Abstract
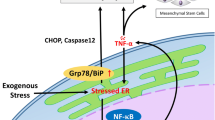
Severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) is a common critical disease of the digestive system, with high mortality and a lack of effective prevention and treatment measures. Despite mesenchymal stromal cell transplantation having the potential to treat SAP, its clinical application prospect is limited, and the mechanism is unclear. Here, we reveal the therapeutic role of exosomes from TNF-α-preconditioned human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells (HUCMSCs) in attenuating SAP and show that it is partly dependent on exosomal metabolites. Bioactive metabolomics analysis showed that 48 metabolites be significantly differentially expressed between the two groups (Exo-Ctrl group versus Exo-TNF-α group). Then, the further functional experiments indicated that 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol could be a key molecule mediating the therapeutic effect of TNF-α-preconditioned HUCMSCs. The animal experiments showed that 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol reduced inflammation and oxidative stress in the pancreatic tissue and inhibited acinar cell autophagy in a rat model of SAP. Mechanistically, we revealed that 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol activated the mTOR pathway to inhibit acinar cell autophagy and alleviate SAP. In summary, our study demonstrated that exosomes from TNF-α-preconditioned HUMSCs inhibit the autophagy of acinar cells of SAP by shuttling 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol and inhibiting the mTOR pathway. This study revealed the vital role and therapeutic potential of metabolite-derived exosomes in SAP, providing a new promising method to prevent and therapy SAP.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- SAP:
-
Severe acute pancreatitis
- AP:
-
Pancreatitis
- HUCMSCs:
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells
- MDT:
-
Multidisciplinary team
- MSCs:
-
Mesenchymal stromal cells
- EVs:
-
Extracellular vesicles
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- NTA:
-
Nanoparticle tracking analysis
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
References
Petrov MS, Yadav D (2019) Global epidemiology and holistic prevention of pancreatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:175–184
Xiao AY, Tan ML, Wu LM, Asrani VM, Windsor JA, Yadav D, Petrov MS (2016) Global incidence and mortality of pancreatic diseases: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of population-based cohort studies. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 1:45–55
Leppaniemi A, Tolonen M, Tarasconi A, Segovia-Lohse H, Gamberini E, Kirkpatrick AW, Ball CG, Parry N, Sartelli M, Wolbrink D, van Goor H, Baiocchi G, Ansaloni L, Biffl W, Coccolini F, Di Saverio S, Kluger Y, Moore E, Catena F (2019) 2019 WSES guidelines for the management of severe acute pancreatitis. World J Emerg Surg 14:27
Boxhoorn L, Voermans RP, Bouwense SA, Bruno MJ, Verdonk RC, Boermeester MA, van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG (2020) Acute pancreatitis. Lancet 396:726–734
Baron TH, DiMaio CJ, Wang AY, Morgan KA (2020) American Gastroenterological Association clinical practice update: management of pancreatic necrosis. Gastroenterology 158(67–75):e1
Galipeau J, Sensebe L (2018) Mesenchymal stromal cells: clinical challenges and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Stem Cell 22:824–833
Viswanathan S, Shi Y, Galipeau J, Krampera M, Leblanc K, Martin I, Nolta J, Phinney DG, Sensebe L (2019) Mesenchymal stem versus stromal cells: International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy (ISCT(R)) Mesenchymal Stromal Cell committee position statement on nomenclature. Cytotherapy 21:1019–1024
Jung KH, Song SU, Yi T, Jeon MS, Hong SW, Zheng HM, Lee HS, Choi MJ, Lee DH, Hong SS (2011) Human bone marrow-derived clonal mesenchymal stem cells inhibit inflammation and reduce acute pancreatitis in rats. Gastroenterology 140:998
Ma Z, Zhou J, Yang T, Xie W, Song G, Song Z, Chen J (2021) Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for pancreatitis: progress and challenges. Med Res Rev 41:2474–2488
