Abstract
Retrotransposons are genetic elements present across all eukaryotic genomes. While their role in evolution is considered as a potentially beneficial natural source of genetic variation, their activity is classically considered detrimental due to their potentially harmful effects on genome stability. However, studies are increasingly shedding light on the regulatory function and beneficial role of somatic retroelement reactivation in non-pathological contexts. Here, we review recent findings unveiling the regulatory potential of retrotransposons, including their role in noncoding RNA transcription, as modulators of mammalian transcriptional and epigenome landscapes. We also discuss technical challenges in deciphering the multifaceted activity of retrotransposable elements, highlighting an unforeseen central role of this neglected portion of the genome both in early development and in adult life.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Retrotransposons, which account for more than 40% of the human and mouse genomes, propagate themselves through transcription and reverse-transcription machinery based on a "copy-and-paste" mechanism [1, 2]. This class of transposable elements (TE) is divided into different orders [3]. LTR (Long Terminal Repeats) retrotransposons comprise about 8% and 10% of the human and mouse genomes, respectively [4, 5]. LTRs are autonomous elements only active in mice and other species [6], not humans [7]. A typical full-length LTR has LTRs at both ends and a central region carrying three retroviral open reading frames (ORFs): gag, pol, and truncated/mutated Δenv. Mouse and human LTRs can be further classified into several super families that include endogenous retroviruses (ERV) [3].
Among non-LTR retrotransposons, which are more abundant (17–20%) than LTRs in both human and mouse genomes [8], long interspersed nuclear elements (LINEs) are the major order. These autonomous transposable elements contain two ORFs: ORF1, and ORF2. ORF1 and ORF2 are both required for retrotransposition. ORF1 encodes a ~ 40-kDa protein with nucleic acid-binding and chaperone activity. ORF2 encodes a ~ 150-kDa protein with endonuclease and reverse-transcriptase activity [9,10,11]. A complete retrotransposition event initiates with the transcription of a full-length LINE-1 RNA. The L1 transcript is then exported to the cytoplasm and translated into ORF1p and ORF2p. The binding of the two proteins to the L1 RNA produces a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex, which is imported back into the nucleus. Here, ORF2p uses a free 3′–OH produced through its endonuclease activity on the genomic DNA strand as a primer to reverse transcribe L1 RNA. Then, L1 RNA is removed from the intermediate DNA:RNA hybrid, and a second DNA strand is synthesized by ORF2 to generate a novel L1 insertion. This molecular process is known as target-primed reverse transcription (TPRT) [12]. ORF0, characterized in humans and chimps, comprises 5′ outbound transcripts encoding potentially intriguing peptides involved in L1 mobility, although their function is unknown [13].
Of note, although the human and mouse genomes contain a high number of L1 copies, accumulating evidence indicates that only around 100 copies and 3000 copies, respectively, are capable of retrotransposition [14,15,16]. Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) are another order of retrotransposons. As SINE elements utilize L1-encoded machinery to complete their propagation, they are usually called non‐autonomous retrotransposons. In humans, active SINEs include Alu and SINE‐R‐VNTR‐Alu (SVA) retrotransposons [17,18,19], active SINEs in mice contain the 7SL‐derived B1 elements and the tRNA‐derived B2 elements [20]. While LTRs and LINEs are transcribed by RNA polymerase II [4, 21], transcription of SINEs depend on polymerase III [22].
Retrotransposons may be a source of mutations leading to genomic instability and devastating consequences for the host [23]. Therefore, host genomes have evolved several mechanisms to restrict retrotransposition. Interferon-stimulated factors restrain the retrotransposon pre-integration step through post-translational repression [24]. Hosts also rely on several transcriptional repression strategies: locus-specific deposition of repressive chromatin marks [25], like DNA methylation [26, 27] and histone H3K9 trimethylation [28, 29], small RNAs [30, 31], motif-specific protein repressors like KRAB-ZFP/KAP1 module [32,33,34], which have been extensively discussed elsewhere [35]. Of note, the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex is required for epigenetic repression of young LINE-1 elements [36,37,38]. However, in certain conditions, retrotransposons escape from the multiple layers of host surveillance. This escape may result in new insertion events disrupting normal gene function with dramatic consequences and cytotoxic accumulation of TE intermediates. Deregulated TE activity has been linked to cancer [39], neurological disorders [40], male sterility [41] or fetal oocyte attrition (FOA) [42]. However, TE-induced pathologies are not only caused by retrotransposition, but may be triggered by chimeric transcripts [43], ERV-derived enhancers [44] and ERV-encoded proteins accumulation [45], or a TE-derived cDNA-induced interferon response [46, 47]. The latter plays an important role in defense mechanisms but also in chronic inflammation associated with neurodegenerative pathologies, which were reviewed extensively elsewhere [48, 49].
Retrotransposons as cis-regulatory elements
Several decades ago, Britten and Davidson proposed the "gene battery" theory in which repetitive sequences can be used as a pool to deposit regulatory sequences in specific genomic positions to bring multiple genes under the same regulatory network [50, 51]. By now, the non-random distribution of repetitive elements has been demonstrated extensively and we know that TEs can barcode genes with distinct functions, dictating the time and level of their expression during development by providing regulatory sequences and/or sequestering their associated genes into distinct nuclear domains [52]. It is now becoming clear that retrotransposon integration sites can spread specific functions in a selective evolutionary manner [53, 54]. Indeed, several lines of evidence demonstrate that retroelements can modulate the expression of proximal or distal target genes by acting as a cis-regulatory element [44, 55], as cryptic splice sites, or as polyadenylation sites [56,57,58,59,60].
Among LTRs co-opted by host genomes, e.g., MT-C [61] and the primate-specific MLT2B3 LTR [62], most act as promoters. For example, during mouse early development, many transcripts produced at the 2-cell stage are initiated from MERVL derived LTR, suggesting that this co-opted sequence has played a leading role in cell-fate regulation in placental mammals [63, 64] (Fig. 1a). In human neuronal progenitor cells, epigenetic de-repression of evolutionarily younger L1 provides alternative promoters for many neuronal protein-coding genes [26].
