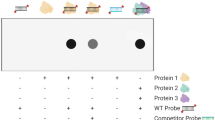
Abstract
Sequence-specific protein-DNA interactions (PDIs) are critical for regulating many cellular processes, including transcription, DNA replication, repair, and rearrangement. We review recent experimental advances in high-throughput technologies designed to characterize PDIs and discuss recent studies that use these tools, including ChIP-chip/seq, SELEX-based approaches, yeast one-hybrid, bacterial one-hybrid, protein binding microarray, and protein microarray. The results of these studies have challenged some long-standing concepts of PDI and provide valuable insights into the complex transcriptional regulatory networks.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Darnell JE Jr (2002) Transcription factors as targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2:740–749
Lane D, Prentki P, Chandler M (1992) Use of gel retardation to analyze protein-nucleic acid interactions. Microbiol Rev 56:509–528
Hampshire AJ, Rusling DA, Broughton-Head VJ, Fox KR (2007) Footprinting: a method for determining the sequence selectivity, affinity and kinetics of DNA-binding ligands. Methods 42:128–140
Tuerk C, Gold L (1990) Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 249:505–510
Wingender E, Dietze P, Karas H, Knuppel R (1996) TRANSFAC: a database on transcription factors and their DNA binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res 24:238–241
Sandelin A, Alkema W, Engstrom P, Wasserman WW, Lenhard B (2004) JASPAR: an open-access database for eukaryotic transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D91–D94
Walhout AJ (2006) Unraveling transcription regulatory networks by protein-DNA and protein-protein interaction mapping. Genome Res 16:1445–1454
Vaquerizas JM, Kummerfeld SK, Teichmann SA, Luscombe NM (2009) A census of human transcription factors: function, expression and evolution. Nat Rev Genet 10:252–263
Massie CE, Mills IG (2008) ChIPping away at gene regulation. EMBO Rep 9:337–343
Iyer VR, Horak CE, Scafe CS, Botstein D, Snyder M, Brown PO (2001) Genomic binding sites of the yeast cell-cycle transcription factors SBF and MBF. Nature 409:533–538
Ren B, Robert F, Wyrick JJ, Aparicio O, Jennings EG, Simon I, Zeitlinger J, Schreiber J, Hannett N, Kanin E et al (2000) Genome-wide location and function of DNA binding proteins. Science 290:2306–2309
Wei CL, Wu Q, Vega VB, Chiu KP, Ng P, Zhang T, Shahab A, Yong HC, Fu Y, Weng Z et al (2006) A global map of p53 transcription-factor binding sites in the human genome. Cell 124:207–219
Johnson DS, Mortazavi A, Myers RM, Wold B (2007) Genome-wide mapping of in vivo protein-DNA interactions. Science 316:1497–1502
Robertson G, Hirst M, Bainbridge M, Bilenky M, Zhao Y, Zeng T, Euskirchen G, Bernier B, Varhol R, Delaney A et al (2007) Genome-wide profiles of STAT1 DNA association using chromatin immunoprecipitation and massively parallel sequencing. Nat Methods 4:651–657
Harbison CT, Gordon DB, Lee TI, Rinaldi NJ, Macisaac KD, Danford TW, Hannett NM, Tagne JB, Reynolds DB, Yoo J et al (2004) Transcriptional regulatory code of a eukaryotic genome. Nature 431:99–104
Lee TI, Rinaldi NJ, Robert F, Odom DT, Bar-Joseph Z, Gerber GK, Hannett NM, Harbison CT, Thompson CM, Simon I et al (2002) Transcriptional regulatory networks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science 298:799–804
Gordan R, Hartemink AJ, Bulyk ML (2009) Distinguishing direct versus indirect transcription factor-DNA interactions. Genome Res 19:2090–2100
Matys V, Kel-Margoulis OV, Fricke E, Liebich I, Land S, Barre-Dirrie A, Reuter I, Chekmenev D, Krull M, Hornischer K et al (2006) TRANSFAC and its module TRANSCompel: transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D108–D110
Roulet E, Busso S, Camargo AA, Simpson AJ, Mermod N, Bucher P (2002) High-throughput SELEX SAGE method for quantitative modeling of transcription-factor binding sites. Nat Biotechnol 20:831–835