Keshtkar S, Azarpira N, Ghahremani MH (2018) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: novel frontiers in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther 9:63
Ha DH, Kim HK, Lee J, Kwon HH, Park GH, Yang SH, Jung JY, Choi H, Lee JH, Sung S, Yi YW, Cho BS (2020) Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomes for immunomodulatory therapeutics and skin regeneration. Cells 9:1157
Mendt M, Rezvani K, Shpall E (2019) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for clinical use. Bone Marrow Transpl 54:789–792
Liang YC, Wu YP, Li XD, Chen SH, Ye XJ, Xue XY, Xu N (2019) TNF-alpha-induced exosomal miR-146a mediates mesenchymal stem cell-dependent suppression of urethral stricture. J Cell Physiol 234:23243–23255
Ma H, Zhang S, Xu Y, Zhang R, Zhang X (2018) Analysis of differentially expressed microRNA of TNF-alpha-stimulated mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes from their culture supernatant. Arch Med Sci 14:1102–1111
Ti D, Hao H, Tong C, Liu J, Dong L, Zheng J, Zhao Y, Liu H, Fu X, Han W (2015) LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells modify macrophage polarization for resolution of chronic inflammation via exosome-shuttled let-7b. J Transl Med 13:308
Su W, Wan Q, Huang J, Han L, Chen X, Chen G, Olsen N, Zheng SG, Liang D (2015) Culture medium from TNF-alpha-stimulated mesenchymal stem cells attenuates allergic conjunctivitis through multiple antiallergic mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol 136(423–32):e8
Zhang S, Jiang L, Hu H, Wang H, Wang X, Jiang J, Ma Y, Yang J, Hou Y, Xie D, Zhang Q (2020) Pretreatment of exosomes derived from hUCMSCs with TNF-alpha ameliorates acute liver failure by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 in macrophage. Life Sci 246:117401
Yin G, Hu G, Wan R, Yu G, Cang X, Xiong J, Ni J, Hu Y, Xing M, Fan Y, Xiao W, Qiu L, Tang M, Zhao Y, Wang S, Wang X (2016) Role of microvesicles from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 45:1282–1293
Wang N, Ma J, Ren Y, Xiang S, Jia R (2019) Secreted klotho from exosomes alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in acute pancreatitis. Am J Transl Res 11:3375–3383
Zhang W, Wang Y, Kong J, Dong M, Duan H, Chen S (2017) Therapeutic efficacy of neural stem cells originating from umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in diabetic retinopathy. Sci Rep 7:408
Wang J, Jia H, Zhang B, Yin L, Mao F, Yu J, Ji C, Xu X, Yan Y, Xu W, Qian H (2018) HucMSC exosome-transported 14-3-3zeta prevents the injury of cisplatin to HK-2 cells by inducing autophagy in vitro. Cytotherapy 20:29–44
Harrell CR, Jovicic N, Djonov V, Arsenijevic N, Volarevic V (2019) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes and other extracellular vesicles as new remedies in the therapy of inflammatory diseases. Cells 8:1605
Piazza I, Kochanowski K, Cappelletti V, Fuhrer T, Noor E, Sauer U, Picotti P (2018) A map of protein-metabolite interactions reveals principles of chemical communication. Cell 172(358–372):e23
Husted AS, Trauelsen M, Rudenko O, Hjorth SA, Schwartz TW (2017) GPCR-mediated signaling of metabolites. Cell Metab 25:777–796
Cheng J, Li W, Kang B, Zhou Y, Song J, Dan S, Yang Y, Zhang X, Li J, Yin S, Cao H, Yao H, Zhu C, Yi W, Zhao Q, Xu X, Zheng M, Zheng S, Li L, Shen B, Wang YJ (2015) Tryptophan derivatives regulate the transcription of Oct4 in stem-like cancer cells. Nat Commun 6:7209
Matsumura T, Uryu O, Matsuhisa F, Tajiri K, Matsumoto H, Hayakawa Y (2020) N-acetyl-l-tyrosine is an intrinsic triggering factor of mitohormesis in stressed animals. EMBO Rep 21:e49211
Hua J, He ZG, Qian DH, Lin SP, Gong J, Meng HB, Yang TS, Sun W, Xu B, Zhou B, Song ZS (2014) Angiopoietin-1 gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis and reduce acute pancreatitis in rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:3580–3595
