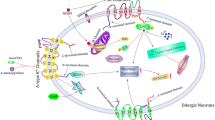
Abstract
The channel kinase (chanzyme) transient receptor potential melastatin-like 7 (TRPM7) has a unique dual protein structure composed of an ion channel with an α-kinase domain on its C-terminus. In the nervous system, under physiological conditions, TRPM7 contributes to critical neurobiological processes ranging from synaptic transmission to cognitive functions. Following certain pathological triggers, TRPM7 mediates neurotoxicity, neuro-injuries, and neuronal death. Here, we summarize the current knowledge of TRPM7 functions in neuronal systems in health and disease. The molecular mechanisms by which this chanzyme might regulate synaptic and cognitive functions are discussed. We also discuss the lack of knowledge regarding the molecular mechanisms responsible for turning TRPM7 into “a vicious tool” that mediates neuronal death following certain pathological triggers. Some synthetic and natural pharmacological modulators of the TRPM7 channel and its α-kinase are reviewed. We suggest that based on current knowledge, we should reshape our thinking regarding the implications of TRPM7 in neurological and neurodegenerative disorders. Moreover, we propose a paradigm shift concerning the targeting of TRPM7 as a therapeutic approach for treating certain neurological diseases. We agree that TRPM7 overexpression or overactivation may mediate neurodegenerative processes following certain triggers. However, TRPM7 dysfunction and/or downregulation might also be among the pathological changes leading to neurodegeneration. Consequently, further investigations are required before we decide whether blocking or activating the chanzyme is the correct therapeutic approach to treat certain neurological and/or neurodegenerative diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TRPM7:
-
Transient receptor potential melastatin-like 7
- Zn2+ :
-
Zinc
- Mg2+ :
-
Magnesium
- Ca2+ :
-
Calcium
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- GABA:
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid
- Akt:
-
Serine–threonine kinase
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex
- eEF2:
-
Eukaryotic elongation factor-2
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- APP:
-
The amyloid precursor protein
- Aβ:
-
A-beta peptide
- TRPM6:
-
Transient receptor potential melastatin-like 6
- NMDA:
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartic acid
- 2-APB:
-
2-Aminoethyl diphenyl borinate
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
References
Nadler MJ, Hermosura MC, Inabe K, Perraud AL, Zhu Q, Stokes AJ, Kurosaki T, Kinet JP, Penner R, Scharenberg AM, Fleig A (2001) LTRPC7 is a Mg.ATP-regulated divalent cation channel required for cell viability. Nature 411(6837):590–595
Runnels LW, Yue L, Clapham DE (2001) TRP-PLIK, a bifunctional protein with kinase and ion channel activities. Science 291(5506):1043–1047
Monteilh-Zoller MK, Hermosura MC, Nadler MJ, Scharenberg AM, Penner R, Fleig A (2003) TRPM7 provides an ion channel mechanism for cellular entry of trace metal ions. J Gen Physiol 121(1):49–60
Fleig A, Penner R (2004) The TRPM ion channel subfamily: molecular, biophysical and functional features. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25(12):633–639
Schmitz C, Perraud AL, Johnson CO, Inabe K, Smith MK, Penner R, Kurosaki T, Fleig A, Scharenberg AM (2003) Regulation of vertebrate cellular Mg2 + homeostasis by TRPM7. Cell 114(2):191–200
Sahni J, Scharenberg AM (2008) TRPM7 ion channels are required for sustained phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling in lymphocytes. Cell Metab 8(1):84–93
