2021), pp. 754–755
K. Orman, Pavlov’s Dog: a simple circuit implementation using a volatile memristor. Electrica 20, 81–86 (2020)
K. Orman, Y. Babacan, Memory Circuit Elements and Applications (Academic Studies in Engineering Sciences, 2020), pp. 77–101
K. Orman, Y. Babacan, The implementation of logic gates using only memristor based neuristor. Informacije MIDEM 51, 113–117 (2021)
Y.V. Pershin, M. Di Ventra, Emulation of floating memcapacitors and meminductors using current conveyors. Electron. Lett. 47, 243–244 (2011)
P.K. Sharma, R.K. Ranjan, F. Khateb, M. Kumngern, Charged controlled MEM-element emulator and its application in a chaotic system. IEEE Access 8, 171397–171407 (2020)
P. Srivastava, R.K. Gupta, R.K. Sharma, R.K. Ranjan, MOS-only memristor emulator. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 39, 5848–5861 (2020)
D.B. Strukov, G.S. Snider, D.R. Stewart, R.S. Williams, The missing memristor found. Nature 453, 80–83 (2008)
J. Sun, X. Zhao, J. Fang, Y. Wang, Autonomous memristor chaotic systems of infinite chaotic attractors and circuitry realization. Nonlinear Dyn. 94, 2879–2887 (2018)
Z.G.Ç. Taşkıran, M. Sağbaş, U.E. Ayten, H. Sedef, A new universal mutator circuit for memcapacitor and meminductor Elements. AEU Int. J. Electron. C 119, 153180 (2020)
A. Thomas, Memristor-based neural networks. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 46, 093001 (2013)
Ö.F. Tozlu, F. Kaçar, Y. Babacan, Electronically controllable neuristor based logic gates and their applications. AEU Int. J. Electron. C 138, 153834 (2021)
J. Vista, A. Ranjan, Design of memcapacitor emulator using DVCCTA. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 66, 1–8 (2019)
X.Y. Wang, A.L. Fitch, H.H.C. Iu, W.G. Qi, Design of a memcapacitor emulator based on a memristor. Phys. Lett. A 376, 394–399 (2012)
H.G. Wu, Y. Ye, B.C. Bao, M. Chen, Q. Xu, Memristor initial boosting behaviors in a two-memristor-based hyperchaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fract. 121, 178–185 (2019)
A. Yesil, Y. Babacan, F. Kacar, A new DDCC based memristor emulator circuit and its applications. Microelectronics J 45, 282–287 (2014)
A. Yesil, Y. Babacan, F. Kacar, Electronically tunable memristor based on VDCC. AEU Int. J. Electron. C 107, 282–290 (2019)
A. Yesil, Y. Babacan, F. Kacar, An electronically controllable, fully floating memristor based on active elements: DO-OTA and DVCC. AEU Int. J. Electron. C 123, 153315 (2020)
A. Yesil, Y. Babacan, Electronically controllable memcapacitor circuit with experimental results. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 68, 1443–1447 (2021)
D. Yu, X. Zhao, T. Sun, H.H.C. Iu, T. Fernando, A simple floating mutator for emulating memristor, memcapacitor, and meminductor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 67, 1334–1338 (2020)
C. Zheng, D. Yu, H.H.C. Iu, T. Fernando, T. Sun, J.K. Eshraghian, H. Guo, A novel universal interface for constructing memory elements for circuit applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 66, 4793–4806 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The authors have no conflicts of interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. All authors equally participated in the implementation of circuit designs, simulations, finding results, and preparing of the manuscript. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics declarations
Accepted principles of ethical and professional conduct have been followed by the authors.
Consent to Participate
All the authors consent to participate in this research study.
Consent for Publication
All the authors consent to publish the present work.
Human and animal rights
Not applicable
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gur, M., Akar, F., Orman, K. et al. Electronically Controllable Fully Floating Memcapacitor Circuit. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 6481–6493 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02448-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-023-02448-6