Thery C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, Antoniou A, Arab T, Archer F, Atkin-Smith GK, Ayre DC, Bach JM, Bachurski D, Baharvand H, Balaj L, Baldacchino S, Bauer NN, Baxter AA, Bebawy M, Beckham CB, Zavec A, Benmoussa A, Berardi AC, Bergese P, Bielska E, Blenkiron C, Bobis-Wozowicz S, Boilard E, Boireau W, Bongiovanni A, Borras FE, Bosch S, Boulanger CM, Breakefield X, Breglio AM, Brennan MA, Brigstock DR, Brisson A, Broekman ML, Bromberg JF, Bryl-Gorecka P, Buch S, Buck AH, Burger D, Busatto S, Buschmann D, Bussolati B, Buzas EI, Byrd JB, Camussi G, Carter DR, Caruso S, Chamley LW, Chang YT, Chen C, Chen S, Cheng L, Chin AR, Clayton A, Clerici SP, Cocks A, Cocucci E, Coffey RJ, Cordeiro-da-Silva A, Couch Y, Coumans FA, Coyle B, Crescitelli R, Criado MF, D’Souza-Schorey C, Das S, de Datta Chaudhuri A, Candia PD, De Santana EF, Wever OD, Portillo HA, Demaret T, Deville S, Devitt A, Dhondt BD, Vizio D, Dieterich LC, Dolo VD, Rubio AP, Dominici M, Dourado MR, Driedonks TA, Duarte FV, Duncan HM, Eichenberger RM, Ekstrom KE, Andaloussi S, Elie-Caille C, Erdbrugger U, Falcon-Perez JM, Fatima F, Fish JE, Flores-Bellver M, Forsonits A-B et al (2018) Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicl 7:1535750
Ma Z, Song G, Zhao D, Liu D, Liu X, Dai Y, He Z, Qian D, Gong J, Meng H, Zhou BO, Yang T, Song Z (2018) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate severe acute pancreatitis in rats via hemeoxygenase-1-mediated anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Cytotherapy 21(2):162–174
Yang HH, Jiang HL, Tao JH, Zhang CY, Xiong JB, Yang JT, Liu YB, Zhong WJ, Guan XX, Duan JX, Zhang YF, Liu SK, Jiang JX, Zhou Y, Guan CX (2022) Mitochondrial citrate accumulation drives alveolar epithelial cell necroptosis in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Exp Mol Med 54(11):2077–2091
Song G, Liu D, Geng X, Ma Z, Wang Y, Xie W, Qian D, Meng H, Zhou B, Song Z (2019) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate severe acute pancreatitis-induced multiple-organ injury in rats via suppression of autophagy. Exp Cell Res 385:111674
Deleyto-Seldas N, Efeyan A (2021) The mTOR-autophagy axis and the control of metabolism. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:655731
Hines OJ, Pandol SJ (2019) Management of severe acute pancreatitis. BMJ 367:l6227
Harrell CR, Jankovic MG, Fellabaum C, Volarevic A, Djonov V, Arsenijevic A, Volarevic V (2019) Molecular mechanisms responsible for anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived factors. Adv Exp Med Biol 1084:187–206
Bagno L, Hatzistergos KE, Balkan W, Hare JM (2018) Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for cardiovascular disease: progress and challenges. Mol Ther 26:1610–1623
Vizoso FJ, Eiro N, Cid S, Schneider J, Perez-Fernandez R (2017) Mesenchymal stem cell secretome: toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. Int J Mol Sci 18:1852
Wu P, Zhang B, Shi H, Qian H, Xu W (2018) MSC-exosome: a novel cell-free therapy for cutaneous regeneration. Cytotherapy 20:291–301
Liew LC, Katsuda T, Gailhouste L, Nakagama H, Ochiya T (2017) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: a glimmer of hope in treating Alzheimer’s disease. Int Immunol 29:11–19
Borger V, Bremer M, Ferrer-Tur R, Gockeln L, Stambouli O, Becic A, Giebel B (2017) Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles and their potential as novel immunomodulatory therapeutic agents. Int J Mol Sci 18:1450
Liu GY, Liu Y, Lu Y, Qin YR, Di GH, Lei YH, Liu HX, Li YQ, Wu C, Hu XW, Duan HF (2016) Short-term memory of danger signals or environmental stimuli in mesenchymal stem cells: implications for therapeutic potential. Cell Mol Immunol 13:369–378
Mead B, Chamling X, Zack DJ, Ahmed Z, Tomarev S (2020) TNFalpha-mediated priming of mesenchymal stem cells enhances their neuroprotective effect on retinal ganglion cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 61:6
Yu Z, Wen Y, Jiang N, Li Z, Guan J, Zhang Y, Deng C, Zhao L, Zheng SG, Zhu Y, Su W, Zhuo Y (2022) TNF-alpha stimulation enhances the neuroprotective effects of gingival MSCs derived exosomes in retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury via the MEG3/miR-21a-5p axis. Biomaterials 284:121484
Li Q, Li J, Sun L, Sun Y, Zhao F, Liu P, Peng X, Xuan X, Li Y, Wang P, Tan C, Du Y (2021) Exosomes derived from LPS-stimulated human thymic mesenchymal stromal cells enhance inflammation via thrombospondin-1. Biosci Rep 41:BSR20203573
Josephs SF, Ichim TE, Prince SM, Kesari S, Marincola FM, Escobedo AR, Jafri A (2018) Unleashing endogenous TNF-alpha as a cancer immunotherapeutic. J Transl Med 16:242
