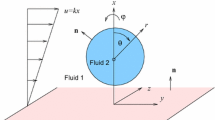
Abstract
The problem of flow past fluid spheres was first solved by Rybczynski and Hadmard where they had assumed both the flow field to be Newtonian. However, there are many practical cases where one or both of these immiscible fluids are non-Newtonian. One such case of importance is emulsions, where the non-Newtonian droplets are in the Newtonian liquid. To facilitate studies in this area, we present a systematic investigation on the motion of a Reiner–Rivlin fluid sphere(drop) contaminated with a monomolecular layer of surfactant film and dispersed in a spherical container having Newtonian fluid. The effect of surfactants is taken into account by the thermodynamic approach, which assumes a linear difference in the surface tension from the equilibrium value. The interfacial tension gradient caused by the surfactant adsorption at the drop surface generates surface forces exerted within the boundary region of the drop. The effect of the variable interfacial tension induces the Marangoni flow which causes the motion of the neighboring liquids by viscous traction and generates the Marangoni force which acts on the drop surface. The result shows that the drag force increases with the non-Newtonian cross-viscous parameter of the drop. The normalized force also increases with non-Newtonian cross-viscous parameter and when the Reiner–Rivlin viscous forces dominate the Newtonian viscous forces, which is offset in the presence of surface tension gradient forces. Further, as the surface tension gradient and non-Newtonian cross-viscous parameter of non-Newtonian fluid increases, the motion inside the drop slows down. The center of the internal circulation vortex migrates in Reiner–Rivlin fluid drop toward its center, when the Reiner–Rivlin viscous forces dominates the Newtonian viscous forces.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Einstein, A.: Eine neue bestimmung der moleküldimensionen. Annalen der Physik 324(2), 289–306 (1906)
Einstein, A.: Berichtigung zu meiner arbeit:eine neue bestimmung der moleküdimensionen. Annalen der Physik 339(3), 591–592 (1911)
Taylor, G.I.: The viscosity of a fluid containing small drops of another fluid. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Contain Papers Math. Phys. Char. 138(834), 41–48 (1932)
Reiner, M.: A mathematical theory of dilatancy. Am. J. Math. 67(3), 350–362 (1945)
Rivlin, R.S.: The hydrodynamics of non-newtonian fluids. I. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 193, 260–281 (1948)
Truesdell, C., Noll, W.: The non-linear field theories of mechanics. In: The non-linear field theories of mechanics, pp. 1–579. Springer (2004)
Häkkinen, S.: A constitutive law for sea ice and some applications. Math. Modell. 9(2), 81–90 (1987)
Caswell, B.: Non-Newtonian flow at lowest order, the role of the Reiner–Rivlin stress. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 133(1), 1–13 (2006)
Massoudi, M.: A generalization of Reiner’s mathematical model for wet sand. Mech. Res. Commun. 38(5), 378–381 (2011)
Wu, W.T., Aubry, N., Massoudi, M.: Flow of granular materials modeled as a non-linear fluid. Mech. Res. Commun. 52, 62–68 (2013)
Schowalter, W.R., Chaffey, C.E., Brenner, H.: Rheological behavior of a dilute emulsion. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 26(2), 152–160 (1968)
Shmakova, L.M.: Rheological behavior of a dilute suspension of spherical particles in a non-Newtonian liquid. J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 19(6), 776–779 (1978)
Aris, R.: Vectors, Tensors and the Basic Equations of Fluid Mechanics. Courier Corporation, Chelmsford (2012)
Rathna, S.L.: Slow motion of a non-Newtonian liquid past a sphere. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 15(4), 427–434 (1962)
Foster, R.D., Slattery, J.C.: Creeping flow past a sphere of a Reiner–Rivlin fluid. Appl. Sci. Res. Sect. A 12(3), 213–222 (1963)
Ramkissoon, H.: Stokes flow past a slightly deformed fluid sphere. Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Physik (ZAMP) 37(6), 859–866 (1986)
Ramkissoon, H.: Stokes flow past a non-Newtonian fluid spheroid. ZAMM J. Appl. Math. Mech. 78(1), 61–66 (1998)
Ramkissoon, H.: Polar flow past a Reiner–Rivlin liquid sphere. J. Math. Sci. 10(2), 63–68 (1999)
Jaiswal, B.R., Gupta, B.R.: Drag on Reiner–Rivlin liquid sphere placed in a micropolar fluid with non-zero boundary condition for microrotations. Int. J. Appl. Math. Mech. 10(7), 90–103 (2014)
Ramkissoon, H., Rahaman, K.: Non-Newtonian fluid sphere in a spherical container. Acta Mech. 149(1–4), 239–245 (2001)
Jaiswal, B.R., Gupta, B.R.: Brinkman flow of a viscous fluid past a Reiner–Rivlin liquid sphere immersed in a saturated porous medium. Trans. Porous Media 107(3), 907–925 (2015)
Jaiswal, B.R., Gupta, B.R.: Cell models for viscous flow past a swarm of Reiner–Rivlin liquid spherical drops. Meccanica 52(1–2), 69–89 (2017)
