Abstract
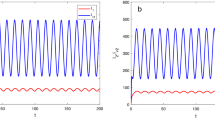
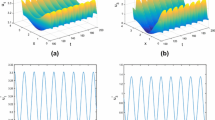
Malaria is one of the most common mosquito-borne diseases in the world. To understand the joint effects of the vector-bias, seasonality, spatial heterogeneity multi-strain and the extrinsic incubation period of the parasite on the dynamics of malaria, we formulate a time-periodic two-strain malaria reaction–diffusion model with delay and nonlocal terms. We then consider threshold conditions that determine whether malaria will spread. More specifically, the basic reproduction number \(\mathcal {R}_{i}\) for single strain-i and invasion number \(\hat{\mathcal {R}}_{i}\) for each strain-\(i~(i=1,2)\) are derived. Our results imply that if \(\max \{\mathcal {R}_{1},\mathcal {R}_{2}\}<1\), then the disease-free periodic solution is globally attractive; if \(\mathcal {R}_{i}>1>\mathcal {R}_{j}~(i,j=1,2, i\ne j)\), then competitive exclusion, where the jth strain dies out and the ith strain persists; if \(\min \{\hat{\mathcal {R}}_{1},\hat{\mathcal {R}}_{2},\mathcal {R}_1,\mathcal {R}_2\}>1\), then the disease persists. Our numerical simulations show that spatially heterogeneous infection can increase the basic reproduction number and the omission of the vector-bias effect will underestimate the infection risk of the disease.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacaër, N., Guernaoui, S.: The epidemic threshold of vector-borne diseases with seasonality. J. Math. Biol. 53(3), 421–436 (2006)
Bai, Z., Peng, R., Zhao, X.-Q.: A reaction–diffusion malaria model with seasonality and incubation period. J. Math. Biol. 77(1), 201–228 (2018)
Chamchod, F., Britton, N.F.: Analysis of a vector-bias model on malaria transmission. Bull. Math. Biol. 73(3), 639–657 (2011)
Chiyaka, C., Garira, W., Dube, S.: Effects of treatment and drug resistance on the transmission dynamics of malaria in endemic areas. Theor. Popul. Biol. 75(1), 14–29 (2009)
Chu, H., Bai, Z.: A two-strain reaction–diffusion malaria model with seasonality and vector-bias. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 74(1), 21 (2023)
Esteva, L., Gumel, A.B., De LeN, C.V.: Qualitative study of transmission dynamics of drug-resistant malaria. Math. Comput. Modell. 50(3–4), 611–630 (2009)
Feng, Z., Qiu, Z., Sang, Z., Lorenzo, C., Glasser, J.: Modeling the synergy between HSV-2 and HIV and potential impact of HSV-2 therapy. Math. Biosci. 245(2), 171–187 (2013)
Hale, J.: Asymptotic Behavior of Dissipative Systems. American Mathematical Society, Providence (1988)
Hess, P.: Periodic–Parabolic Boundary Value Problems and Positivity. Longman Scientific and Technical, Harlow (1991)
Jin, Y., Zhao, X.-Q.: Spatial dynamics of a nonlocal periodic reaction–diffusion model with stage structure. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 40(6), 2496–2516 (2009)
Kato, T.: Perturbation Theory for Linear Operators. Springer, Berlin (1976)
Kesavan, S.K., Reddy, N.P.: On the feeding strategy and the mechanics of blood sucking in insects. J. Theoret. Biol. 113(4), 781–783 (1985)
Kingsolver, J.G.: Mosquito host choice and the epidemiology of malaria. Am. Nat. 130(6), 811–827 (1987)
Lacroix, R., Mukabana, W.R., Gouagna, L.C., Koella, J.C.: Malaria infection increases attractiveness of humans to mosquitoes. PLOS Biol. 3(9), e298 (2005)
Liang, X., Zhang, L., Zhao, X.-Q.: Basic reproduction ratios for periodic abstract functional differential equations (with application to a spatial model for lyme disease). J. Dyn. Differ. Equ. 31(3), 1247–1278 (2017)
Liang, X., Zhao, X.-Q.: Asymptotic speeds of spread and traveling waves for monotone semiflows with applications. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 60(1), 1–40 (2007)
Lou, Y., Zhao, X.-Q.: A climate-based malaria transmission model with structured vector population. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 70(6), 2023–2044 (2010)