Jolma A, Kivioja T, Toivonen J, Cheng L, Wei G, Enge M, Taipale M, Vaquerizas JM, Yan J, Sillanpaa MJ et al (2010) Multiplexed massively parallel SELEX for characterization of human transcription factor binding specificities. Genome Res 20:861–873
Bulyk ML, Huang X, Choo Y, Church GM (2001) Exploring the DNA-binding specificities of zinc fingers with DNA microarrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:7158–7163
Warren CL, Kratochvil NC, Hauschild KE, Foister S, Brezinski ML, Dervan PB, Phillips GN Jr, Ansari AZ (2006) Defining the sequence-recognition profile of DNA-binding molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:867–872
Berger MF, Philippakis AA, Qureshi AM, He FS, Estep PW 3rd, Bulyk ML (2006) Compact, universal DNA microarrays to comprehensively determine transcription-factor binding site specificities. Nat Biotechnol 24:1429–1435
Berger MF, Badis G, Gehrke AR, Talukder S, Philippakis AA, Pena-Castillo L, Alleyne TM, Mnaimneh S, Botvinnik OB, Chan ET et al (2008) Variation in homeodomain DNA binding revealed by high-resolution analysis of sequence preferences. Cell 133:1266–1276
Badis G, Chan ET, van Bakel H, Pena-Castillo L, Tillo D, Tsui K, Carlson CD, Gossett AJ, Hasinoff MJ, Warren CL et al (2008) A library of yeast transcription factor motifs reveals a widespread function for Rsc3 in targeting nucleosome exclusion at promoters. Mol Cell 32:878–887
Zhu C, Byers KJ, McCord RP, Shi Z, Berger MF, Newburger DE, Saulrieta K, Smith Z, Shah MV, Radhakrishnan M et al (2009) High-resolution DNA-binding specificity analysis of yeast transcription factors. Genome Res 19:556–566
Badis G, Berger MF, Philippakis AA, Talukder S, Gehrke AR, Jaeger SA, Chan ET, Metzler G, Vedenko A, Chen X et al (2009) Diversity and complexity in DNA recognition by transcription factors. Science 324:1720–1723
Chen CY, Schwartz RJ (1995) Identification of novel DNA binding targets and regulatory domains of a murine tinman homeodomain factor, nkx-2.5. J Biol Chem 270:15628–15633
Yokoe H, Anholt RR (1993) Molecular cloning of olfactomedin, an extracellular matrix protein specific to olfactory neuroepithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:4655–4659
Li JJ, Herskowitz I (1993) Isolation of ORC6, a component of the yeast origin recognition complex by a one-hybrid system. Science 262:1870–1874
Reece-Hoyes JS, Deplancke B, Barrasa MI, Hatzold J, Smit RB, Arda HE, Pope PA, Gaudet J, Conradt B, Walhout AJ (2009) The C. elegans Snail homolog CES-1 can activate gene expression in vivo and share targets with bHLH transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res 37:3689–3698
Zeng J, Yan J, Wang T, Mosbrook-Davis D, Dolan KT, Christensen R, Stormo GD, Haussler D, Lathrop RH, Brachmann RK et al (2008) Genome wide screens in yeast to identify potential binding sites and target genes of DNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e8
Deplancke B, Dupuy D, Vidal M, Walhout AJ (2004) A gateway-compatible yeast one-hybrid system. Genome Res 14:2093–2101
Deplancke B, Mukhopadhyay A, Ao W, Elewa AM, Grove CA, Martinez NJ, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Reece-Hoyes JS, Hope IA et al (2006) A gene-centered C. elegans protein-DNA interaction network. Cell 125:1193–1205
Meng X, Brodsky MH, Wolfe SA (2005) A bacterial one-hybrid system for determining the DNA-binding specificity of transcription factors. Nat Biotechnol 23:988–994
Noyes MB, Christensen RG, Wakabayashi A, Stormo GD, Brodsky MH, Wolfe SA (2008) Analysis of homeodomain specificities allows the family-wide prediction of preferred recognition sites. Cell 133:1277–1289
Chen CS, Zhu H (2006) Protein microarrays. Biotechniques 40:423, 425, 427 passim
Tao SC, Chen CS, Zhu H (2007) Applications of protein microarray technology. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 10:706–718