Retrotransposons as cis-regulatory elements. a Example of transposable elements functioning as alternative promoters in 2C-like ES cells. Embryonic stem (ES) cells, the pluripotent cells derived from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst, are able to differentiate into all embryo tissues. However, a subpopulation of ES cells can be distinguished for its ability to differentiate into both embryo and extra-embryonic tissues (totipotency). These cells recapitulate the same transcriptional state of totipotent 2 cells, where MERV elements are transcriptionally active and work as alternative promoters for two-cell stage specific genes. b Example of transposable elements functioning as enhancers. ERV and L1 enriched enhancers in cranial neural crest cells (CNCC) affect the expression of genes involved in craniofacial development. Divergent enhancers between human and chimp contribute to species-specific facial phenotypes. The differential activity of these species-biased enhancers also affects intra-human facial variation
Enhancers act as central lineage-specific players in orchestrating complex gene expression program underlying developmental and tissue-specific transcriptional programs [65, 66]. One example is represented by the eutherian specific MER20 elements that integrate information to regulate pregnancy-related gene expression in endometrial stromal cells in placental mammals [67]. Interestingly, retroelements have been shown to contribute to enhancer-mediated craniofacial morphological variation in primate evolution [68] (Fig. 1b).
Identification and functional characterization of enhancers elucidate several common features, including unique epigenomic signature, ncRNA transcription, and TF binding sites [69,70,71,72]. Comprehensive common TF binding motif analysis and epigenomic modification profile dissection have shown that retrotransposons exhibit similar enhancer signatures [73,74,75,76,77,78]. For example, RLTR13D6/RLTR9 and RLTR13D5/RLTR13B family elements acquire enhancer features in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and trophoblast stem cells (TSCs), respectively. However, only a minor dysfunctional effect on transcription was observed when these elements were perturbed by CRISPR-mediated transcriptional inhibition [79]. This result exposes a weakness of bioinformatics-based genome-wide correlation analysis and prediction as they do not prove functional aspects of TE-derived enhancers [80]. Therefore, several studies have rigorously tested putative enhancers through gain- or loss-of-function CRISPR-based approaches to determine their enhancer potential. Fuentes et al., systematically perturbed the ~ 700 copies of HERVK element LTR5HS present in the human genome by combining CARGO (Chimeric Array of gRNA Oligos) with CRISPR technology and showed that activation/silencing of LTR5HS consistently modulated the expression profile of hundreds of human genes [81]. Pontis et al., downregulated evolutionarily recent SVA, HERVK, and HERVH TE subgroups (TEENhancers) in naive hESC and demonstrated that these elements markedly influence transcription during human embryonic genome activation (EGA) by acting as stage-specific enhancers [82]. A role for ERVs as cis-regulatory elements was also found in the innate immunity response by demonstrating their contribution in shaping the evolution of the IFN-response transcriptional network in human [83]. On the other hand, TE-derived enhancers act in complex regulatory contexts. Their activity intersects additively, synergistically, hierarchically, or competitively with other enhancers embedded in the same regulatory landscape [84].
In addition to immobilized retroelements that modulate transcriptomic homeostasis, our team's recent work has also demonstrated that developmentally regulated de novo insertions in somatic cells contribute to shaping the tissue-specific transcriptional landscape. When mouse fibroblasts were reprogrammed into dopaminergic neurons (iDA), reactivation and retrotransposition of L1 elements occurred. De novo insertions mostly landed near neuronal genes and affected proximal chromatin accessibility, thus creating new transcriptional units, especially of lncRNA [85].
Novel non-coding RNA derived from retrotransposons
The first evidence for developmental functions of LINE-1 RNA came from a seminal study from Torres-Padilla's group on early mouse embryogenesis, where they demonstrated how early-stage transcription of L1 is important for blastocyst formation as it is the key driving force modulating global chromatin structure in cis [86, 87]. Nano-CAGE RNA-seq analysis showed TE stage-specific reactivation, with LINE-1 highly expressed in pre-implantation embryos and downregulated as the differentiation proceeded [87]. Perturbing the tightly regulated level of nuclear LINE-1 RNA resulted in global chromatin accessibility impairment and reduction of blastocyst formation [86]. Reverse transcriptase activity inhibition did not affect blastocyst formation, and cytoplasmic injection of exogenous L1 RNA did not revert the effect of nuclear L1 RNA silencing [86]. These observations strongly suggest a central role for endogenous chromatin associated L1 transcripts at early development stages in controlling chromatin opening, most probably in cis, independent of retrotransposition (Fig. 2a). Of note, the positive effects of L1 RNA were independent of DNA damage. Percharde et al., dissected the mechanism underlying the role of L1 RNA in ESC. They demonstrated that LINE1 RNA acts in cis as a nuclear scaffold to facilitate rDNA expression and repression of DUX, the master activator of the 2-cell embryo program, thus maintaining ESC self-renewal [88] (Fig. 2a).
Retrotransposons as non-coding RNA. a Example of TE-derived RNA functioning as non-coding RNA during early development. In pre-implantation embryos L1 are transcriptionally active. L1 RNA association to chromatin led to global chromatin relaxation. L1 RNA associates with KAP1 and Nucleolin at rDNA loci inducing their transcription, while repressing DUX and 2C-specific genes to proceed with the development. b Example of TE-derived RNA functioning as non-coding RNA in stress response. In resting cells SINE B2 RNA associates with stress response genes inhibiting RNA Pol II elongation. When cells are stressed the binding of EZH2 to stress loci enhances the self-cleavage activity of the B2 ribozyme, thus releasing Pol II and allowing transcription of stress response loci
In situ analysis of several mammalian cell lines revealed a class of repeat-containing RNAs, mostly L1-enriched, broadly and stably associated with euchromatin. These "chromosomal RNAs" are highly stable, accumulate in the nucleus, and remain localized strictly with the interphase chromosome territory in cis, where they may help maintain open chromatin structures [89]. In addition to these extensively studied transcripts derived from L1, other TE-derived RNAs have been proven to have regulatory functions [90]. LINE-2 is a source of functional miRNA in the human brain [91], and Alu element-containing RNAs (aluRNA) were found to be involved in maintaining nucleolar structure and rRNA synthesis [92]. HERVH-derived transcripts provide functional binding sites for a combination of naive pluripotency transcription factors such as LBP9 and OCT4. Their interaction activates hESC-specific alternative and chimeric transcripts, including long non-coding RNAs that modulate pluripotency and maintain human embryonic stem cell identity [93].