Chen KH, Xu XH, Liu Y, Hu Y, Jin MW, Li GR (2014) TRPM7 channels regulate proliferation and adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Cell Physiol 229(1):60–67
Desai BN, Krapivinsky G, Navarro B, Krapivinsky L, Carter BC, Febvay S, Delling M, Penumaka A, Ramsey IS, Manasian Y, Clapham DE (2012) Cleavage of TRPM7 releases the kinase domain from the ion channel and regulates its participation in Fas-induced apoptosis. Dev Cell 22(6):1149–1162
Jin J, Desai BN, Navarro B, Donovan A, Andrews NC, Clapham DE (2008) Deletion of Trpm7 disrupts embryonic development and thymopoiesis without altering Mg(2 +) homeostasis. Science 322(5902):756–760
Jin J, Wu LJ, Jun J, Cheng X, Xu H, Andrews NC, Clapham DE (2011) The channel kinase, TRPM7, is required for early embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(5):E225–E233
Ryazanova LV, Rondon LJ, Zierler S, Hu Z, Galli J, Yamaguchi TP, Mazur A, Fleig A, Ryazanov AG (2010) TRPM7 is essential for Mg(2+) homeostasis in mammals. Nat Commun 1:109
Perraud AL, Zhao X, Ryazanov AG, Schmitz C (2010) The channel-kinase TRPM7 regulates phosphorylation of the translational factor eEF2 via eEF2-k. Cell Signal 23(3):586–593
Krapivinsky G, Krapivinsky L, Manasian Y, Clapham DE (2014) The TRPM7 chanzyme is cleaved to release a chromatin-modifying kinase. Cell 157(5):1061–1072
Fleig A, Chubanov V (2014) Trpm7. Handb Exp Pharmacol 222:521–546
Abumaria N, Li W, Liu Y (2018) TRPM7 functions in non-neuronal and neuronal systems: perspectives on its role in the adult brain. Behav Brain Res 340:81–86
Aarts M, Iihara K, Wei WL, Xiong ZG, Arundine M, Cerwinski W, MacDonald JF, Tymianski M (2003) A key role for TRPM7 channels in anoxic neuronal death. Cell 115(7):863–877
Jiang H, Tian SL, Zeng Y, Li LL, Shi J (2008) TrkA pathway(s) is involved in regulation of TRPM7 expression in hippocampal neurons subjected to ischemic-reperfusion and oxygen-glucose deprivation. Brain Res Bull 76(1–2):124–130
Sun HS, Jackson MF, Martin LJ, Jansen K, Teves L, Cui H, Kiyonaka S, Mori Y, Jones M, Forder JP, Golde TE, Orser BA, Macdonald JF, Tymianski M (2009) Suppression of hippocampal TRPM7 protein prevents delayed neuronal death in brain ischemia. Nat Neurosci 12(10):1300–1307
Chen W, Xu B, Xiao A, Liu L, Fang X, Liu R, Turlova E, Barszczyk A, Zhong X, Sun CL, Britto LR, Feng ZP, Sun HS (2015) TRPM7 inhibitor carvacrol protects brain from neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury. Mol Brain 8:11
Xu HL, Liu MD, Yuan XH, Liu CX (2018) Suppression of cortical TRPM7 protein attenuates oxidative damage after traumatic brain injury via Akt/endothelial nitric oxide synthase pathway. Neurochem Int 112:197–205
Liu Y, Chen C, Liu Y, Li W, Wang Z, Sun Q, Zhou H, Chen X, Yu Y, Wang Y, Abumaria N (2018) TRPM7 is required for normal synapse density, learning, and memory at different developmental stages. Cell Rep 23(12):3480–3491
Krapivinsky G, Mochida S, Krapivinsky L, Cibulsky SM, Clapham DE (2006) The TRPM7 ion channel functions in cholinergic synaptic vesicles and affects transmitter release. Neuron 52(3):485–496
Low SE, Amburgey K, Horstick E, Linsley J, Sprague SM, Cui WW, Zhou W, Hirata H, Saint-Amant L, Hume RI, Kuwada JY (2011) TRPM7 is required within zebrafish sensory neurons for the activation of touch-evoked escape behaviors. J Neurosci 31(32):11633–11644
Ratnam M, Chan J, Lesani N, Sidorova-Darmos E, Eubanks JH, Aarts MM (2018) mRNA expression of transient receptor potential melastatin (TRPM) channels 2 and 7 in perinatal brain development. Int J Dev Neurosci 69:23–31
