Theobroma cacao
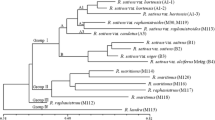
) genotypes. Six primers were sufficient to distinguish all but three pairs of the 62 accessions examined. A UPGMA dendrogram was used to provide a measure of the genetic variability between genotypes. The scale was supplied by the inclusion of Theobroma grandiflora as an ’out group’ and also by the use of two contrasting progenies as ’in groups’. The ’in groups’ were obtained from the self-pollination of one plant (SPEC 54.1) known to be highly homozygous and also of a second, highly heterozygous, clone (P 19B). These reference points allowed several documentation errors to be resolved and provided a basis for identifying unwanted or low-priority material. Implications of the work for the routine maintenance of large germplasm collections are briefly discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 January 1999 / Accepted: 25 May 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charters, Y., Wilkinson, M. The use of self-pollinated progenies as ’in-groups’ for the genetic characterization of cocoa germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 100, 160–166 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00002903
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00002903