RNAs from SINE B2 repeats in mouse and SINE Alu repeats in human, control gene expression by binding RNA polymerase II and suppressing transcription [94,95,96]. RNAs from these elements have been known for years to be upregulated during the response to various types of cellular stress. Both SINE Alu and B2 RNAs bind and inhibit RNA Pol II [97]. B2 RNAs and Alu RNAs are self-cleaving; upon stress, these RNAs become destabilized and release stalled Pol II to activate stress response genes [98, 99]. Interestingly the cleavage reaction is facilitated by binding to the Polycomb component Ezh2, in this case, an activator [98, 99]. Thus, SINE RNAs appear to play a key role in stress response by suppressing or activating transcription based on their processing status (Fig. 2b). In addition to transcriptional regulation, SINE B2 regulates gene expression post-transcriptionally, by either blocking mRNA nuclear export [100] or by enhancing mRNA translation through the “SINEUP” mechanism [101, 102]. Recent studies report that TEs’ RNA half-life is strongly affected by m6A RNA modification, showing that m6A protects cells from aberrant TE transcript accumulation [103, 104].
Orchestrating 3D genome architecture as boundaries or compartmentalization factors
Growing evidence supports a pivotal role for retrotransposons in maintaining higher-order chromatin structure and 3D genome organization in mammals [105].The spatial distribution of SINE and LINE retroelements has unveiled a differential re-location of those elements into active A compartments at the nucleus interior and inactive B compartments at the periphery of the nucleus (Lamina-associated domains, LADs) and nucleolus (Nucleolus-associated domains, NADs), respectively. This spatial segregation is highly conserved across all eukaryotes and is required to maintain euchromatin/heterochromatin compartmentalization [52, 106,107,108] (Fig. 3a). Lu et al. recently showed that L1 RNA preferentially binds to L1-enriched genomic loci in ESC by ChIRP-seq [52]. Antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) against L1 RNA triggered a dramatic re-location of L1 enriched chromosomal regions from the nucleolus and inactive LADs to the nuclear interior and, in turn, their de-repression [52]. Intriguingly, one recent study highlights a novel mechanism where L1 DNA and RNA induce HP1α phase separation promoting heterochromatin compartmentalization [109]. These data indicate a role for L1 RNA in nuclear organization, where L1 RNA binding to L1 DNA silences L1-enriched genes by directing genomic regions to inactive compartments (Fig. 3a).
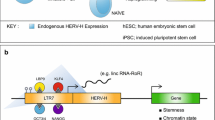
Retrotransposons as 3D genome architecture orchestrators. a L1 RNA associates to L1 DNA and mediates the sequestration of L1-enriched genes in the inactive compartment (B), at the nuclear periphery, for silencing. NAD Nucleolar-Associated Domain, LAD Lamina-Associated Domain. Active genes are barcoded by SINEs and localized in the nuclear interior (compartment A) where they are actively transcribed. SINE elements are enriched for CTCF binding sites, represent TADs (Topologically Associated Domains) boundaries and contribute to chromatin looping. b In hESC, transcriptionally active HERV-H forms pluripotent specific TAD boundaries which weaken during differentiation to cardiomyocytes. Transcription at HERV-H loci is crucial for maintaining chromatin looping at HERV-H-dependent TADs
Retrotransposons act as either boundary elements or docking sites to facilitate folding and compartmentalization of the genome, whose CTCF binding site bordered topologically associated domains (TADs) are important 3D units. Using Capture-4Tran and 4Tran-PCR, Raviram et al. discovered several young mouse ERV families (IAPEz, ETnERV, RLTR6, and MuLV-int/RLTR) engaged in long-range intra-chromosomal interaction and looping formation in specific chromatin compartments [107]. In hESC, transcriptionally active HERV-H form TAD boundaries that are specific to pluripotent stem cells and their frequency weaken during differentiation to cardiomyocites [107] (Fig. 3b). Indeed, Hi-C and ChIA-PET have shown that retrotransposon sequences are important anchoring sites for CTCF loops [110]. In particular, SINE elements are highly enriched for CTCF binding and over-represented at TAD boundaries [110] (Fig. 3a). Interestingly, CTCF ChIP-seq analysis in six mammalian lineages unveiled a pool of SINEs containing CTCF binding sites that are not evolutionary conserved [105]. These data suggest that TE expansion has produced new CTCF binding sites. Thus, altered chromatin architecture and gene regulatory networks may have contributed to the species-specific evolution of mammalian genome structures [74, 111].
However, the pervasive and non-specific distribution of retrotransposons in the genome has raised concerns regarding the functional aspects of co-localization between retroelements and boundary elements, which has been considered a random phenomenon. To establish a functional link between TEs and genome folding, Zhang and Ren investigated a primate-specific HERV-H family's ability to create TADs in human pluripotent stem cells [108]. By editing endogenous HERV-H sequences, they proved that HERV-H elements are essential TADs boundary elements. As further evidence, PiggyBac assisted insertion of HERV-H induces de novo organization of TADs at acceptor loci [108].
New methods to study retrotransposition-independent functions of retrotransposons
In the last decade, advances in the field have shed some light on retrotransposons' role and dynamics during early embryo development, cell differentiation, and specific pathological circumstances. Genomic and epigenomic genome-wide studies have uncovered the importance of retrotransposons in the genome, even if these studies are mainly correlational. However, many questions have not been fully addressed because of the complex nature of repetitive elements. Thus, the improvement and development of new technologies are fundamental to achieving a more in-depth understanding of retrotransposons' functional impact on genome evolution, structure and function, and its mechanisms.
Improved genome editing technologies have allowed modulation of expression/repression of genomic loci, including transposable elements [112,113,114,115]. In particular, CRISPR-activation/interference has been used to evaluate LTR elements' ability to act as enhancer elements [79, 81]. Church and colleagues have successfully knocked out human LINE-1 elements using base editors in HEK293T, and human iPS stem cells [116]. As mentioned, there are around 100 and 3000 active LINE-1 elements in the human (L1-Hs) and mouse (L1-Gf, -Tf, and -A family) genomes, respectively [8]. A detailed map of active LINE-1 loci is fundamental to manipulating these elements' expression through CRISPR-based technologies and testing the effects on genome functions and dynamics.
Interestingly, Ranjan and Gene used a system based on the fusion of an RNA endonuclease with a nuclease-dead Cas9 (dCas9) to target and eliminate toxic microsatellite repeat RNA [117], a transcript produced from a locus that cannot be targeted by an sgRNA with the canonical CRISPRi methods. This approach can be extended to all the other classes of transcripts produced by repetitive or particularly complex loci [117]. RNA editing technology can be applied to follow the dynamics of repetitive RNAs by CRISPR-Cas13-based RNA-labeling with higher specificity than probe hybridization-based probe assays (e.g., fluorescent in-situ hybridization, FISH) [118]. This approach has been used to track lncRNA NEAT1 with a just one sgRNA combined with dCas13b-EGFP [119].
