Abstract
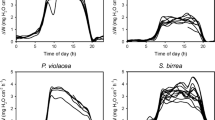
The use of a heat-pulse technique to monitor sap flow from which transpiration can be deduced was evaluated in ungrafted grapevines (Vitis vinifera L., cv. Sultana) under glasshouse and field conditions. There was a significant degree of agreement between daily transpiration deduced from heat-pulse velocity (T hp) and that determined directly by gravimetry in the glasshouse and by calibration using the Penman-Monteith equation in the field. Comparison throughout the growing season of T hp to transpiration calculated with the full Penman-Monteith equation produced a high coefficient of determination (r 2=0.69). A similar comparison of T hp with transpiration calculated with only the aerodynamic component of the Penman-Monteith equation produced a non-linear relationship, due to the equation over-estimating transpiration relative to T hp at high vapour pressure deficits (i.e. above 2.5 kPa). Values for total seasonal transpiration measured with heat-pulse sensors or calculated with either the full Penman-Monteith equation or with only the modified aerodynamic component of the equation were within 10% of each other. Transpiration (T hp) in grapevines with an adequate supply of soil water was shown to be coupled to ambient air conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yunusa, I., Walker, R., Loveys, B. et al. Determination of transpiration in irrigated grapevines: comparison of the heat-pulse technique with gravimetric and micrometeorological methods. Irrig Sci 20, 1–8 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006714
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00006714