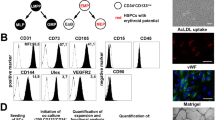
Abstract
Cellular pro-angiogenic therapies may be applicable for the treatment of peripheral vascular diseases. Interactions between mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) may provide such a treatment option. With the exception of some studies in man, experiments have only been performed in immunodeficient mice and rats. We studied an immunocompetent syngeneic mouse model. We isolated MSCs from bone marrow and EPCs from the lung of adult C57/Bl.6 mice and co-injected them in Matrigel subcutaneously in adult C57/Bl.6 mice. We demonstrate development of both blood vessels and lymphatics. Grafted EPCs integrated into the lining of the two vessel types, whereas MSCs usually did not incorporate into the vessel wall. Injections of each separate cell type did not, or hardly, reveal de novo angiogenesis. The release of VEGF-A by MSCs has been shown before, but its inhibitors, e.g., soluble VEGF receptors, have not been studied. We performed qualitative and quantitative studies of the proteins released by EPCs, MSCs, and cocultures of the cells. Despite the secretion of VEGF inhibitors (sVEGFR-1, sVEGFR-2) by EPCs, VEGF-A was secreted by MSCs at bioavailable amounts (350 pg/ml). We confirm the secretion of PlGF, FGF-1, MCP-1, and PDGFs by EPCs/MSCs and suggest functions for VEGF-B, amphiregulin, fractalkine, CXCL10, and CXCL16 during MSC-induced hem- and lymphangiogenesis. We assume that lymphangiogenesis is induced indirectly by growth factors from immigrating leukocytes, which we found in close association with the lymphatic networks. Inflammatory responses to the cellular markers GFP and cell-tracker red (CMPTX) used for tracing of EPCs or MSCs were not observed. Our studies demonstrate the feasibility of pro-angiogenic/lymphangiogenic therapies in immunocompetent animals and indicate new MSC/EPC-derived angiogenic factors.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Isner JM, Pieczek A, Schainfeld R, Blair R, Haley L, Asahara T, Rosenfield K, Razvi S, Walsh K, Symes JF (1996) Clinical evidence of angiogenesis after arterial gene transfer of phVEGF165 in patient with ischaemic limb. Lancet 348:370–374
Caplan AI, Correa D (2011) The MSC: an injury drugstore. Cell Stem Cell 9:11–15
Lin RZ, Moreno-Luna R, Zhou B, Pu WT, Melero-Martin JM (2012) Equal modulation of endothelial cell function by four distinct tissue-specific mesenchymal stem cells. Angiogenesis 15:443–455
Tammela T, Alitalo K (2010) Lymphangiogenesis: molecular mechanisms and future promise. Cell 140:460–476
Au P, Tam J, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2008) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells facilitate engineering of long-lasting functional vasculature. Blood 111:4551–4558
Melero-Martin JM, De Obaldia ME, Kang SY, Khan ZA, Yuan L, Oettgen P, Bischoff J (2008) Engineering robust and functional vascular networks in vivo with human adult and cord blood-derived progenitor cells. Circ Res 103:194–202
Seebach C, Henrich D, Wilhelm K, Barker JH, Marzi I (2012) Endothelial progenitor cells improve directly and indirectly early vascularization of mesenchymal stem cell-driven bone regeneration in a critical bone defect in rats. Cell Transplant
Usami K, Mizuno H, Okada K, Narita Y, Aoki M, Kondo T, Mizuno D, Mase J, Nishiguchi H, Kagami H, Ueda M (2009) Composite implantation of mesenchymal stem cells with endothelial progenitor cells enhances tissue-engineered bone formation. J Biomed Mater Res A 90:730–741
Sales VL, Mettler BA, Lopez-Ilasaca M, Johnson JA Jr, Mayer JE Jr (2007) Endothelial progenitor and mesenchymal stem cell-derived cells persist in tissue-engineered patch in vivo: application of green and red fluorescent protein-expressing retroviral vector. Tissue Eng 13:525–535
Dubois C, Liu X, Claus P et al (2010) Differential effects of progenitor cell populations on left ventricular remodeling and myocardial neovascularization after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:2232–2243
Lasala GP, Silva JA, Kusnick BA, Minguell JJ (2011) Combination stem cell therapy for the treatment of medically refractory coronary ischemia: a Phase I study. Cardiovasc Revasc Med 12:29–34