Mounting evidence suggests that retrotransposon-derived transcripts may behave like lncRNAs. Global RNA-DNA/chromatin interaction profiles have been mapped using RNA-centered genome-wide analysis. For instance, LINE-1 was found to be preferentially bound to LINE-1 DNA-rich regions of the genome [52]. To understand the function of the thousands of transcripts originated from retrotransposons and other repetitive DNA elements, it is necessary to characterize the RNA–protein interactome to reveal potential regulatory roles of repetitive RNAs in genome structure and gene expression. Towards that end, the improvement of gRNA driven proximal protein labeling assays (e.g., CRISPR-APEX2 technology) [120,121,122] or RNA pull-down coupled with protein mass spectrometry methods (e.g., ChIRP-MS and RAP-MS) have been instrumental [123,124,125]. However, immunoprecipitation/pull-down-based assays show several pitfalls when applied to RNAs derived from repetitive sequences or retrotransposons because proper experimental controls and high-specificity probe sets are lacking [126, 127].
Applying these techniques to in vivo studies in animal models or human biopsies is exceptionally challenging because of the limited amount of starting material. The evolution of protein mass spectrometry instruments, like the recent release of 4D (m/z, retention time, ion mobility and signal intensity) proteomics platform, has significantly reduced the peptide detection limit, making it possible to study RNA–protein interactions quantitatively with low input samples [128,129,130].
Another unresolved and controversial question is whether transcription of retrotransposons or retrotransposon-derived transcripts is a real driver of biological processes [86, 88]. Chromatin-associated lncRNA species enrichment [131] and specific RNA Pol II elongation form precipitation [132] coupled with long-read RNA-seq [133] could address this outstanding question.
Concluding remarks and future perspective
Initially, retrotransposons were exclusively considered hazardous genetic elements that required strict epigenetic mechanisms for silencing. Now, largely thanks to the development of novel technologies, mounting evidence unveils an essential role of retrotransposon dynamics in fundamental physiological cell functions, from co-option as regulatory elements to orchestrate cell type specific transcriptional programs, chromatin remodeling, 3D genome organization up to immune systems involved in tissue homeostasis and defense mechanisms. A deeper integration of retrotransposons and host genome in which the dynamic nature of mobile elements includes not only DNA but also RNA impacting both nuclear and cytoplasmic functions may be envisaged.
How have these processes evolved? The relatively abundant amounts and quality of ncRNAs produced by these elements in response to environmental signals and the emerging role of RNA in nuclear structure and function, may indicate how these two apparently separated portions of the eukaryotic genome began talking to each other. The two systems could have merged into a unified functional unit, and perhaps further evolved based on epigenome-mediated somatic phenotype variation. As summarized above, retrotransposon-derived RNAs have a strong regulatory potential due to their interaction with proteins involved in chromatin and transcriptional regulation, indicating an exciting new frontier in epigenome biology, developmental processes and control of functional tissue homeostasis. Indeed, finely regulated expression of retrotransposons is essential for proper genome function, as their aberrant expression is strictly correlated to embryo development failure and the onset of several pathologies associated with accelerated aging, cancer, and chronic inflammation.
The development of new technologies, and improvements of the available one, will deepen our understanding of how the host genome balances the detrimental and beneficial effects of retroelements in evolution, development, and pathological conditions.
References
Venter JC, Adams MD, Myers EW, Li PW, Mural RJ, Sutton GG et al (2001) The sequence of the human genome. Science 291(5507):1304–1351. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1058040
Mouse Genome Sequencing C, Waterston RH, Lindblad-Toh K, Birney E, Rogers J, Abril JF et al (2002) Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome. Nature 420(6915):520–562. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01262
Wicker T, Sabot F, Hua-Van A, Bennetzen JL, Capy P, Chalhoub B et al (2007) A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat Rev Genet 8(12):973–982. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2165
Cordaux R, Batzer MA (2009) The impact of retrotransposons on human genome evolution. Nat Rev Genet 10(10):691–703. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2640
Stocking C, Kozak CA (2008) Murine endogenous retroviruses. Cell Mol Life Sci 65(21):3383–3398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8497-0
Gagnier L, Belancio VP, Mager DL (2019) Mouse germ line mutations due to retrotransposon insertions. Mob DNA 10:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13100-019-0157-4
Dewannieux M, Harper F, Richaud A, Letzelter C, Ribet D, Pierron G et al (2006) Identification of an infectious progenitor for the multiple-copy HERV-K human endogenous retroelements. Genome Res 16(12):1548–1556. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.5565706
Friedli M, Trono D (2015) The developmental control of transposable elements and the evolution of higher species. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 31:429–451. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100814-125514
Feng Q, Moran JV, Kazazian HH Jr, Boeke JD (1996) Human L1 retrotransposon encodes a conserved endonuclease required for retrotransposition. Cell 87(5):905–916. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81997-2
Mathias SL, Scott AF, Kazazian HH Jr, Boeke JD, Gabriel A (1991) Reverse transcriptase encoded by a human transposable element. Science 254(5039):1808–1810. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1722352
Martin SL, Bushman FD (2001) Nucleic acid chaperone activity of the ORF1 protein from the mouse LINE-1 retrotransposon. Mol Cell Biol 21(2):467–475. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.21.2.467-475.2001
Richardson SR, Morell S, Faulkner GJ (2014) L1 retrotransposons and somatic mosaicism in the brain. Annu Rev Genet 48:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-120213-092412
Denli AM, Narvaiza I, Kerman BE, Pena M, Benner C, Marchetto MC et al (2015) Primate-specific ORF0 contributes to retrotransposon-mediated diversity. Cell 163(3):583–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.025
Sookdeo A, Hepp CM, McClure MA, Boissinot S (2013) Revisiting the evolution of mouse LINE-1 in the genomic era. Mob DNA 4(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1759-8753-4-3
Payer LM, Burns KH (2019) Transposable elements in human genetic disease. Nat Rev Genet 20(12):760–772. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-019-0165-8