Maksoud S, El Hokayem J (2023) The cytokine/chemokine response in Leishmania/HIV infection and co-infection. Heliyon 9:e15055
Heldring N, Mager I, Wood MJ, Le Blanc K, Andaloussi SE (2015) Therapeutic potential of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles. Hum Gene Ther 26:506–517
Wang X, Morelli MB, Matarese A, Sardu C, Santulli G (2020) Cardiomyocyte-derived exosomal microRNA-92a mediates post-ischemic myofibroblast activation both in vitro and ex vivo. ESC Heart Fail 7:284–288
Morelli MB, Shu J, Sardu C, Matarese A, Santulli G (2019) Cardiosomal microRNAs are essential in post-infarction myofibroblast phenoconversion. Int J Mol Sci 21:201
Sukma Dewi I, Celik S, Karlsson A, Hollander Z, Lam K, McManus JW, Tebbutt S, Ng R, Keown P, McMaster R, McManus B, Ohman J, Gidlof O (2017) Exosomal miR-142-3p is increased during cardiac allograft rejection and augments vascular permeability through down-regulation of endothelial RAB11FIP2 expression. Cardiovasc Res 113:440–452
Zheng B, Yin WN, Suzuki T, Zhang XH, Zhang Y, Song LL, Jin LS, Zhan H, Zhang H, Li JS, Wen JK (2017) Exosome-mediated miR-155 transfer from smooth muscle cells to endothelial cells induces endothelial injury and promotes atherosclerosis. Mol Ther 25:1279–1294
Mills J, Capece M, Cocucci E, Tessari A, Palmieri D (2019) Cancer-derived extracellular vesicle-associated MicroRNAs in intercellular communication: one cell’s trash is another cell’s treasure. Int J Mol Sci 20:6109
Chuang HY, Su YK, Liu HW, Chen CH, Chiu SC, Cho DY, Lin SZ, Chen YS, Lin CM (2019) Preclinical evidence of STAT3 inhibitor pacritinib overcoming temozolomide resistance via downregulating miR-21-enriched exosomes from M2 glioblastoma-associated macrophages. J Clin Med 8:959
Santos JC, Lima NDS, Sarian LO, Matheu A, Ribeiro ML, Derchain SFM (2018) Exosome-mediated breast cancer chemoresistance via miR-155 transfer. Sci Rep 8:829
Yu S, Li Y, Liao Z, Wang Z, Wang Z, Li Y, Qian L, Zhao J, Zong H, Kang B, Zou WB, Chen K, He X, Meng Z, Chen Z, Huang S, Wang P (2020) Plasma extracellular vesicle long RNA profiling identifies a diagnostic signature for the detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gut 69:540–550
Gambardella J, Coppola A, Izzo R, Fiorentino G, Trimarco B, Santulli G (2021) Role of endothelial miR-24 in COVID-19 cerebrovascular events. Crit Care 25:306
Hertog MG, Feskens EJ, Hollman PC, Katan MB, Kromhout D (1993) Dietary antioxidant flavonoids and risk of coronary heart disease: the Zutphen Elderly Study. Lancet 342:1007–1011
Arando A, Delgado JV, Bermudez-Oria A, Leon JM, Fernandez-Prior A, Nogales S, Perez-Marin CC (2020) Effect of olive-derived antioxidants (3,4-dihydroxyphenylethanol and 3,4 dihydroxyphenylglycol) on sperm motility and fertility in liquid ram sperm stored at 15 degrees C or 5 degrees C. Reprod Domest Anim 55:325–332
de Roos B, Zhang X, Rodriguez Gutierrez G, Wood S, Rucklidge GJ, Reid MD, Duncan GJ, Cantlay LL, Duthie GG, O’Kennedy N (2011) Anti-platelet effects of olive oil extract: in vitro functional and proteomic studies. Eur J Nutr 50:553–562
Bermudez-Oria A, Rodriguez-Gutierrez G, Rodriguez-Juan E, Gonzalez-Benjumea A, Fernandez-Bolanos J (2018) Molecular interactions between 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol and pectin and antioxidant capacity of this complex in vitro. Carbohydr Polym 197:260–268
Hashimoto T, Ibi M, Matsuno K, Nakashima S, Tanigawa T, Yoshikawa T, Yabe-Nishimura C (2004) An endogenous metabolite of dopamine, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethanol, acts as a unique cytoprotective agent against oxidative stress-induced injury. Free Radic Biol Med 36:555–564
Fernandez-Prior A, Bermudez-Oria A, Millan-Linares MDC, Fernandez-Bolanos J, Espejo-Calvo JA, Rodriguez-Gutierrez G (2021) Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity of hydroxytyrosol and 3,4-dihydroxyphenyglycol purified from table olive effluents. Foods 10:227
Rodriguez-Perez MD, Perez de Algaba I, Martin-Aurioles E, Arrebola MM, Ortega-Hombrados L, Verdugo C, Fernandez-Prior MA, Bermudez-Oria A, De La Cruz JP, Gonzalez-Correa JA (2022) Neuroprotective effect of 3’,4’-dihydroxyphenylglycol in type-1-like diabetic rats-influence of the hydroxytyrosol/3’,4’-dihydroxyphenylglycol ratio. Nutrients 14:1146
