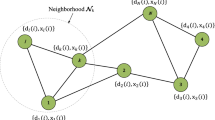
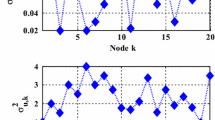
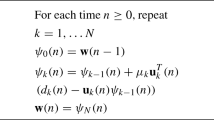Abstract
The quantum calculus provides an extra degree of freedom to search the local and global minima by inducing a q-parameter. Motivated by this fact, a quantum calculus-based noisy links incremental least mean squares (NL-qILMS) algorithm is proposed. Moreover, for the proposed NL-qILMS, we also devised various time-varying techniques for the selection of the optimal q-parameter to improve the performance. Furthermore, the closed-form solutions for the steady-state mean square deviation, excess mean square deviation and mean square error are derived. The analytical results are validated through simulation. Finally, extensive simulations have been done to evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm for various choices of optimal q-values.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Notes
For the sake of compactness, the proposed NL-qILMS algorithm with (12) is termed as qSD1-ILMS.
The proposed NL-qILMS algorithm with (13) is termed as qSD2-ILMS.
The proposed NL-qILMS algorithm with (14) is termed as qML-ILMS.
The proposed NL-qILMS algorithm with (15) is termed as qSN-ILMS.
The proposed NL-qILMS algorithm with (16) is termed as qP-ILMS.
The matrix \(\hat{\mathbf{G}}_{k}(i)\) is decoupled as \(\mu _{k}{} \mathbf{G}_{k}(i)\) for the analysis.
Here we dropped the time index for simplicity.
Note that \(R_{\mathbf {x},k}=\lambda _{k} I\), \(S_{k} = \sigma _{r,k}^{2}I\), \(\bar{G}_{k}=g_{k}I\), additionally for small step-size \(\bar{F}_{k}\) is reduced to, \(\bar{F}_{k} \approx (1 - 2 \mu _{k} \lambda g_{k})I\) and \(\hat{g}_{k}(i)=\mu _{k,\mathrm{min}}\) as \(i\rightarrow \infty \).
References
A. Ahmed, F.S. McFadden, R.K. Rayudu, q-calculus based extended kalman filter for the dynamic state estimation of a synchronous generator, in 2016 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies - Asia (ISGT-Asia) (2016), pp. 1139–1144
A. Ahmed, M. Moinuddin, U.M. Al-Saggaf, q-state space least mean family of algorithms. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0569-7
A.U. Al-Saggaf, M. Arif, U.M. Al-Saggaf, M. Moinuddin, The q-normalized least mean square algorithm, in 2016 6th International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced Systems (ICIAS) (2016), pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIAS.2016.7824098
U.M. Al-Saggaf, M. Moinuddin, M. Arif, A. Zerguine, The q-least mean squares algorithm. Signal Process. 111(C), 50–60 (2015)
U.M. Al-Saggaf, M. Moinuddin, A. Zerguine, An efficient least mean squares algorithm based on q-gradient, in 2014 48th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (2014), pp. 891–894. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACSSC.2014.7094580
M. Arif, M. Moinuddin, I. Naseem, A.U. Alsaggaf, U.M. Al-Saggaf, Diffusion quantum-least mean square algorithm with steady-state analysis. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 41, 3306–3327 (2022)
M. Arif, I. Naseem, M. Ashraf, M. Moinuddin, Design of incremental optimum error nonlinearity for distributed networks, in 2017 International Conference on Innovations in Electrical Engineering and Computational Technologies (ICIEECT) (2017), pp. 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIEECT.2017.7916525
M. Arif, I. Naseem, M. Moinuddin, State-space fractional-least mean square algorithm, in 2017 First International Conference on Latest trends in Electrical Engineering and Computing Technologies (INTELLECT) (2017), pp. 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/INTELLECT.2017.8277637
M. Arif, I. Naseem, M. Moinuddin, U.M. Al-Saggaf, Design of optimum error nonlinearity for channel estimation in the presence of class-a impulsive noise, in 2016 6th International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced Systems (ICIAS) (2016), pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIAS.2016.7824137
M. Arif, I. Naseem, M. Moinuddin, U.M. Al-Saggaf, Design of an intelligent q-lms algorithm for tracking a non-stationary channel. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43(6), 2793–2803 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2883-6
M. Arif, I. Naseem, M. Moinuddin, U.M. Al-Saggaf, Modified incremental lms with improved stability via convex combination of two adaptive filters. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 38(9), 4245–4265 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01061-w
M. Arif, I. Naseem, M. Moinuddin, A.U. Alsaggaf, U.M. Al-Saggaf, Energy-efficient ssd-lms algorithm for state-space estimation in distributed networks. Digit. Signal Process. 122, 103,362 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2021.103362
M. Arif, I. Naseem, M. Moinuddin, M.N. Iqbal, Improved optimum error nonlinearities using Cramer–Rao bound estimation. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 38(11), 5169–5186 (2019)
M. Arif, I. Naseem, M. Moinuddin, S.S. Khan, M.M. Ammar, Adaptive noise cancellation using q-LMS, in 2017 International Conference on Innovations in Electrical Engineering and Computational Technologies (ICIEECT) (2017), pp. 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIEECT.2017.7916527
M. Arif, I. Naseem, S.S.U. Qadri, M. Moinnudin, Two-dimensional optimum error nonlinearity for image denoising, in 2017 First International Conference on Latest trends in Electrical Engineering and Computing Technologies (INTELLECT) (2017), pp. 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/INTELLECT.2017.8277638
G. Azarnia, A.A. Sharifi, Steady-state analysis of distributed incremental variable fractional tap-length lms adaptive networks. Wirel. Netw. 27, 4603–4614 (2021)
M.O. Bin-Saeed, S.A. Pasha, A. Zerguine, A variable step-size incremental lms solution for low snr applications. Signal Process. 178, 107,730 (2021)