Mills RE, Bennett EA, Iskow RC, Devine SE (2007) Which transposable elements are active in the human genome? Trends Genet 23(4):183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2007.02.006
Dewannieux M, Esnault C, Heidmann T (2003) LINE-mediated retrotransposition of marked Alu sequences. Nat Genet 35(1):41–48. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1223
Raiz J, Damert A, Chira S, Held U, Klawitter S, Hamdorf M et al (2012) The non-autonomous retrotransposon SVA is trans-mobilized by the human LINE-1 protein machinery. Nucleic Acids Res 40(4):1666–1683. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr863
Hancks DC, Goodier JL, Mandal PK, Cheung LE, Kazazian HH Jr (2011) Retrotransposition of marked SVA elements by human L1s in cultured cells. Hum Mol Genet 20(17):3386–3400. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr245
Dewannieux M, Heidmann T (2005) L1-mediated retrotransposition of murine B1 and B2 SINEs recapitulated in cultured cells. J Mol Biol 349(2):241–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.03.068
Thompson PJ, Macfarlan TS, Lorincz MC (2016) Long terminal repeats: from parasitic elements to building blocks of the transcriptional regulatory repertoire. Mol Cell 62(5):766–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.03.029
Varshney D, Vavrova-Anderson J, Oler AJ, Cowling VH, Cairns BR, White RJ (2015) SINE transcription by RNA polymerase III is suppressed by histone methylation but not by DNA methylation. Nat Commun 6:6569. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7569
MacLennan M, Garcia-Canadas M, Reichmann J, Khazina E, Wagner G, Playfoot CJ et al (2017) Mobilization of LINE-1 retrotransposons is restricted by Tex19.1 in mouse embryonic stem cells. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26152
Richardson SR, Narvaiza I, Planegger RA, Weitzman MD, Moran JV (2014) APOBEC3A deaminates transiently exposed single-strand DNA during LINE-1 retrotransposition. Elife 3:e02008. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02008
Bestor TH, Bourc’his D (2004) Transposon silencing and imprint establishment in mammalian germ cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 69:381–387. https://doi.org/10.1101/sqb.2004.69.381
Jonsson ME, Ludvik Brattas P, Gustafsson C, Petri R, Yudovich D, Pircs K et al (2019) Activation of neuronal genes via LINE-1 elements upon global DNA demethylation in human neural progenitors. Nat Commun 10(1):3182. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11150-8
Barau J, Teissandier A, Zamudio N, Roy S, Nalesso V, Herault Y et al (2016) The DNA methyltransferase DNMT3C protects male germ cells from transposon activity. Science 354(6314):909–912. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aah5143
Bulut-Karslioglu A, De La Rosa-Velazquez IA, Ramirez F, Barenboim M, Onishi-Seebacher M, Arand J et al (2014) Suv39h-dependent H3K9me3 marks intact retrotransposons and silences LINE elements in mouse embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell 55(2):277–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.05.029
Liu S, Brind’Amour J, Karimi MM, Shirane K, Bogutz A, Lefebvre L et al (2014) Setdb1 is required for germline development and silencing of H3K9me3-marked endogenous retroviruses in primordial germ cells. Genes Dev 28(18):2041–2055. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.244848.114
Pezic D, Manakov SA, Sachidanandam R, Aravin AA (2014) piRNA pathway targets active LINE1 elements to establish the repressive H3K9me3 mark in germ cells. Genes Dev 28(13):1410–1428. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.240895.114
Aravin AA, Sachidanandam R, Bourc’his D, Schaefer C, Pezic D, Toth KF et al (2008) A piRNA pathway primed by individual transposons is linked to de novo DNA methylation in mice. Mol Cell 31(6):785–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.09.003
Rowe HM, Jakobsson J, Mesnard D, Rougemont J, Reynard S, Aktas T et al (2010) KAP1 controls endogenous retroviruses in embryonic stem cells. Nature 463(7278):237–240. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08674
Jacobs FM, Greenberg D, Nguyen N, Haeussler M, Ewing AD, Katzman S et al (2014) An evolutionary arms race between KRAB zinc-finger genes ZNF91/93 and SVA/L1 retrotransposons. Nature 516(7530):242–245. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13760
Turelli P, Castro-Diaz N, Marzetta F, Kapopoulou A, Raclot C, Duc J et al (2014) Interplay of TRIM28 and DNA methylation in controlling human endogenous retroelements. Genome Res 24(8):1260–1270. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.172833.114
Rodriguez-Terrones D, Torres-Padilla ME (2018) Nimble and ready to mingle: transposon outbursts of early development. Trends Genet 34(10):806–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2018.06.006
Robbez-Masson L, Tie CHC, Conde L, Tunbak H, Husovsky C, Tchasovnikarova IA et al (2018) The HUSH complex cooperates with TRIM28 to repress young retrotransposons and new genes. Genome Res 28(6):836–845. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.228171.117
Tunbak H, Enriquez-Gasca R, Tie CHC, Gould PA, Mlcochova P, Gupta RK et al (2020) The HUSH complex is a gatekeeper of type I interferon through epigenetic regulation of LINE-1s. Nat Commun 11(1):5387. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-19170-5
Douse CH, Tchasovnikarova IA, Timms RT, Protasio AV, Seczynska M, Prigozhin DM et al (2020) TASOR is a pseudo-PARP that directs HUSH complex assembly and epigenetic transposon control. Nat Commun 11(1):4940. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18761-6
Burns KH (2017) Transposable elements in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 17(7):415–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2017.35
Tam OH, Ostrow LW, Gale Hammell M (2019) Diseases of the nERVous system: retrotransposon activity in neurodegenerative disease. Mob DNA 10:32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13100-019-0176-1
Di Giacomo M, Comazzetto S, Saini H, De Fazio S, Carrieri C, Morgan M et al (2013) Multiple epigenetic mechanisms and the piRNA pathway enforce LINE1 silencing during adult spermatogenesis. Mol Cell 50(4):601–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2013.04.026
Malki S, van der Heijden GW, O’Donnell KA, Martin SL, Bortvin A (2014) A role for retrotransposon LINE-1 in fetal oocyte attrition in mice. Dev Cell 29(5):521–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2014.04.027
Jang HS, Shah NM, Du AY, Dailey ZZ, Pehrsson EC, Godoy PM et al (2019) Transposable elements drive widespread expression of oncogenes in human cancers. Nat Genet 51(4):611–617. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0373-3
Deniz O, Ahmed M, Todd CD, Rio-Machin A, Dawson MA, Branco MR (2020) Endogenous retroviruses are a source of enhancers with oncogenic potential in acute myeloid leukaemia. Nat Commun 11(1):3506. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17206-4