Schniedermann J, Rennecke M, Buttler K, Richter G, Stadtler AM, Norgall S, Badar M, Barleon B, May T, Wilting J, Weich HA (2010) Mouse lung contains endothelial progenitors with high capacity to form blood and lymphatic vessels. BMC Cell Biol 11:50
Hemmen K, Reinl T, Buttler K, Behler F, Dieken H, Jansch L, Wilting J, Weich HA (2011) High-resolution mass spectrometric analysis of the secretome from mouse lung endothelial progenitor cells. Angiogenesis 14:163–172
Alajati A, Laib AM, Weber H, Boos AM, Bartol A, Ikenberg K, Korff T, Zentgraf H, Obodozie C, Graeser R, Christian S, Finkenzeller G, Stark GB, Heroult M, Augustin HG (2008) Spheroid-based engineering of a human vasculature in mice. Nat Methods 5:439–445
Alvarez DF, Huang L, King JA, ElZarrad MK, Yoder MC, Stevens T (2008) Lung microvascular endothelium is enriched with progenitor cells that exhibit vasculogenic capacity. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294:L419–L430
Timmermans F, Plum J, Yoder MC, Ingram DA, Vandekerckhove B, Case J (2009) Endothelial progenitor cells: identity defined? J Cell Mol Med 13:87–102
Tartour E, Pere H, Maillere B, Terme M, Merillon N, Taieb J, Sandoval F, Quintin-Colonna F, Lacerda K, Karadimou A, Badoual C, Tedgui A, Fridman WH, Oudard S (2011) Angiogenesis and immunity: a bidirectional link potentially relevant for the monitoring of antiangiogenic therapy and the development of novel therapeutic combination with immunotherapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev 30:83–95
Wilting J, Becker J, Buttler K, Weich HA (2009) Lymphatics and Inflammation. Curr Med Chem 16:4581–4592
Soleimani M, Nadri S (2009) A protocol for isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse bone marrow. Nat Protoc 4:102–106
Hoffmann A, Pelled G, Turgeman G, Eberle P, Zilberman Y, Shinar H, Keinan-Adamsky K, Winkel A, Shahab S, Navon G, Gross G, Gazit D (2006) Neotendon formation induced by manipulation of the Smad8 signalling pathway in mesenchymal stem cells. J Clin Invest 116:940–952
Beckermann BM, Kallifatidis G, Groth A, Frommhold D, Apel A, Mattern J, Salnikov AV, Moldenhauer G, Wagner W, Diehlmann A, Saffrich R, Schubert M, Ho AD, Giese N, Buchler MW, Friess H, Buchler P, Herr I (2008) VEGF expression by mesenchymal stem cells contributes to angiogenesis in pancreatic carcinoma. Br J Cancer 99:622–631
Bando H, Brokelmann M, Toi M, Alitalo K, Sleeman JP, Sipos B, Grone HJ, Weich HA (2004) Immunodetection and quantification of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 in human malignant tumor tissues. Int J Cancer 111:184–191
Bergmann A, Ahmad S, Cudmore M, Gruber AD, Wittschen P, Lindenmaier W, Christofori G, Gross V, Gonzalves A, Grone HJ, Ahmed A, Weich HA (2010) Reduction of circulating soluble Flt-1 alleviates preeclampsia-like symptoms in a mouse model. J Cell Mol Med 14:1857–1867
Weich HA, Bando H, Brokelmann M, Baumann P, Toi M, Barleon B, Alitalo K, Sipos B, Sleeman J (2004) Quantification of vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) by a novel ELISA. J Immunol Methods 285:145–155
Kinnaird T, Stabile E, Burnett MS, Shou M, Lee CW, Barr S, Fuchs S, Epstein SE (2004) Local delivery of marrow-derived stromal cells augments collateral perfusion through paracrine mechanisms. Circulation 109:1543–1549
Albuquerque RJ, Hayashi T, Cho WG et al (2009) Alternatively spliced vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 is an essential endogenous inhibitor of lymphatic vessel growth. Nat Med 15:1023–1030
Ambati BK, Nozaki M, Singh N et al (2006) Corneal avascularity is due to soluble VEGF receptor-1. Nature 443:993–997
Hornig C, Barleon B, Ahmad S, Vuorela P, Ahmed A, Weich HA (2000) Release and complex formation of soluble VEGFR-1 from endothelial cells and biological fluids. Lab Invest 80:443–454
Iwasaki H, Kawamoto A, Tjwa M, Horii M, Hayashi S, Oyamada A, Matsumoto T, Suehiro S, Carmeliet P, Asahara T (2011) PlGF repairs myocardial ischemia through mechanisms of angiogenesis, cardioprotection and recruitment of myo-angiogenic competent marrow progenitors. PLoS ONE 6:e24872