Zhu J, Gopinath K, Murali A, Yi G, Hayward SD, Zhu H, Kao C (2007) RNA-binding proteins that inhibit RNA virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3129–3134
Tao SC, Li Y, Zhou J, Qian J, Schnaar RL, Zhang Y, Goldstein IJ, Zhu H, Schneck JP (2008) Lectin microarrays identify cell-specific and functionally significant cell surface glycan markers. Glycobiology 18:761–769
Hu S, Xie Z, Onishi A, Yu X, Jiang L, Lin J, Rho HS, Woodard C, Wang H, Jeong JS et al (2009) Profiling the human protein-DNA interactome reveals ERK2 as a transcriptional repressor of interferon signaling. Cell 139:610–622
Zhu J, Liao G, Shan L, Zhang J, Chen MR, Hayward GS, Hayward SD, Desai P, Zhu H (2009) Protein array identification of substrates of the Epstein-Barr virus protein kinase BGLF4. J Virol 83:5219–5231
Chen H, Hewison M, Adams JS (2006) Functional characterization of heterogeneous nuclear ribonuclear protein C1/C2 in vitamin D resistance: a novel response element-binding protein. J Biol Chem 281:39114–39120
Hall DA, Zhu H, Zhu X, Royce T, Gerstein M, Snyder M (2004) Regulation of gene expression by a metabolic enzyme. Science 306:482–484
Ho SW, Jona G, Chen CT, Johnston M, Snyder M (2006) Linking DNA-binding proteins to their recognition sequences by using protein microarrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:9940–9945
Ptacek J, Devgan G, Michaud G, Zhu H, Zhu X, Fasolo J, Guo H, Jona G, Breitkreutz A, Sopko R et al (2005) Global analysis of protein phosphorylation in yeast. Nature 438:679–684
Zhu H, Bilgin M, Bangham R, Hall D, Casamayor A, Bertone P, Lan N, Jansen R, Bidlingmaier S, Houfek T et al (2001) Global analysis of protein activities using proteome chips. Science 293:2101–2105
Lin J, Xie Z, Zhu H, Qian J (2010) Understanding protein phosphorylation on a systems level. Brief Funct Genomics 9:32–42
Gong W, He K, Covington M, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Snyder M, Harmer SL, Zhu YX, Deng XW (2008) The development of protein microarrays and their applications in DNA-protein and protein-protein interaction analyses of Arabidopsis transcription factors. Mol Plant 1:27–41
Elemento O, Slonim N, Tavazoie S (2007) A universal framework for regulatory element discovery across all genomes and data types. Mol Cell 28:337–350
Elemento O, Tavazoie S (2005) Fast and systematic genome-wide discovery of conserved regulatory elements using a non-alignment based approach. Genome Biol 6:R18
Xie X, Lu J, Kulbokas EJ, Golub TR, Mootha V, Lindblad-Toh K, Lander ES, Kellis M (2005) Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in human promoters and 3’ UTRs by comparison of several mammals. Nature 434:338–345
Xie X, Mikkelsen TS, Gnirke A, Lindblad-Toh K, Kellis M, Lander ES (2007) Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in conserved regions of the human genome, including thousands of CTCF insulator sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:7145–7150
Yu X, Lin J, Zack DJ, Qian J (2006) Computational analysis of tissue-specific combinatorial gene regulation: predicting interaction between transcription factors in human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res 34:4925–4936
Xie Z, Hu S, Blackshaw S, Zhu H, Qian J (2010) hPDI: a database of experimental human protein–DNA interactions. Bioinformatics 26(2):287–289
Kissinger CR, Liu BS, Martin-Blanco E, Kornberg TB, Pabo CO (1990) Crystal structure of an engrailed homeodomain-DNA complex at 2.8 A resolution: a framework for understanding homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell 63:579–590
Wolberger C, Vershon AK, Liu B, Johnson AD, Pabo CO (1991) Crystal structure of a MAT alpha 2 homeodomain-operator complex suggests a general model for homeodomain-DNA interactions. Cell 67:517–528
Affolter M, Slattery M, Mann RS (2008) A lexicon for homeodomain-DNA recognition. Cell 133:1133–1135