Jonsson ME, Garza R, Sharma Y, Petri R, Sodersten E, Johansson JG et al (2021) Activation of endogenous retroviruses during brain development causes an inflammatory response. Embo J. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2020106423
Simon M, Van Meter M, Ablaeva J, Ke Z, Gonzalez RS, Taguchi T et al (2019) LINE1 derepression in aged wild-type and SIRT6-deficient mice drives inflammation. Cell Metab 29(4):871–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.02.014
De Cecco M, Ito T, Petrashen AP, Elias AE, Skvir NJ, Criscione SW et al (2019) L1 drives IFN in senescent cells and promotes age-associated inflammation. Nature 566(7742):73–78. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0784-9
Jonsson ME, Garza R, Johansson PA, Jakobsson J (2020) Transposable elements: a common feature of neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Genet 36(8):610–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2020.05.004
Saleh A, Macia A, Muotri AR (2019) Transposable elements, inflammation, and neurological disease. Front Neurol 10:894. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00894
Britten RJ, Davidson EH (1969) Gene regulation for higher cells: a theory. Science 165(3891):349–357. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.165.3891.349
Davidson EH, Britten RJ (1979) Regulation of gene expression: possible role of repetitive sequences. Science 204(4397):1052–1059. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.451548
Lu JY, Shao W, Chang L, Yin Y, Li T, Zhang H et al (2020) Genomic repeats categorize genes with distinct functions for orchestrated regulation. Cell Rep 30(10):3296–3311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.048
Sultana T, Zamborlini A, Cristofari G, Lesage P (2017) Integration site selection by retroviruses and transposable elements in eukaryotes. Nat Rev Genet 18(5):292–308. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2017.7
Lowe CB, Bejerano G, Haussler D (2007) Thousands of human mobile element fragments undergo strong purifying selection near developmental genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(19):8005–8010. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0611223104
Chuong EB, Elde NC, Feschotte C (2017) Regulatory activities of transposable elements: from conflicts to benefits. Nat Rev Genet 18(2):71–86. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2016.139
Zhang XO, Wang HB, Zhang Y, Lu X, Chen LL, Yang L (2014) Complementary sequence-mediated exon circularization. Cell 159(1):134–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.001
Roy-Engel AM, El-Sawy M, Farooq L, Odom GL, Perepelitsa-Belancio V, Bruch H et al (2005) Human retroelements may introduce intragenic polyadenylation signals. Cytogenet Genome Res 110(1–4):365–371. https://doi.org/10.1159/000084968
Liang D, Wilusz JE (2014) Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev 28(20):2233–2247. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.251926.114
Lee JY, Ji Z, Tian B (2008) Phylogenetic analysis of mRNA polyadenylation sites reveals a role of transposable elements in evolution of the 3’-end of genes. Nucleic Acids Res 36(17):5581–5590. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn540
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, Liu J et al (2013) Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 19(2):141–157. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.035667.112
Peaston AE, Evsikov AV, Graber JH, de Vries WN, Holbrook AE, Solter D et al (2004) Retrotransposons regulate host genes in mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Dev Cell 7(4):597–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2004.09.004
Dunn CA, Medstrand P, Mager DL (2003) An endogenous retroviral long terminal repeat is the dominant promoter for human beta1,3-galactosyltransferase 5 in the colon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(22):12841–12846. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2134464100
Macfarlan TS, Gifford WD, Driscoll S, Lettieri K, Rowe HM, Bonanomi D et al (2012) Embryonic stem cell potency fluctuates with endogenous retrovirus activity. Nature 487(7405):57–63. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11244
Maksakova IA, Thompson PJ, Goyal P, Jones SJ, Singh PB, Karimi MM et al (2013) Distinct roles of KAP1, HP1 and G9a/GLP in silencing of the two-cell-specific retrotransposon MERVL in mouse ES cells. Epigenet Chromatin 6(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8935-6-15
Long HK, Prescott SL, Wysocka J (2016) Ever-changing landscapes: transcriptional enhancers in development and evolution. Cell 167(5):1170–1187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.09.018
Andersson R, Sandelin A (2020) Determinants of enhancer and promoter activities of regulatory elements. Nat Rev Genet 21(2):71–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-019-0173-8
Lynch VJ, Leclerc RD, May G, Wagner GP (2011) Transposon-mediated rewiring of gene regulatory networks contributed to the evolution of pregnancy in mammals. Nat Genet 43(11):1154–1159. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.917
Prescott SL, Srinivasan R, Marchetto MC, Grishina I, Narvaiza I, Selleri L et al (2015) Enhancer divergence and cis-regulatory evolution in the human and chimp neural crest. Cell 163(1):68–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.036
Ong CT, Corces VG (2012) Enhancers: emerging roles in cell fate specification. Embo Rep 13(5):423–430. https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2012.52
Calo E, Wysocka J (2013) Modification of enhancer chromatin: what, how, and why? Mol Cell 49(5):825–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2013.01.038
Natoli G, Andrau JC (2012) Noncoding transcription at enhancers: general principles and functional models. Annu Rev Genet 46:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-110711-155459
Furlong EEM, Levine M (2018) Developmental enhancers and chromosome topology. Science 361(6409):1341–1345. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau0320
Cao Y, Chen G, Wu G, Zhang X, McDermott J, Chen X et al (2019) Widespread roles of enhancer-like transposable elements in cell identity and long-range genomic interactions. Genome Res 29(1):40–52. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.235747.118
Sundaram V, Cheng Y, Ma Z, Li D, Xing X, Edge P et al (2014) Widespread contribution of transposable elements to the innovation of gene regulatory networks. Genome Res 24(12):1963–1976. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.168872.113
Ito J, Sugimoto R, Nakaoka H, Yamada S, Kimura T, Hayano T et al (2017) Systematic identification and characterization of regulatory elements derived from human endogenous retroviruses. PLoS Genet 13(7):e1006883. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006883
Kunarso G, Chia NY, Jeyakani J, Hwang C, Lu X, Chan YS et al (2010) Transposable elements have rewired the core regulatory network of human embryonic stem cells. Nat Genet 42(7):631–634. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.600
