Abstract
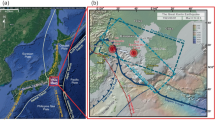
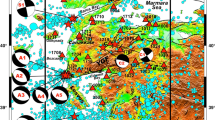
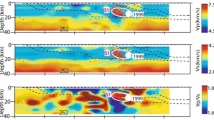
The 2004 Mid Niigata Prefecture earthquake (M JMA 6.8) and its aftershock sequences generated complicated, i.e., several conjugate fault planes in their source region. In order to understand the generating process of these earthquakes, we estimated a 3-D distribution of relative scattering coefficients in the source region. The large slip area during the main shock rupture seems to be bounded by strong heterogeneous zones with larger scattering coefficients. Hypocenters of the main shock and major large aftershocks with M 5-6 classes tend to be located close to stronger scattering areas. We found that one of these strong heterogeneities already existed before the occurrence of the M 5.9 aftershock on November 8. We suppose that heterogeneous structures in the source region of this earthquake sequence affected the initiation and growth of ruptures of the main shock and major large aftershocks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishigami, K. Crustal Heterogeneity in the Source Region of the 2004 Mid Niigata Prefecture Earthquake: Inversion Analysis of Coda Envelopes. Pure appl. geophys. 163, 601–616 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-005-0024-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-005-0024-8