Treisman J, Gonczy P, Vashishtha M, Harris E, Desplan C (1989) A single amino acid can determine the DNA binding specificity of homeodomain proteins. Cell 59:553–562
Wolfe SA, Grant RA, Elrod-Erickson M, Pabo CO (2001) Beyond the “recognition code”: structures of two Cys2His2 zinc finger/TATA box complexes. Structure 9:717–723
Dioum EM, Wauson EM, Cobb MH (2009) MAP-ping unconventional protein-DNA interactions. Cell 139:462–463
Casci T (2009) Gene expression: regulators hidden in human proteome. Nat Rev Genet 10:820
Gancedo C, Flores CL (2008) Moonlighting proteins in yeasts. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 72:197–210
Huberts DHEW, van der Klei IJ (2010) Moonlighting proteins: an intriguing mode of multitasking. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1803:520–525
Carroll JS, Liu XS, Brodsky AS, Li W, Meyer CA, Szary AJ, Eeckhoute J, Shao W, Hestermann EV, Geistlinger TR et al (2005) Chromosome-wide mapping of estrogen receptor binding reveals long-range regulation requiring the forkhead protein FoxA1. Cell 122:33–43
Carr A, Biggin MD (1999) A comparison of in vivo and in vitro DNA-binding specificities suggests a new model for homeoprotein DNA binding in Drosophila embryos. Embo J 18:1598–1608
Wei GH, Badis G, Berger MF, Kivioja T, Palin K, Enge M, Bonke M, Jolma A, Varjosalo M, Gehrke AR et al (2010) Genome-wide analysis of ETS-family DNA-binding in vitro and in vivo. Embo J 29:2147–2160
Horie-Inoue K, Takayama K, Bono HU, Ouchi Y, Okazaki Y, Inoue S (2006) Identification of novel steroid target genes through the combination of bioinformatics and functional analysis of hormone response elements. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 339:99–106
Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK (2001) Coregulator codes of transcriptional regulation by nuclear receptors. J Biol Chem 276:36865–36868
Simpson RT (1990) Nucleosome positioning can affect the function of a cis-acting DNA element in vivo. Nature 343:387–389
Hallikas OK, Aaltonen JM, von Koskull H, Lindberg LA, Valmu L, Kalkkinen N, Wahlstrom T, Kataoka H, Andersson L, Lindholm D et al (2006) Identification of antibodies against HAI-1 and integrin alpha6beta4 as immunohistochemical markers of human villous cytotrophoblast. J Histochem Cytochem 54:745–752
Fordyce PM, Gerber D, Tran D, Zheng J, Li H, DeRisi JL, Quake SR (2010) De novo identification and biophysical characterization of transcription-factor binding sites with microfluidic affinity analysis. Nat Biotechnol 28:970–975
Ptashne M, Gann A (2002) Genes and signals. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Carlson CD, Warren CL, Hauschild KE, Ozers MS, Qadir N, Bhimsaria D, Lee Y, Cerrina F, Ansari AZ (2010) Specificity landscapes of DNA binding molecules elucidate biological function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:4544–4549
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE (2000) The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res 28:235–242
Rohs R, Jin X, West SM, Joshi R, Honig B, Mann RS (2010) Origins of specificity in protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem 79:233–269
Portales-Casamar E, Thongjuea S, Kwon AT, Arenillas D, Zhao X, Valen E, Yusuf D, Lenhard B, Wasserman WW, Sandelin A (2010) JASPAR 2010: the greatly expanded open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D105–D110
Newburger DE, Bulyk ML (2009) UniPROBE: an online database of protein binding microarray data on protein-DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D77–D82
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to NIH for funding support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Z., Hu, S., Qian, J. et al. Systematic characterization of protein-DNA interactions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68, 1657–1668 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0617-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0617-y