Chuong EB, Rumi MA, Soares MJ, Baker JC (2013) Endogenous retroviruses function as species-specific enhancer elements in the placenta. Nat Genet 45(3):325–329. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2553
Faulkner GJ, Kimura Y, Daub CO, Wani S, Plessy C, Irvine KM et al (2009) The regulated retrotransposon transcriptome of mammalian cells. Nat Genet 41(5):563–571. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.368
Todd CD, Deniz O, Taylor D, Branco MR (2019) Functional evaluation of transposable elements as enhancers in mouse embryonic and trophoblast stem cells. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.44344
Brind’Amour J, Mager DL (2019) Reality check for transposon enhancers. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.47900
Fuentes DR, Swigut T, Wysocka J (2018) Systematic perturbation of retroviral LTRs reveals widespread long-range effects on human gene regulation. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.35989
Pontis J, Planet E, Offner S, Turelli P, Duc J, Coudray A et al (2019) Hominoid-specific transposable elements and KZFPs facilitate human embryonic genome activation and control transcription in naive human ESCs. Cell Stem Cell 24(5):724–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2019.03.012
Chuong EB, Elde NC, Feschotte C (2016) Regulatory evolution of innate immunity through co-option of endogenous retroviruses. Science 351(6277):1083–1087. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad5497
Berthelot C, Villar D, Horvath JE, Odom DT, Flicek P (2018) Complexity and conservation of regulatory landscapes underlie evolutionary resilience of mammalian gene expression. Nat Ecol Evol 2(1):152–163. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-017-0377-2
Della Valle F, Thimma MP, Caiazzo M, Pulcrano S, Celii M, Adroub SA et al (2020) Transdifferentiation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts into dopaminergic neurons reactivates LINE-1 repetitive elements. Stem Cell Rep 14(1):60–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2019.12.002
Jachowicz JW, Bing X, Pontabry J, Boskovic A, Rando OJ, Torres-Padilla ME (2017) LINE-1 activation after fertilization regulates global chromatin accessibility in the early mouse embryo. Nat Genet 49(10):1502–1510. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3945
Fadloun A, Le Gras S, Jost B, Ziegler-Birling C, Takahashi H, Gorab E et al (2013) Chromatin signatures and retrotransposon profiling in mouse embryos reveal regulation of LINE-1 by RNA. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20(3):332–338. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2495
Percharde M, Lin CJ, Yin Y, Guan J, Peixoto GA, Bulut-Karslioglu A et al (2018) A LINE1-nucleolin partnership regulates early development and ESC identity. Cell 174(2):391–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.05.043
Hall LL, Carone DM, Gomez AV, Kolpa HJ, Byron M, Mehta N et al (2014) Stable C0T–1 repeat RNA is abundant and is associated with euchromatic interphase chromosomes. Cell 156(5):907–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.042
Kapusta A, Kronenberg Z, Lynch VJ, Zhuo X, Ramsay L, Bourque G et al (2013) Transposable elements are major contributors to the origin, diversification, and regulation of vertebrate long noncoding RNAs. PLoS Genet 9(4):e1003470. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003470
Petri R, Brattas PL, Sharma Y, Jonsson ME, Pircs K, Bengzon J et al (2019) LINE-2 transposable elements are a source of functional human microRNAs and target sites. PLoS Genet 15(3):e1008036. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008036
Caudron-Herger M, Pankert T, Seiler J, Nemeth A, Voit R, Grummt I et al (2015) Alu element-containing RNAs maintain nucleolar structure and function. Embo J 34(22):2758–2774. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201591458
Lu X, Sachs F, Ramsay L, Jacques PE, Goke J, Bourque G et al (2014) The retrovirus HERVH is a long noncoding RNA required for human embryonic stem cell identity. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21(4):423–425. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2799
Allen TA, Von Kaenel S, Goodrich JA, Kugel JF (2004) The SINE-encoded mouse B2 RNA represses mRNA transcription in response to heat shock. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11(9):816–821. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb813
Espinoza CA, Allen TA, Hieb AR, Kugel JF, Goodrich JA (2004) B2 RNA binds directly to RNA polymerase II to repress transcript synthesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11(9):822–829. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb812
Tajaddod M, Tanzer A, Licht K, Wolfinger MT, Badelt S, Huber F et al (2016) Transcriptome-wide effects of inverted SINEs on gene expression and their impact on RNA polymerase II activity. Genome Biol 17(1):220. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-1083-0
Mariner PD, Walters RD, Espinoza CA, Drullinger LF, Wagner SD, Kugel JF et al (2008) Human Alu RNA is a modular transacting repressor of mRNA transcription during heat shock. Mol Cell 29(4):499–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2007.12.013
Zovoilis A, Cifuentes-Rojas C, Chu HP, Hernandez AJ, Lee JT (2016) Destabilization of B2 RNA by EZH2 activates the stress response. Cell 167(7):1788–1802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.041
Hernandez AJ, Zovoilis A, Cifuentes-Rojas C, Han L, Bujisic B, Lee JT (2020) B2 and ALU retrotransposons are self-cleaving ribozymes whose activity is enhanced by EZH2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117(1):415–425. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1917190117
Karijolich J, Zhao Y, Alla R, Glaunsinger B (2017) Genome-wide mapping of infection-induced SINE RNAs reveals a role in selective mRNA export. Nucleic Acids Res 45(10):6194–6208. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx180
Carrieri C, Cimatti L, Biagioli M, Beugnet A, Zucchelli S, Fedele S et al (2012) Long non-coding antisense RNA controls Uchl1 translation through an embedded SINEB2 repeat. Nature 491(7424):454–457. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11508
Espinoza S, Scarpato M, Damiani D, Manago F, Mereu M, Contestabile A et al (2020) SINEUP non-coding RNA targeting GDNF rescues motor deficits and neurodegeneration in a mouse model of parkinson’s disease. Mol Ther 28(2):642–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.08.005
Liu J, Dou X, Chen C, Chen C, Liu C, Xu MM et al (2020) N (6)-methyladenosine of chromosome-associated regulatory RNA regulates chromatin state and transcription. Science 367(6477):580–586. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aay6018
Chelmicki T, Roger E, Teissandier A, Dura M, Bonneville L, Rucli S et al (2021) m(6)A RNA methylation regulates the fate of endogenous retroviruses. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-03135-1
Schmidt D, Schwalie PC, Wilson MD, Ballester B, Goncalves A, Kutter C et al (2012) Waves of retrotransposon expansion remodel genome organization and CTCF binding in multiple mammalian lineages. Cell 148(1–2):335–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.058