Yamane S, Ishida S, Hanamoto Y, Kumagai K, Masuda R, Tanaka K, Shiobara N, Yamane N, Mori T, Juji T, Fukui N, Itoh T, Ochi T, Suzuki R (2008) Proinflammatory role of amphiregulin, an epidermal growth factor family member whose expression is augmented in rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Inflamm (Lond) 5:5
Konerding MA, Gibney BC, Houdek JP, Chamoto K, Ackermann M, Lee GS, Lin M, Tsuda A, Mentzer SJ (2012) Spatial dependence of alveolar angiogenesis in post-pneumonectomy lung growth. Angiogenesis 15:23–32
Hsia CC (2004) Lessons from a canine model of compensatory lung growth. Curr Top Dev Biol 64:17–32
Laros CD, Westermann CJ (1987) Dilatation, compensatory growth, or both after pneumonectomy during childhood and adolescence. A thirty-year follow-up study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 93:570–576
Baluk P, Tammela T, Ator E, Lyubynska N, Achen MG, Hicklin DJ, Jeltsch M, Petrova TV, Pytowski B, Stacker SA, Yla-Herttuala S, Jackson DG, Alitalo K, McDonald DM (2005) Pathogenesis of persistent lymphatic vessel hyperplasia in chronic airway inflammation. J Clin Invest 115:247–257
Traktuev DO, Prater DN, Merfeld-Clauss S, Sanjeevaiah AR, Saadatzadeh MR, Murphy M, Johnstone BH, Ingram DA, March KL (2009) Robust functional vascular network formation in vivo by cooperation of adipose progenitor and endothelial cells. Circ Res 104:1410–1420
Foubert P, Matrone G, Souttou B, Lere-Dean C, Barateau V, Plouet J, Le Ricousse-Roussanne S, Levy BI, Silvestre JS, Tobelem G (2008) Coadministration of endothelial and smooth muscle progenitor cells enhances the efficiency of proangiogenic cell-based therapy. Circ Res 103:751–760
Breiteneder-Geleff S, Soleiman A, Kowalski H, Horvat R, Amann G, Kriehuber E, Diem K, Weninger W, Tschachler E, Alitalo K, Kerjaschki D (1999) Angiosarcomas express mixed endothelial phenotypes of blood and lymphatic capillaries: podoplanin as a specific marker for lymphatic endothelium. Am J Pathol 154:385–394
Wilting J, Papoutsi M, Christ B, Nicolaides KH, von Kaisenberg CS, Borges J, Stark GB, Alitalo K, Tomarev SI, Niemeyer C, Rossler J (2002) The transcription factor Prox1 is a marker for lymphatic endothelial cells in normal and diseased human tissues. FASEB J 16:1271–1273
Liu HS, Jan MS, Chou CK, Chen PH, Ke NJ (1999) Is green fluorescent protein toxic to the living cells? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 260:712–717
Grabski E, Waibler Z, Schule S, Kloke BP, Sender LY, Panitz S, Cichutek K, Schweizer M, Kalinke U (2011) Comparative analysis of transduced primary human dendritic cells generated by the use of three different lentiviral vector systems. Mol Biotechnol 47:262–269
Kawakami N, Sakane N, Nishizawa F, Iwao M, Fukada SI, Tsujikawa K, Kohama Y, Ikawa M, Okabe M, Yamamoto H (1999) Green fluorescent protein-transgenic mice: immune functions and their application to studies of lymphocyte development. Immunol Lett 70:165–171
Rehman J, Traktuev D, Li J, Merfeld-Clauss S, Temm-Grove CJ, Bovenkerk JE, Pell CL, Johnstone BH, Considine RV, March KL (2004) Secretion of angiogenic and antiapoptotic factors by human adipose stromal cells. Circulation 109:1292–1298
Shibuya M (2001) Structure and dual function of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (Flt-1). Int J Biochem Cell Biol 33:409–420
Vuorela P, Helske S, Hornig C, Alitalo K, Weich H, Halmesmaki E (2000) Amniotic fluid–soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 in preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol 95:353–357
Laib AM, Bartol A, Alajati A, Korff T, Weber H, Augustin HG (2009) Spheroid-based human endothelial cell microvessel formation in vivo. Nat Protoc 4:1202–1215
Karakida S, Kawano Y, Utsunomiya Y, Furukawa Y, Sasaki T, Narahara H (2011) Effect of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor and amphiregulin on the MAP kinase-induced production of vascular endothelial growth factor by human granulosa cells. Growth Factors 29:271–277
Olofsson B, Pajusola K, Kaipainen A, von Euler G, Joukov V, Saksela O, Orpana A, Pettersson RF, Alitalo K, Eriksson U (1996) Vascular endothelial growth factor B, a novel growth factor for endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:2576–2581