Turlova E, Bae CYJ, Deurloo M, Chen WL, Barszczyk A, Horgen FD, Fleig A, Feng ZP, Sun HS (2016) TRPM7 regulates axonal outgrowth and maturation of primary hippocampal neurons. Mol Neurobiol 53(1):595–610
Decker AR, McNeill MS, Lambert AM, Overton JD, Chen YC, Lorca RA, Johnson NA, Brockerhoff SE, Mohapatra DP, MacArthur H, Panula P, Masino MA, Runnels LW, Cornell RA (2013) Abnormal differentiation of dopaminergic neurons in zebrafish trpm7 mutant larvae impairs development of the motor pattern. Dev Biol 386(2):428–439
Brauchi S, Krapivinsky G, Krapivinsky L, Clapham DE (2008) TRPM7 facilitates cholinergic vesicle fusion with the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(24):8304–8308
Middelbeek J, Vrenken K, Visser D, Lasonder E, Koster J, Jalink K, Clark K, van Leeuwen FN (2016) The TRPM7 interactome defines a cytoskeletal complex linked to neuroblastoma progression. Eur J Cell Biol 95(11):465–474
MacDonald JF, Belrose JC, Xie YF, Jackson MF (2012) Nonselective cation channels and links to hippocampal ischemia, aging, and dementia. Adv Exp Med Biol 961:433–447
Asrar S, Aarts M (2013) TRPM7, the cytoskeleton and neuronal death. Channels (Austin) 7(1):6–16
Visser D, Middelbeek J, van Leeuwen FN, Jalink K (2014) Function and regulation of the channel-kinase TRPM7 in health and disease. Eur J Cell Biol 93(10–12):455–465
Sun Y, Sukumaran P, Schaar A, Singh BB (2015) TRPM7 and its role in neurodegenerative diseases. Channels (Austin) 9(5):253–261
Yang CP, Zhang ZH, Zhang LH, Rui HC (2016) Neuroprotective role of MicroRNA-22 in a 6-hydroxydopamine-induced cell model of parkinson’s disease via regulation of its target gene TRPM7. J Mol Neurosci 60(4):445–452
Oh HG, Chung S (2017) Activation of transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7) channel increases basal autophagy and reduces amyloid beta-peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 493(1):494–499
Huang Y, Leng TD, Inoue K, Yang T, Liu M, Horgen FD, Fleig A, Li J, Xiong ZG (2018) TRPM7 channels play a role in high glucose-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and neuronal cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 293(37):14393–14406. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA117.001032
Zhang J, Zhao F, Zhao Y, Wang J, Pei L, Sun N, Shi J (2011) Hypoxia induces an increase in intracellular magnesium via transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7) channels in rat hippocampal neurons in vitro. J Biol Chem 286(23):20194–20207
Kim Y, Oh HG, Cho YY, Kwon OH, Park MK, Chung S (2016) Stress hormone potentiates Zn2 + -induced neurotoxicity via TRPM7 channel in dopaminergic neuron. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 470(2):362–367
Wei WL, Sun HS, Olah ME, Sun X, Czerwinska E, Czerwinski W, Mori Y, Orser BA, Xiong ZG, Jackson MF, Tymianski M, MacDonald JF (2007) TRPM7 channels in hippocampal neurons detect levels of extracellular divalent cations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(41):16323–16328
Nakashima AS, Dyck RH (2009) Zinc and cortical plasticity. Brain Res Rev 59(2):347–373
Slutsky I, Abumaria N, Wu LJ, Huang C, Zhang L, Li B, Zhao X, Govindarajan A, Zhao MG, Zhuo M, Tonegawa S, Liu G (2010) Enhancement of learning and memory by elevating brain magnesium. Neuron 65(2):165–177
Abumaria N, Yin B, Zhang L, Li XY, Chen T, Descalzi G, Zhao L, Ahn M, Luo L, Ran C, Zhuo M, Liu G (2011) Effects of elevation of brain magnesium on fear conditioning, fear extinction, and synaptic plasticity in the infralimbic prefrontal cortex and lateral amygdala. J Neurosci 31(42):14871–14881