Levine B, Kroemer G (2008) Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell 132:27–42
Gukovskaya AS, Gukovsky I, Algul H, Habtezion A (2017) Autophagy, inflammation, and immune dysfunction in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 153:1212–1226
Gukovskaya AS, Gukovsky I (2012) Autophagy and pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 303:G993–G1003
Feng D, Park O, Radaeva S, Wang H, Yin S, Kong X, Zheng M, Zakhari S, Kolls JK, Gao B (2012) Interleukin-22 ameliorates cerulein-induced pancreatitis in mice by inhibiting the autophagic pathway. Int J Biol Sci 8:249–257
Hashimoto D, Ohmuraya M, Hirota M, Yamamoto A, Suyama K, Ida S, Okumura Y, Takahashi E, Kido H, Araki K, Baba H, Mizushima N, Yamamura K (2008) Involvement of autophagy in trypsinogen activation within the pancreatic acinar cells. J Cell Biol 181:1065–1072
Kong L, Deng J, Zhou X, Cai B, Zhang B, Chen X, Chen Z, Wang W (2021) Sitagliptin activates the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 signalling pathway to alleviate oxidative stress and excessive autophagy in severe acute pancreatitis-related acute lung injury. Cell Death Dis 12:928
Zhang X, Chu J, Sun H, Zhao D, Ma B, Xue D, Zhang W, Li Z (2020) MiR-155 aggravates impaired autophagy of pancreatic acinar cells through targeting Rictor. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 52:192–199
Yang H, Ma S, Guo Y, Cui D, Yao J (2019) Bidirectional effects of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on severe acute pancreatitis in a rat model. Dose Response 17:1559325819825905
Saxton RA, Sabatini DM (2017) mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell 168:960–976
Mossmann D, Park S, Hall MN (2018) mTOR signalling and cellular metabolism are mutual determinants in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 18:744–757
Xue R, Yang J, Wu J, Meng Q, Hao J (2017) Coenzyme Q10 inhibits the activation of pancreatic stellate cells through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Oncotarget 8:92300–92311
Cui LH, Li CX, Zhuo YZ, Yang L, Cui NQ, Zhang SK (2019) Saikosaponin d ameliorates pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting autophagy of pancreatic stellate cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Chem Biol Interact 300:18–26
Liu MW, Wei R, Su MX, Li H, Fang TW, Zhang W (2018) Effects of Panax notoginseng saponins on severe acute pancreatitis through the regulation of mTOR/Akt and caspase-3 signaling pathway by upregulating miR-181b expression in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 18:51
Song G, Zhou J, Song R, Liu D, Yu W, Xie W, Ma Z, Gong J, Meng H, Yang T, Song Z (2020) Long noncoding RNA H19 regulates the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in rats with severe acute pancreatitis by sponging miR-138-5p and miR-141-3p. Stem Cell Res Ther 11:420
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Xingyun Wang from Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine for his support and guidance on Metabonomic analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82200717 and 81670582).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. ZM, WX, TL, ZH, and JH performed the experiments and participated in drafting the manuscript. XY, JZ, WW, TY, and ZS performed conception design, data collection, and analysis. SS and JX performed study design, data interpretation, and supervised the review. All authors have read and approved the article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The animal study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine (SHDSYY-2022-2330).
Consent for publication
All authors have read and approved of its submission to this journal.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Z., Xie, W., Luo, T. et al. Exosomes from TNF-α preconditioned human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells inhibit the autophagy of acinar cells of severe acute pancreatitis via shuttling bioactive metabolites. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 80, 257 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-023-04861-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-023-04861-1