Lou, Y., Zhao, X.-Q.: A reaction–diffusion malaria model with incubation period in the vector population. J. Math. Biol. 62(4), 543–568 (2011)
Macdonald, G.: The Epidemiology and Control Of Malaria. Oxford University Press, London (1957)
Mallet, J.: The struggle for existence: how the notion of carrying capacity, K, obscures the links between demography, Darwinian evolution, and speciation. Evol. Ecol. Res. 14, 627–665 (2012)
Magal, P., Zhao, X.-Q.: Global attractors and steady states for uniformly persistent dynamical systems. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 37(1), 251–275 (2005)
Martin, R.H., Smith, H.L.: Abstract functional differential equations and reaction–diffusion systems. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 321(1), 1–44 (1990)
Metz, J.A.J., Diekmann, O.: The Dynamics of Physiologically Structured Populations. Springer, New York (1986)
Mirski, T., Bartoszcze, M., Bielawska-Drozd, A.: Impact of climate change on infectious diseases. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 21(3), 525–532 (2012)
Ross, R.: The Prevention of Malaria. John Murray, London (1911)
Ruan, S., Xiao, D., Beier, J.C.: On the delayed Ross–Macdonald model for malaria transmission. Bull. Math. Biol. 70(4), 1098–1114 (2008)
Shi, Y., Zhao, H.: Analysis of a two-strain malaria transmission model with spatial heterogeneity and vector-bias. J. Math. Biol. 82(4), 1–44 (2021)
Smith, H.L.: Monotone dynamical systems: an introduction to the theory of competitive and cooperative systems. In: Mathematical Surveys and Monographs, vol. 41. American Mathematical Society, Providence (1995)
Thieme, H.R.: Convergence results and a Poincare–Bendixson trichotomy for asymptotically autonomous differential equations. J. Math. Biol. 30(7), 755–763 (1992)
Thieme, H.R.: Spectral bound and reproduction number for infinite-dimensional population structure and time heterogeneity. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 70(1), 188–211 (2009)
Watts, D., Burke, D., Harrison, B., Whitmire, R., Nisalak, A.: Effect of temperature on the vector effciency of Aedes aegypti for dengue 2 virus. Army Med. Res. Inst. Infect. Dis. 36, 143–152 (1987)
Wang, X., Zhao, X.-Q.: A periodic vector-bias malaria model with incubation period. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 77(1), 181–201 (2017)
Wang, X., Zhao, X.-Q.: A climate-based malaria model with the use of bed nets. J. Math. Biol. 77(1), 1–25 (2018)
Wu, J.: Theory and Applications of Partial Functional Differential Equations. Springer, New York (1996)
Zhang, L., Wang, Z.C., Zhao, X.-Q.: Threshold dynamics of a time periodic reaction–diffusion epidemic model with latent period. J. Differ. Equ. 258(9), 3011–3036 (2015)
Zhao, L., Wang, Z.C., Ruan, S.: Dynamics of a time-periodic two-strain SIS epidemic model with diffusion and latent period. Nonlinear Anal. Real Word Appl. 51, 102966 (2020)
Zhao, X.-Q.: Basic reproduction ratios for periodic compartmental models with time delay. J. Dyn. Differ. Equ. 29(1), 67–82 (2017)
Zhao, X.-Q.: Dynamical Systems in Population Biology. Springer, London (2017)
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to the anonymous referee for his/her careful reading and helpful suggestions which led to an improvement of our original manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supported in part by the NSF of China (No. 12171381), the Shaanxi Fundamental Science Research Project for Mathematics and Physics (No. 22JSY029) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. QTZX23034 and QTZX23004).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, R., Wu, SL. A two-strain malaria transmission model with seasonality and incubation period. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 74, 217 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-023-02112-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-023-02112-8
Keywords
- Vector-bias malaria model
- Two-strain
- Seasonality
- Extrinsic incubation period
- Threshold dynamics
- Basic reproduction number