Abstract.
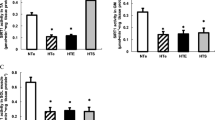
Excessive nutrients, especially amino acids, impair insulin action on glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle. We tested the hypothesis that the branched-chain amino acid leucine reduces acute insulin action in primary myotubes via a negative feedback mechanism involving ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1). The effect of S6K1 on glucose metabolism was determined by applying RNA interference (siRNA). Leucine (5 mM) reduced glucose uptake and incorporation to glycogen by 13% and 22%, respectively, compared to the scramble siRNA-transfected control at the basal level. Leucine also reduced insulin-stimulated Akt phosphorylation, glucose uptake and glucose incorporation to glycogen (39%, 39% and 37%, respectively), and this reduction was restored after S6K1 silencing. Depletion of S6K1 enhanced basal glucose utilization and protected against the development of impaired insulin action, in response to excessive leucine. In conclusion, S6K1 plays an important role in the regulation of insulin action on glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 22 December 2008; received after revision 19 February 2009; accepted 23 February 2009
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deshmukh, A., Salehzadeh, F., Metayer-Coustard, S. et al. Post-transcriptional gene silencing of ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 restores insulin action in leucine-treated skeletal muscle. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 1457–1466 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-8818-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-8818-y