M.O. Bin Saeed, A. Zerguine, An incremental variable step-size lms algorithm for adaptive networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 67(10), 2264–2268 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSII.2019.2953199
W.H.R. Chan, M. Wildemeersch, T.Q.S. Quek, Diffusion control in multi-agent networks, in 2015 54th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) (2015), pp. 4190–4195. https://doi.org/10.1109/CDC.2015.7402872
T. Ernst, The history of q-calculus and a new-method. U.U.D.M. Report 2000:16, Department of Mathematics, Uppsala University, Sweden (2000)
F.H. Jackson, On q-functions and a certain difference operator. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 46, 253–281 (1908)
F.H. Jackson, On q-definite integrals. Q. J. Pure Appl. Math. 41, 193–203 (1910)
A. Khalili, M.A. Tinati, A. Rastegarnia, An incremental block lms algorithm for distributed adaptive estimation, in 2010 IEEE International Conference on Communication Systems (IEEE, 2010), pp. 493–496
A. Khalili, M.A. Tinati, A. Rastegarnia, Performance analysis of distributed incremental lms algorithm with noisy links. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 7(1), 756067 (2011)
A. Khalili, M.A. Tinati, A. Rastegarnia, Amplify-and-forward scheme in incremental lms adaptive network with noisy links: minimum transmission power design. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 66(3), 262–265 (2012)
J. Koekoev, A note on the q-derivative operatorx. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 176, 627–634 (1993)
M. Korki, H. Zayyani, Weighted diffusion continuous mixed p-norm algorithm for distributed estimation in non-uniform noise environment. Signal Process. 164, 225–233 (2019)
S. Liu, Y. Ma, Y. Huang, Sea clutter cancellation for passive radar sensor exploiting multi-channel adaptive filters. IEEE Sens. J. 19(3), 982–995 (2018)
C.G. Lopes, A.H. Sayed, Distributed adaptive incremental strategies: Formulation and performance analysis, in 2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing Proceedings, vol. 3 (2006), pp. III–III. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2006.1660721
C.G. Lopes, A.H. Sayed, Incremental adaptive strategies over distributed networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 55(8), 4064–4077 (2007)
C.G. Lopes, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion least-mean squares over adaptive networks: formulation and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(7), 3122–3136 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2008.917383
W. Mikhael, F. Wu, L. Kazovsky, G. Kang, L. Fransen, Adaptive filters with individual adaptation of parameters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 33(7), 677–686 (1986)
S.K. Mishra, G. Panda, M.A.T. Ansary, B. Ram, On q-newton’s method for unconstrained multiobjective optimization problems. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 63(1), 391–410 (2020)
M.G. Rabbat, R.D. Nowak, Decentralized source localization and tracking [wireless sensor networks], in 2004 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, vol. 3 (2004), p. 921. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2004.1326696
M.G. Rabbat, R.D. Nowak, Quantized incremental algorithms for distributed optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 23(4), 798–808 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSAC.2005.843546
A.H. Sayed, Adaptive Filters (Wiley-IEEE Press, Hoboken, 2008)
T. Shan, T. Kailath, Adaptive algorithms with an automatic gain control feature. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 35(1), 122–127 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1109/31.1709
T. Shan, Y. Ma, R. Tao, S. Liu, Multi-channel nlms-based sea clutter cancellation in passive bistatic radar. IEICE Electron. Express p. 11-20140,872 (2014)
P. Song, H. Zhao, Robust diffusion affine projection m-estimate algorithm for distributed estimation over network. IFAC-PapersOnLine 52(24), 290–293 (2019)
A.C. Soterroni, R.L. Galski, F.M. Ramos, The q-gradient vector for unconstrained continuous optimization problems, in Operations Research Proceedings 2010. ed. by B. Hu, K. Morasch, S. Pickl, M. Siegle (Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2011), pp. 365–370
A.C. Soterroni, R.L. Galski, F.M. Ramos, The q-gradient method for continuous global optimization, in AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1558, no. 1 (2013), pp. 2389–2393 https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4826022
N. Takahashi, I. Yamada, Link probability control for probabilistic diffusion least-mean squares over resource-constrained networks, in 2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (2010), pp. 3518–3521. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2010.5495952
L. Xiao, S. Boyd, S. Lai, A space-time diffusion scheme for peer-to-peer least-squares estimation, in 2006 5th International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (2006), pp. 168–176. https://doi.org/10.1145/1127777.1127806
L. Xiao, S. Boyd, S. Lall, A scheme for robust distributed sensor fusion based on average consensus, in IPSN 2005. Fourth International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (2005), pp. 63–70. https://doi.org/10.1109/IPSN.2005.1440896
S. Yim, H. Lee, W. Song, A proportionate diffusion lms algorithm for sparse distributed estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 62(10), 992–996 (2010)
H. Zayyani, Robust minimum disturbance diffusion lms for distributed estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 68(1), 521–525 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of the Karachi Institute of Economics and Technology, Pakistan, to make this work possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arif, M., Khan, S.S., Qadri, S.S.U. et al. Efficient Time-Varying q-Parameter Design for q-Incremental Least Mean Square Algorithm with Noisy Links. Circuits Syst Signal Process 41, 5699–5718 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02048-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02048-w