Cudmore MJ, Hewett PW, Ahmad S, Wang KQ, Cai M, Al-Ani B, Fujisawa T, Ma B, Sissaoui S, Ramma W, Miller MR, Newby DE, Gu Y, Barleon B, Weich H, Ahmed A (2012) The role of heterodimerization between VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 in the regulation of endothelial cell homeostasis. Nat Commun 3:972
Carmeliet P, Moons L, Luttun A et al (2001) Synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor contributes to angiogenesis and plasma extravasation in pathological conditions. Nat Med 7:575–583
Hauser S, Weich HA (1993) A heparin-binding form of placenta growth factor (PlGF-2) is expressed in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and in placenta. Growth Factors 9:259–268
Oh SJ, Kurz H, Christ B, Wilting J (1998) Platelet-derived growth factor-B induces transformation of fibrocytes into spindle-shaped myofibroblasts in vivo. Histochem Cell Biol 109:349–357
Jeltsch M, Kaipainen A, Joukov V, Meng X, Lakso M, Rauvala H, Swartz M, Fukumura D, Jain RK, Alitalo K (1997) Hyperplasia of lymphatic vessels in VEGF-C transgenic mice. Science 276:1423–1425
Oh SJ, Jeltsch MM, Birkenhager R, McCarthy JE, Weich HA, Christ B, Alitalo K, Wilting J (1997) VEGF and VEGF-C: specific induction of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in the differentiated avian chorioallantoic membrane. Dev Biol 188:96–109
Bohmer R, Neuhaus B, Buhren S, Zhang D, Stehling M, Bock B, Kiefer F (2010) Regulation of developmental lymphangiogenesis by Syk(+) leukocytes. Dev Cell 18:437–449
Bazan JF, Bacon KB, Hardiman G, Wang W, Soo K, Rossi D, Greaves DR, Zlotnik A, Schall TJ (1997) A new class of membrane-bound chemokine with a CX3C motif. Nature 385:640–644
Shimaoka T, Kume N, Minami M, Hayashida K, Kataoka H, Kita T, Yonehara S (2000) Molecular cloning of a novel scavenger receptor for oxidized low density lipoprotein, SR-PSOX, on macrophages. J Biol Chem 275:40663–40666
Rhode A, Pauza ME, Barral AM, Rodrigo E, Oldstone MB, von Herrath MG, Christen U (2005) Islet-specific expression of CXCL10 causes spontaneous islet infiltration and accelerates diabetes development. J Immunol 175:3516–3524
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Tobias May for providing lentiviral vectors and Mrs. B. Pawletta and Mrs. I. Hollatz for their expert technical assistance in progenitor cell culture. Many thanks to Mr. B. Manshausen for his valuable contribution to the preparation of immunohistological specimens.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
18_2013_1460_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary material 1 Secretion of angiogenesis regulators from MSCs, EPCs and co-cultures. Mouse angiogenesis antibody-array analysis of conditioned media from MSCs, EPCs and co-cultures after 72 h. 1 ml of the conditioned media was applied to each array. Graphs represent the mean pixel density of each two spots. Densitometric analysis was performed with ImageJ 1.40 g. Note the absence of VEGF-A in the co-cultures (TIFF 6483 kb)
Supplementary material 2 Three-dimensional representation of EPCs in de novo formed vessels. Matrigel plugs containing MSCs and GFP-transfected EPCs (ratio 1:1). Immunofluorescence studies with anti-CD31 (red) and anti-GFP (green) antibodies show de novo formation of vessels by endothelial cells of the host and GFP-transfected EPCs. Note the integration of GFP+ EPC into a CD31+ vessel. Magnification 400× (MPG 3866 kb)
Supplementary material 3 Three-dimensional representation of EPCs in de novo formed lymphatics. Matrigel plugs containing MSCs and GFP-transfected EPCs (ratio 1:1). Immunofluorescence studies with anti-podoplanin+ (red) and anti-GFP+ (green). GFP-positive cells are observed in podoplanin+ lymphatics. Cells only positive for GFP obviously demonstrate newly formed blood vessels. Magnification 200× (MPG 3882 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buttler, K., Badar, M., Seiffart, V. et al. De novo hem- and lymphangiogenesis by endothelial progenitor and mesenchymal stem cells in immunocompetent mice. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 71, 1513–1527 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-013-1460-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-013-1460-8