Abstract
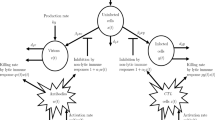
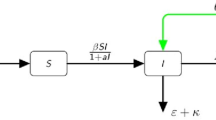
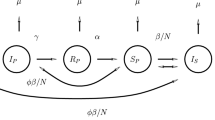
We put forward a reaction–diffusion cooperative system for the West Nile virus in a spatial heterogeneous and time almost periodic environment with free boundaries. The existence, uniqueness and regularity estimates of the global solution for this epidemic model are given. Focused on the effects of spatial heterogeneity and time almost periodicity, we introduce the principal Lyapunov exponent \(\lambda (t)\) dependent on t and get the initial infected critical size \(L^*\) which plays a vital part in analyzing the threshold dynamics and the long-time asymptotic behaviors of the solution. We build the spreading–vanishing dichotomy regimes of this model and obtain several criteria determining the spreading or vanishing. Our analysis result suggests that the solution converges to a positive time almost periodic function \(\left( U^*(x,t),V^*(x,t)\right) \) locally uniformly when the spreading occurs. We discover that the initial disease infected domain and the front expanding rate have momentous impacts on the permanence and extinction of the disease. Moreover, we give the lower and the upper bound estimates about the asymptotic spreading speeds of the double free fronts when the spreading happens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wonham, M.J., De-Camino-Beck, T., Lewis, M.A.: An epidemiological model for West Nile virus: invasion analysis and control applications. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 271(1538), 501–507 (2004)
Cruz-Pacheco, G., Esteva, L., Monta-Hirose, J.A., Vargas, C.: Modelling the dynamics of West Nile Virus. Bull. Math. Biol. 67(6), 1157–1172 (2005)
Bowman, C., Gumel, A.B., Driessche, P.v.d, Wu, J., Zhu, H.: A mathematical model for assessing control strategies against West Nile virus. Bull. Math. Biol. 67(5), 1107–1133 (2005)
Abdelrazec, A., Lenhart, S., Zhu, H.: Transmission dynamics of West Nile virus in mosquitoes and corvids and non-corvids. J. Math. Biol. 68(6), 1553–1582 (2014)
Chen, J., Huang, J., Beier, J., Cantrell, R., Cosner, C., Fuller, D., Zhang, G., Ruan, S.: Modeling and control of local outbreaks of West Nile virus in the United States. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 21(8), 2423–2449 (2016)
Lewis, M., Rencławowicz, J., Driessche, P.V.D.: Traveling waves and spread rates for a West Nile virus model. Bull. Math. Biol. 68(1), 3–23 (2006)
Maidana, N.A., Yang, H.M.: Spatial spreading of West Nile Virus described by traveling waves. J. Theor. Biol. 258(3), 403–417 (2009)
Chen, X., Friedman, A.: A free boundary problem for an elliptic–hyperbolic system: an application to tumor growth. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 35(4), 974–986 (2003)
Lin, Z.: A free boundary problem for a predator–prey model. Nonlinearity 20(8), 1883–1892 (2007)
Du, Y., Lin, Z.: Spreading–vanishing dichotomy in the diffusive logistic model with a free boundary. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 42(1), 377–405 (2010)
Wang, M.: On some free boundary problems of the prey–predator model. J. Differ. Equ. 256(10), 3365–3394 (2014)
Wang, Y., Guo, S.: A SIS reaction–diffusion model with a free boundary condition and nonhomogeneous coefficients. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. B 24(4), 1627–1652 (2019)
Liu, S., Huang, H., Wang, M.: A free boundary problem for a prey–predator model with degenerate diffusion and predator-stage structure. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. B 25(5), 1649–1670 (2020)
Lin, Z., Zhu, H.: Spatial spreading model and dynamics of West Nile virus in birds and mosquitoes with free boundary. J. Math. Biol. 75(6–7), 1381–1409 (2017)
Tarboush, A.K., Lin, Z., Zhang, M.: Spreading and vanishing in a West Nile virus model with expanding fronts. Sci. China Math. 60(5), 841–860 (2017)
Cheng, C., Zheng, Z.: Dynamics and spreading speed of a reaction–diffusion system with advection modeling West Nile virus. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 493(1), 124507 (2021)
Allen, L.J.S., Bolker, B.M., Lou, Y., Nevai, A.L.: Asymptotic profiles of the steady states for an SIS epidemic reaction–diffusion model. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 21(1), 1–20 (2008)
Zhou, P., Xiao, D.: The diffusive logistic model with a free boundary in heterogeneous environment. J. Differ. Equ. 256(6), 1927–1954 (2014)
Zhao, J., Wang, M.: A free boundary problem of a predator–prey model with higher dimension and heterogeneous environment. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 16, 250–263 (2014)
Wang, M.: The diffusive logistic equation with a free boundary and sign-changing coefficient. J. Differ. Equ. 258(4), 1252–1266 (2015)