Falk M, Feodorova Y, Naumova N, Imakaev M, Lajoie BR, Leonhardt H et al (2019) Heterochromatin drives compartmentalization of inverted and conventional nuclei. Nature 570(7761):395–399. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1275-3
Raviram R, Rocha PP, Luo VM, Swanzey E, Miraldi ER, Chuong EB et al (2018) Analysis of 3D genomic interactions identifies candidate host genes that transposable elements potentially regulate. Genome Biol 19(1):216. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1598-7
Zhang Y, Li T, Preissl S, Amaral ML, Grinstein JD, Farah EN et al (2019) Transcriptionally active HERV-H retrotransposons demarcate topologically associating domains in human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Genet 51(9):1380–1388. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0479-7
Lu JY, Chang L, Li T, Wang T, Yin Y, Zhan G et al (2021) Homotypic clustering of L1 and B1/Alu repeats compartmentalizes the 3D genome. Cell Res. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-00466-6
Choudhary MN, Friedman RZ, Wang JT, Jang HS, Zhuo X, Wang T (2020) Co-opted transposons help perpetuate conserved higher-order chromosomal structures. Genome Biol 21(1):16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-019-1916-8
Diehl AG, Ouyang N, Boyle AP (2020) Transposable elements contribute to cell and species-specific chromatin looping and gene regulation in mammalian genomes. Nat Commun 11(1):1796. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15520-5
Doudna JA, Charpentier E (2014) Genome editing. The new frontier of genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9. Science 346(6213):1258096. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1258096
Hsu PD, Lander ES, Zhang F (2014) Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell 157(6):1262–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.010
Yeo NC, Chavez A, Lance-Byrne A, Chan Y, Menn D, Milanova D et al (2018) An enhanced CRISPR repressor for targeted mammalian gene regulation. Nat Methods 15(8):611–616. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-018-0048-5
Chavez A, Scheiman J, Vora S, Pruitt BW, Tuttle M, Iyer EP et al (2015) Highly efficient Cas9-mediated transcriptional programming. Nat Methods 12(4):326–328. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3312
Smith CJ, Castanon O, Said K, Volf V, Khoshakhlagh P, Hornick A et al (2020) Enabling large-scale genome editing at repetitive elements by reducing DNA nicking. Nucleic Acids Res 48(9):5183–5195. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa239
Batra R, Nelles DA, Pirie E, Blue SM, Marina RJ, Wang H et al (2017) Elimination of toxic microsatellite repeat expansion RNA by RNA-targeting Cas9. Cell 170(5):899–912
Qi LS, Larson MH, Gilbert LA, Doudna JA, Weissman JS, Arkin AP et al (2013) Repurposing CRISPR as an RNA-guided platform for sequence-specific control of gene expression. Cell 152(5):1173–1183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.022
Yang LZ, Wang Y, Li SQ, Yao RW, Luan PF, Wu H et al (2019) Dynamic imaging of RNA in living cells by CRISPR-Cas13 systems. Mol Cell 76(6):981–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.10.024
Gao XD, Tu LC, Mir A, Rodriguez T, Ding Y, Leszyk J et al (2018) C-BERST: defining subnuclear proteomic landscapes at genomic elements with dCas9-APEX2. Nat Methods 15(6):433–436. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-018-0006-2
Myers SA, Wright J, Peckner R, Kalish BT, Zhang F, Carr SA (2018) Discovery of proteins associated with a predefined genomic locus via dCas9-APEX-mediated proximity labeling. Nat Methods 15(6):437–439. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-018-0007-1
Yi W, Li J, Zhu X, Wang X, Fan L, Sun W et al (2020) CRISPR-assisted detection of RNA-protein interactions in living cells. Nat Methods 17(7):685–688. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-020-0866-0
Ramanathan M, Porter DF, Khavari PA (2019) Methods to study RNA-protein interactions. Nat Methods 16(3):225–234. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-019-0330-1
Chu C, Zhang QC, da Rocha ST, Flynn RA, Bharadwaj M, Calabrese JM et al (2015) Systematic discovery of Xist RNA binding proteins. Cell 161(2):404–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.025
McHugh CA, Chen CK, Chow A, Surka CF, Tran C, McDonel P et al (2015) The Xist lncRNA interacts directly with SHARP to silence transcription through HDAC3. Nature 521(7551):232–236. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14443
Raj A, Rinn JL (2019) Illuminating genomic dark matter with RNA imaging. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a032094
Simon MD, Machyna M (2019) Principles and practices of hybridization capture experiments to study long noncoding RNAs that act on chromatin. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a032276
Meier F, Brunner AD, Koch S, Koch H, Lubeck M, Krause M et al (2018) Online parallel accumulation-serial fragmentation (PASEF) with a novel trapped ion mobility mass spectrometer. Mol Cell Proteom 17(12):2534–2545. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.TIR118.000900
Prianichnikov N, Koch H, Koch S, Lubeck M, Heilig R, Brehmer S et al (2020) MaxQuant software for ion mobility enhanced shotgun proteomics. Mol Cell Proteom 19(6):1058–1069. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.TIR119.001720
Meier F, Brunner AD, Frank M, Ha A, Bludau I, Voytik E et al (2020) diaPASEF: parallel accumulation-serial fragmentation combined with data-independent acquisition. Nat Methods 17(12):1229–1236. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-020-00998-0
Werner MS, Ruthenburg AJ (2015) Nuclear fractionation reveals thousands of chromatin-tethered noncoding RNAs adjacent to active genes. Cell Rep 12(7):1089–1098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.033
Nojima T, Gomes T, Grosso ARF, Kimura H, Dye MJ, Dhir S et al (2015) Mammalian NET-seq reveals genome-wide nascent transcription coupled to RNA processing. Cell 161(3):526–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.027
Drexler HL, Choquet K, Churchman LS (2020) Splicing kinetics and coordination revealed by direct nascent RNA sequencing through nanopores. Mol Cell 77(5):985–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.11.017
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Prof. Christian Froekjaer Jensen for the fruitful discussion and for his contribution to the editing of the manuscript.
Funding
KAUST Baseline fund 01-01-1037, KAUST OSR-2019-CRG8-4042.2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AM, FDV, PL, VO conceived the concept of article, wrote the manuscript. VO coordinated the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Mangiavacchi, A., Liu, P., Della Valle, F. et al. New insights into the functional role of retrotransposon dynamics in mammalian somatic cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 78, 5245–5256 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03851-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03851-5