Sahoo, B., Van Gorder, R.A., Andersson, H.I.: Steady revolving flow and heat transfer of a non-Newtonian Reiner–Rivlin fluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Trans. 39(3), 336–342 (2012)
Sahoo, B., Poncet, S., Labropulu, F.: Suction/injection effects on the swirling flow of a reiner-rivlin fluid near a rough surface. J. Fluids 2015, (2015)
Selvi, R., Shukla, P., Filippov, A.N.: Flow around a liquid sphere filled with a non-Newtonian liquid and placed into a porous medium. Colloid J. 82(2), 152–160 (2020)
Attia, H.A.: Rotating disk flow and heat transfer through a porous medium of a non-Newtonian fluid with suction and injection. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 13(8), 1571–1580 (2008)
Motsa, S., Makukula, Z.: On spectral relaxation method approach for steady von kármán flow of a Reiner–Rivlin fluid with joule heating, viscous dissipation and suction/injection. Open Phys. 11(3), 363–374 (2013)
Kawase, Y., Ulbrecht, J.J.: Newtonian fluid sphere with rigid or mobile interface in a shear-thinning liquid: drag and mass transfer. Chem. Eng. Commun. 8(4–6), 213–231 (1981)
Kawase, Y., Ulbrecht, J.J.: The effect of surfactant on terminal velocity of and mass transfer from a fluid sphere in a non-Newtonian fluid. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 60(1), 87–93 (1982)
Quintana, G.C., Cheh, H.Y., Maldarelli, C.M.: The effect of viscoelasticity on the translation of a surfactant covered Newtonian drop. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 45(1), 81–103 (1992)
Rodrigue, D., De Kee, D., Fong, C.F.: Bubble drag in contaminated non-Newtonian solutions. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 75(4), 794–796 (1997)
Rodrigue, D., De Kee, D., Fong, CFCM.: The slow motion of a single gas bubble in a non-newtonian fluid containing surfactants. J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics 86(1), 211–227 (1999)
Karamanev, D.G.: Rise of gas bubbles in quiescent liquids. AICHE J. 40(8), 1418–1421 (1994)
Rodrigue, D.: A simple correlation for gas bubbles rising in power-law fluids. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 80(2), 289–292 (2002)
Dziubiński, M., Orczykowska, M., Budzyński, P.: Comments on bubble rising velocity in non-Newtonian liquids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 58(11), 2441–2443 (2003)
Karamanev, D., Dewsbury, K., Margaritis, A.: Comments on the free rise of gas bubbles in non-Newtonian liquids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 60(16), 4655–4657 (2005)
Kulkarni, A.A., Joshi, J.B.: Bubble formation and bubble rise velocity in gas- liquid systems: a review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 44(16), 5873–5931 (2005)
Chhabra, R.P.: Bubbles, Drops: and Particles in Non-Newtonian Fluids. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2006)
Kishore, N., Chhabra, R.P., Eswaran, V.: Bubble swarms in power-law liquids at moderate Reynolds numbers: drag and mass transfer. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 86(1), 39–53 (2008)
Dhole, S.D., Chhabra, R.P., Eswaran, V.: Drag of a spherical bubble rising in power law fluids at intermediate Reynolds numbers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 46(3), 939–946 (2007)
Dhole, S.D., Chhabra, R.P., Eswaran, V.: Mass transfer from a spherical bubble rising in power-law fluids at intermediate Reynolds numbers. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Trans. 34(8), 971–978 (2007)
Radl, S., Khinast, J.G.: Prediction of mass transfer coefficients in non-Newtonian fermentation media using first-principles methods. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 97(5), 1329–1334 (2007)
Radl, S., Tryggvason, G., Khinast, J.G.: Flow and mass transfer of fully resolved bubbles in non-Newtonian fluids. AICHE J. 53(7), 1861–1878 (2007)
Ramkissoon, H.: Slow flow of a non-Newtonian liquid past a fluid sphere. Acta Mech. 78(1), 73–80 (1989)
Abramowitz, M., Stegun, I.A.: Handbook of Mathematical Functions (1964)
Happel, J., Brenner, H.: Low Reynolds Number Hydrodynamics: With Special Applications to Particulate Media, vol. 1. Springer, Berlin (1983)
Scriven, L.E.: Dynamics of a fluid interface equation of motion for Newtonian surface fluids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 12(2), 98–108 (1960)
Edwards, D.A., Brenner, H., Wasan, D.T.: Interfacial Transport Processes and Rheology. Bufferworth-Heinemann, Boston (1991)
Acknowledgements
The first author would like to thank Department of Science and Technology, India for its financial support under WOS-A scheme (SR/WOS-A/PM-29/2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raturi, S., Kumar, B.V.R. Effect of insoluble surfactants on the motion of Reiner–Rivlin fluid sphere in a spherical container with Newtonian fluid. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 72, 172 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-021-01600-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-021-01600-z