Ge, J., Lei, C., Lin, Z.: Reproduction numbers and the expanding fronts for a diffusion–advection SIS model in heterogeneous time-periodic environment. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 33, 100–120 (2017)
Ding, W., Peng, R., Wei, L.: The diffusive logistic model with a free boundary in a heterogeneous time-periodic environment. J. Differ. Equ. 263(5), 2736–2779 (2017)
Zhang, M., Lin, Z.: A reaction–diffusion–advection model for Aedes aegypti mosquitoes in a time-periodic environment. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 46, 219–237 (2019)
Peng, R., Zhao, X.Q.: A reaction–diffusion SIS epidemic model in a time-periodic environment. Nonlinearity 25(5), 1451–1471 (2012)
Zhang, L., Wang, Z.C.: A time-periodic reaction–diffusion epidemic model with infection period. Zeitschrift Für Angewandte Mathematik Und Physik 67, 117 (2016)
Shan, C., Fan, G., Zhu, H.: Periodic phenomena and driving mechanisms in transmission of West Nile virus with maturation time. J. Dyn. Differ. Equ. 32(2), 1003–1026 (2020)
Shen, W., Yi, Y.: Convergence in almost periodic fisher and Kolmogorov models. J. Math. Biol. 37(1), 84–102 (1998)
Huang, J., Shen, W.: Speeds of spread and propagation for KPP models in time almost and space periodic media. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 8(3), 790–821 (2009)
Wang, B.G., Zhao, X.Q.: Basic reproduction ratios for almost periodic compartmental epidemic models. J. Dyn. Differ. Equ. 25(2), 535–562 (2013)
Wang, B.G., Li, W.T., Wang, Z.C.: A reaction–diffusion SIS epidemic model in an almost periodic environment. Zeitschrift Für Angewandte Mathematik Und Physik Zamp 66(6), 3085–3108 (2016)
Qiang, L., Wang, B.G., Wang, Z.C.: A reaction–diffusion epidemic model with incubation period in almost periodic environments. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 66, 1–24 (2020)
Zhao, X.Q.: Global attractivity in monotone and subhomogeneous almost periodic systems. J. Differ. Equ. 187(2), 494–509 (2003)
Wang, M.: Existence and uniqueness of solutions of free boundary problems in heterogeneous environments. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. B 24(2), 415–421 (2019)
Ladyzhenskaia, O.A., Solonnikov, V.A., Ural’tseva, N.N.: Linear and Quasi-linear Equations of Parabolic Type, vol. 23. American Mathematical Society (1968)
Wang, M.: Nonlinear Second Order Parabolic Equations, vol. 1. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2021)
Wang, M.: Sobolev Spaces. High Education Press, Beijing (2013).. ((in Chinese))
Dan, H.: Geometric Theory of Semilinear Parabolic Equations, vol. 840. Springer, Berlin (1981)
Pazy, A.: Semigroups of Linear Operators and Applications to Partial Differential Equations, vol. 44. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Shen, W., Yi, Y.: Almost Automorphic and Almost Periodic Dynamics in Skew-Product Semiflow. Memorirs of the American Mathematical Society (1998)
Hutson, V., Shen, W., Vickers, G.T.: Estimates for the principal spectrum point for certain time-dependent parabolic operators. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 129(6), 1669–1679 (2001)
Mierczyński, J., Shen, W.: Lyapunov exponents and asymptotic dynamics in random Kolmogorov models. J. Evol. Equ. 4(3), 371–390 (2004)
Li, F., Liang, X., Shen, W.: Diffusive KPP equations with free boundaries in time almost periodic environments: I. Spreading and vanishing dichotomy. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 36(6), 3317–3338 (2016)
Fink, A.M.: Almost Periodic Differential Equations. Springer, Berlin (1974)
Smith, H., Zhao, X.Q.: Robust persistence for semidynamical systems. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 47(9), 6169–6179 (2001)
Wang, Z., Nie, H., Du, Y.: Spreading speed for a West Nile virus model with free boundary. J. Math. Biol. 79(2), 1–34 (2019)
Li, F., Liang, X., Shen, W.: Diffusive KPP equations with free boundaries in time almost periodic environments: II. Spreading speeds and semi-wave solutions. J. Differ. Equ. 261(4), 2403–2445 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors are supported by the NSF of China (Nos. 11671382, 12031020), CAS Key Project of Frontier Sciences (No. QYZDJ-SSW-JSC003), the Key Lab. of Random Complex Structures and Data Sciences CAS and National Center for Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Sciences CAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, C., Zheng, Z. Analysis of a reaction–diffusion system about West Nile virus with free boundaries in the almost periodic heterogeneous environment. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 73, 84 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-022-01729-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-022-01729-5
Keywords
- Almost periodic
- Free boundary
- Principal Lyapunov exponent
- Spreading–vanishing
- Asymptotic spreading speed