Abstract
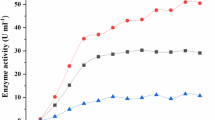
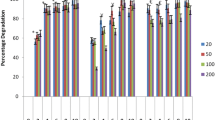
Phenolic compounds, which are present in many industrial wastewaters, have become a cause for worldwide concern due to their persistence, toxicity and health risks. Enzymatic approaches to remove phenol have been tried for some years as they have several advantages compared with the conventional methods. This paper reports some studies on the use of the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium which produces the enzyme lignin peroxidases for the removal of phenol, chlorophenol, and dyes. Batch studies in Erylenmeyer flasks showed complete removal of phenol (500 × 10−3 kg/m3) in 30 h. It was also seen that phenol has a significant inhibitory effect on the biomass growth and the enzyme synthesis if added in the early stages of the growth. However, phenol was effectively removed when added after attaining the maximum enzyme activity. 90% of the dyes were removed in about three days, whereas only 62% of the added 4-chlorophenol was removed in about ten days.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 January 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manimekalai, R., Swaminathan, T. Removal of hazardous compounds by lignin peroxidase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium . Bioprocess Engineering 22, 29–33 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009096
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009096