Dribben WH, Eisenman LN, Mennerick S (2010) Magnesium induces neuronal apoptosis by suppressing excitability. Cell Death Dis 1:e63
Dodge FA Jr, Rahamimoff R (1967) Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol 193(2):419–432
Chubanov V, Schafer S, Ferioli S, Gudermann T (2014) Natural and synthetic modulators of the TRPM7 channel. Cells 3(4):1089–1101
Chubanov V, Ferioli S, Gudermann T (2017) Assessment of TRPM7 functions by drug-like small molecules. Cell Calcium 67:166–173
Prakriya M, Lewis RS (2002) Separation and characterization of currents through store-operated CRAC channels and Mg2 + -inhibited cation (MIC) channels. J Gen Physiol 119(5):487–507
Chokshi R, Fruasaha P, Kozak JA (2012) 2-Aminoethyl diphenyl borinate (2-APB) inhibits TRPM7 channels through an intracellular acidification mechanism. Channels 6(5):362–369
Kozak JA, Kerschbaum HH, Cahalan MD (2002) Distinct properties of CRAC and MIC channels in RBL cells. J Gen Physiol 120(2):221–235
Chen HC, Xie J, Zhang Z, Su LT, Yue L, Runnels LW (2010) Blockade of TRPM7 channel activity and cell death by inhibitors of 5-lipoxygenase. PLoS One 5(6):e11161
Chubanov V, Mederos Y, Schnitzler M, Meissner M, Schafer S, Abstiens K, Hofmann T, Gudermann T (2012) Natural and synthetic modulators of SK (K(ca)2) potassium channels inhibit magnesium-dependent activity of the kinase-coupled cation channel TRPM7. Br J Pharmacol 166(4):1357–1376
Siddiqui T, Lively S, Ferreira R, Wong R, Schlichter LC (2014) Expression and contributions of TRPM7 and KCa2.3/SK3 channels to the increased migration and invasion of microglia in anti-inflammatory activation states. PLoS One. 9(8):e106087. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0106087
Leng TD, Lin J, Sun HW, Zeng Z, O’Bryant Z, Inoue K, Xiong ZG (2015) Local anesthetic lidocaine inhibits TRPM7 current and TRPM7-mediated zinc toxicity. CNS Neurosci Ther 21(1):32–39
Parnas M, Peters M, Dadon D, Lev S, Vertkin I, Slutsky I, Minke B (2009) Carvacrol is a novel inhibitor of Drosophila TRPL and mammalian TRPM7 channels. Cell Calcium 45(3):300–309
Zierler S, Yao G, Zhang Z, Kuo WC, Porzgen P, Penner R, Horgen FD, Fleig A (2011) Waixenicin A inhibits cell proliferation through magnesium-dependent block of transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7) channels. J Biol Chem 286(45):39328–39335
Qin X, Yue ZC, Sun BN, Yang WZ, Xie J, Ni E, Feng Y, Mahmood R, Zhang YH, Yue LX (2013) Sphingosine and FTY720 are potent inhibitors of the transient receptor potential melastatin 7 (TRPM7) channels. Br J Pharmacol 168(6):1294–1312
Hofmann T, Schafer S, Linseisen M, Sytik L, Gudermann T, Chubanov V (2014) Activation of TRPM7 channels by small molecules under physiological conditions. Pflugers Arch. 466(12):2177–2189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-014-1488-0
Ryazanova LV, Dorovkov MV, Ansari A, Ryazanov AG (2004) Characterization of the protein kinase activity of TRPM7/ChaK1, a protein kinase fused to the transient receptor potential ion channel. J Biol Chem 279(5):3708–3716
Soltoff SP (2007) Rottlerin: an inappropriate and ineffective inhibitor of PKC delta. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28(9):453–458
Song C, Bae Y, Jun J, Lee H, Kim ND, Lee KB, Hur W, Park JY, Sim T (2017) Identification of TG100-115 as a new and potent TRPM7 kinase inhibitor, which suppresses breast cancer cell migration and invasion. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1861(4):947–957
