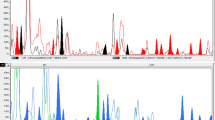
Vigna
subgenus Ceratotropis (V. angularis, V. minima, V. nakashimae, V. reflexo-pilosa, V. riukiuensis and V. umbellata) was investigated using AFLP methodology. Species in the V. minima complex, V. minima, V. nakashimae and V. riukiuensis, had greater intra-specific polymorphism than the other species analyzed. Vigna species from East Asia analysed could be clearly distinguished. The relationship between species was consistent using different analyses and showed V. riukiuensis and V. nakashimae are closely related. The phenetic distance between species (1-Jaccard's similarity coefficient) ranged from 0.279 between V. riukiuensis and V. nakashimae to 0.688 between V. reflexo-pilosa and V. minima. Genetic distance based on inferred nucleotide diversity (π) ranged from 0.012 between V. riukiuensis and V. nakashimae and 0.053 between both V. riukiuensis and V. nakashimae and V. reflexo-pilosa. The diversity (Ha) within species, based on Shannon's information index of phenotypic diversity, was lowest in V. reflexo-pilosa (0.006) and highest in V. minima (0.095). Korean and Japanese populations of V. nakashimae had distinct polymorphism. Vigna riukiuensis populations from Miyako island were genetically different from populations of other islands of southern Okinawa.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 21 April 2000/ Accepted in revised form 5 September 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, M., Doi, K., Kaga, A. et al. Analysis of the Genetic Diversity in the Vigna minima Complex and Related Species in East Asia. J Plant Res 113, 375–386 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00013945
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00013945