Abstract
Objective
The present study defines the expression of Toll-like Receptor 2 (TLR2), and the modulatory role of Glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3β inhibitor on TLR2/Nuclear Factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling following myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (MI-R) injury in rats.
Methods
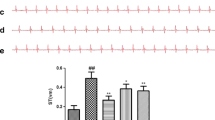
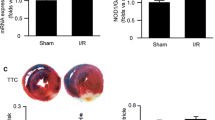
Real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) were used to analyze the presence and quantity of TLR2 mRNA and protein. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α mRNA and interleukin-6 (IL-6) mRNA were analyzed by RT-PCR. The activation of NF-κB was detected by Western Blot and the myocardial infarct size by Evans blue-TTC staining.
Results
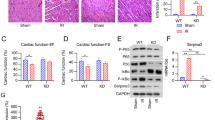
Following 30 min of myocardial ischemia, a significant up-regulation of TLR2 mRNA was revealed by RT-PCR from 1 to 24 h post reperfusion. IHC demonstrated high protein expression levels of TLR2. Administration of the GSK-3β inhibitor 4-benzyl-2-methyl-1, 2, 4-thiadiazolidine-3, 5-dione (TDZD-8) 5 min prior to reperfusion following 1 h reperfusion down-regulated mRNA levels of TLR2 and downstream proinflammatory cytokines (P < 0.05 vs. MI-R), decreased the activity of NF-κB and the size of the myocardial infarct (P < 0.05 vs. MI-R).
Conclusion
Our results demonstrate that TLR2 and its signaling components are activated by MI-R. TDZD-8 administration attenuates TLR2/NF-κB signaling, suggesting a possible mechanism whereby GSK-3β inhibition improves the outcome of MI-R.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsan MF, Gao B. Endogenous ligands of Toll-like receptors. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;76:514–9.
Aliprantis AO, Yang RB, Weiss DS, Odowski PG, Zychlinsky A. The apoptotic signaling pathway activated by Toll-like receptor-2. EMBO J 2002;19:3325–36.
Tang SC, Arumugam TV, Xu X, Cheng A, Mughal MR, Jo DG, et al. Pivotal role for neuronal Toll-like receptors in ischemic brain injury and functional deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:13798–803.
Ziegler G, Harhausen D, Schepers C, Hoffmann O, Röhr C, Prinz V, et al. TLR2 has a detrimental role in mouse transient focal cerebral ischemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;359:574–9.
Favre J, Musette P, Douin-Echinard V, Laude K, Henry JP, Arnal JF, et al. Toll-like receptors 2-deficient mice are protected against postischemic coronary endothelial dysfunction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:1064–71.
Sakata Y, Dong JW, Vallejo JG, Huang CH, Baker JS, Tracey KJ, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 modulates left ventricular function following ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292(1):H503–9.
Nozaki N, Shishido T, Takeishi Y, Kubota I. Modulation of doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction in toll-like receptor-2- knockout mice. Circulation. 2004;110(18):2869–74.
Woodgett JR. Molecular cloning and expression of glycogen synthase kinase-3/factor A. EMBO J. 1990;9:2431–8.
Martin M, Rehani K, Jope RS, Michalek SM. Toll-like receptor-mediated cytokine production is differentially regulated by glycogen synthase kinase 3. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(8):777–84.
Tanno M, Tsuchida A, Nozawa Y, Matsumoto T, Hasegawa T, Miura T, et al. Roles of tyrosine kinase and protein kinase C in infarct size limitation by repetitive ischemic preconditioning in the rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2000;35(3):345–52.
Cuzzocreas S, Mazzon E, Esposito E, Muia C, Abdelrahman M, Paola RD, Crisafulli C, Bramanti P, Thiemermann C. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibition attenuates the development of ischaemia/reperfusion injury of the gut. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33(5):880–93.
Frantz S, Kelly RA, Bourcier T. Role of TLR-2 in the activation of nuclear factor kappaB by oxidative stress in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(7):5197–203.
Lee H, Jo EK, Choi SY, Oh SB, Park K, Kim JS, et al. Necrotic neuronal cells induce inflammatory Schwann cell activation via TLR2 and TLR3: implication in Wallerian degeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;350(3):742–7.
Hazeki K, Nigorikawa K, Hazeki O. Role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in innate immunity. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007;30(9):1617–23.
Hoeflich KP, Luo J, Rubie EA, Tsao MS, Jin O, Woodgett JR. Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cell survival and NF-kappaB activation. Nature. 2000;406:86–90.
Demarchi F, Bertoli C, Sandy P, Schneider C. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta regulates NF-kappa b1/p105 stability. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:39583–90.
Dugo L, Collin M, Thiemermann C. Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta as a target for the therapy of shock and inflammation. Shock. 2007;27(2):113–23.
Shen E, Fan J, Peng T. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta suppresses tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in cardiomyocytes during lipopolysaccharide stimulation. J Cell Biochem. 2008;104(1):329–38.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank Dr. Ling Tao (Department of Cardiology, Xi Jing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University) for her help and careful revision of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: S. Stimpson.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, HK., Yin, Z., Zhang, RQ. et al. GSK-3β inhibitor modulates TLR2/NF-κB signaling following myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Inflamm. Res. 58, 377–383 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-009-0002-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-009-0002-1