Doukas J, Wrasidlo W, Noronha G, Dneprovskaia E, Fine R, Weis S, Hood J, Demaria A, Soll R, Cheresh D (2006) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma/delta inhibition limits infarct size after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(52):19866–19871
Ikonomidou C, Turski L (2002) Why did NMDA receptor antagonists fail clinical trials for stroke and traumatic brain injury? Lancet Neurol 1(6):383–386
Clarkson AN, Huang BS, Macisaac SE, Mody I, Carmichael ST (2010) Reducing excessive GABA-mediated tonic inhibition promotes functional recovery after stroke. Nature 468(7321):305–309
Li S, Overman JJ, Katsman D, Kozlov SV, Donnelly CJ, Twiss JL, Giger RJ, Coppola G, Geschwind DH, Carmichael ST (2010) An age-related sprouting transcriptome provides molecular control of axonal sprouting after stroke. Nat Neurosci 13(12):1496–1504
Overman JJ, Clarkson AN, Wanner IB, Overman WT, Eckstein I, Maguire JL, Dinov ID, Toga AW, Carmichael ST (2012) A role for ephrin-A5 in axonal sprouting, recovery, and activity-dependent plasticity after stroke. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(33):E2230–E2239
Kurosinski P, Guggisberg M, Gotz J (2002) Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease-overlapping or synergistic pathologies? Trends Mol Med 8(1):3–5
Anandhan A, Jacome MS, Lei S, Hernandez-Franco P, Pappa A, Panayiotidis MI, Powers R, Franco R (2017) Metabolic dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: bioenergetics, redox homeostasis and central carbon metabolism. Brain Res Bull 133:12–30
Cardoso S, Seica R, Moreira PI (2017) Diabesity and brain energy metabolism: the case of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv Neurobiol 19:117–150
DeKosky ST, Scheff SW (1990) Synapse loss in frontal cortex biopsies in Alzheimer’s disease: correlation with cognitive severity. Ann Neurol 27(5):457–464
Bellucci A, Mercuri NB, Venneri A, Faustini G, Longhena F, Pizzi M, Missale C, Spano P (2016) Review: Parkinson’s disease: from synaptic loss to connectome dysfunction. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 42(1):77–94
Andrasi E, Igaz S, Molnar Z, Mako S (2000) Disturbances of magnesium concentrations in various brain areas in Alzheimer’s disease. Magnes Res 13(3):189–196
Andrasi E, Pali N, Molnar Z, Kosel S (2005) Brain aluminum, magnesium and phosphorus contents of control and Alzheimer-diseased patients. J Alzheimers Dis 7(4):273–284
Bai J, Zhang Z, Liu M, Li C (2015) alpha-synuclein-lanthanide metal ions interaction: binding sites, conformation and fibrillation. BMC Biophys 9:1
Landman N, Jeong SY, Shin SY, Voronov SV, Serban G, Kang MS, Park MK, Di Paolo G, Chung S, Kim TW (2006) Presenilin mutations linked to familial Alzheimer’s disease cause an imbalance in phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(51):19524–19529
Deng Y, Wei J, Cheng J, Zhong P, Xiong Z, Liu A, Lin L, Chen S, Yan Z (2016) Partial amelioration of synaptic and cognitive deficits by inhibiting cofilin dephosphorylation in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 53(4):1419–1432
Acknowledgements
Supported by the Natural Science Foundation (NSF) of China Grants (81573408 and 81270048), Fudan University-Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of science joint Grant (FU-SIMM20174015) and NSF of Shanghai Grant (16ZR1403200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abumaria, N., Li, W. & Clarkson, A.N. Role of the chanzyme TRPM7 in the nervous system in health and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 76, 3301–3310 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03124-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03124-2