Abstract
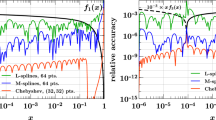
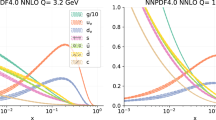
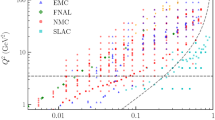
The computation of the parton distribution functions (PDF) or distribution amplitudes (DA) of hadrons from first principles lattice QCD constitutes a central open problem in high energy nuclear physics. In this study, we present and evaluate the efficiency of several numerical methods, well established in the study of inverse problems, to reconstruct the full x-dependence of PDFs. Our starting point are the so called Ioffe time PDFs, which are accessible from Euclidean time simulations in conjunction with a matching procedure. Using realistic mock data tests, we find that the ill-posed incomplete Fourier transform underlying the reconstruction requires careful regularization, for which both the Bayesian approach as well as neural networks are efficient and flexible choices.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
R. Feynman, Photon-hadron interactions, Advanced Books Classics, Avalon Publishing (1998).
K.-F. Liu, Parton degrees of freedom from the path integral formalism, Phys. Rev. D 62 (2000) 074501 [hep-ph/9910306] [INSPIRE].
W. Detmold and C.J.D. Lin, Deep-inelastic scattering and the operator product expansion in lattice QCD, Phys. Rev. D 73 (2006) 014501 [hep-lat/0507007] [INSPIRE].
V. Braun and D. Mueller, Exclusive processes in position space and the pion distribution amplitude, Eur. Phys. J. C 55 (2008) 349 [arXiv:0709.1348] [INSPIRE].
X. Ji, Parton physics on a Euclidean lattice, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 (2013) 262002 [arXiv:1305.1539] [INSPIRE].
Y.-Q. Ma and J.-W. Qiu, Extracting parton distribution functions from lattice QCD calculations, Phys. Rev. D 98 (2018) 074021 [arXiv:1404.6860] [INSPIRE].
A.V. Radyushkin, Quasi-parton distribution functions, momentum distributions and pseudo-parton distribution functions, Phys. Rev. D 96 (2017) 034025 [arXiv:1705.01488] [INSPIRE].
A.J. Chambers et al., Nucleon structure functions from operator product expansion on the lattice, Phys. Rev. Lett. 118 (2017) 242001 [arXiv:1703.01153] [INSPIRE].
C. Best et al., Pion and rho structure functions from lattice QCD, Phys. Rev. D 56 (1997) 2743 [hep-lat/9703014] [INSPIRE].
Zeuthen-Rome (ZeRo) collaboration, Non-perturbative pion matrix element of a twist-2 operator from the lattice, Eur. Phys. J. C 40 (2005) 69 [hep-lat/0405027] [INSPIRE].
C. Alexandrou et al., Nucleon Spin and Momentum Decomposition Using Lattice QCD Simulations, Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 (2017) 142002 [arXiv:1706.02973] [INSPIRE].
M. Oehm et al., 〈x〉 and 〈x 2〉 of the pion PDF from lattice QCD with N f = 2 + 1 + 1 dynamical quark flavors, Phys. Rev. D 99 (2019) 014508 [arXiv:1810.09743] [INSPIRE].
K. Orginos, A. Radyushkin, J. Karpie and S. Zafeiropoulos, Lattice QCD exploration of parton pseudo-distribution functions, Phys. Rev. D 96 (2017) 094503 [arXiv:1706.05373] [INSPIRE].
A. Radyushkin, One-loop evolution of parton pseudo-distribution functions on the lattice, Phys. Rev. D 98 (2018) 014019 [arXiv:1801.02427] [INSPIRE].
J.-H. Zhang, J.-W. Chen and C. Monahan, Parton distribution functions from reduced Ioffe-time distributions, Phys. Rev. D 97 (2018) 074508 [arXiv:1801.03023] [INSPIRE].
T. Izubuchi et al., Factorization theorem relating euclidean and light-cone parton distributions, Phys. Rev. D 98 (2018) 056004 [arXiv:1801.03917] [INSPIRE].
J. Karpie, K. Orginos, A. Radyushkin and S. Zafeiropoulos, Parton distribution functions on the lattice and in the continuum, EPJ Web Conf. 175 (2018) 06032 [arXiv:1710.08288] [INSPIRE].
X. Xiong, X. Ji, J.-H. Zhang and Y. Zhao, One-loop matching for parton distributions: nonsinglet case, Phys. Rev. D 90 (2014) 014051 [arXiv:1310.7471] [INSPIRE].
I.W. Stewart and Y. Zhao, Matching the quasiparton distribution in a momentum subtraction scheme, Phys. Rev. D 97 (2018) 054512 [arXiv:1709.04933] [INSPIRE].
H.-W. Lin, J.-W. Chen, S.D. Cohen and X. Ji, Flavor structure of the nucleon sea from lattice QCD, Phys. Rev. D 91 (2015) 054510 [arXiv:1402.1462] [INSPIRE].
C. Alexandrou et al., Lattice calculation of parton distributions, Phys. Rev. D 92 (2015) 014502 [arXiv:1504.07455] [INSPIRE].
J.-W. Chen et al., Nucleon helicity and transversity parton distributions from lattice QCD, Nucl. Phys. B 911 (2016) 246 [arXiv:1603.06664] [INSPIRE].
C. Alexandrou et al., Light-cone parton distribution functions from lattice QCD, Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 (2018) 112001 [arXiv:1803.02685] [INSPIRE].
J.-H. Zhang et al., Pion distribution amplitude from lattice QCD, Phys. Rev. D 95 (2017) 094514 [arXiv:1702.00008] [INSPIRE].
X. Ji, J.-H. Zhang and Y. Zhao, More on large-momentum effective theory approach to parton physics, Nucl. Phys. B 924 (2017) 366 [arXiv:1706.07416] [INSPIRE].
A.V. Radyushkin, Structure of parton quasi-distributions and their moments, Phys. Lett. B 788 (2019) 380 [arXiv:1807.07509] [INSPIRE].
J. Karpie, K. Orginos and S. Zafeiropoulos, Moments of Ioffe time parton distribution functions from non-local matrix elements, JHEP 11 (2018) 178 [arXiv:1807.10933] [INSPIRE].
J.-W. Chen et al., Parton distribution function with nonperturbative renormalization from lattice QCD, Phys. Rev. D 97 (2018) 014505 [arXiv:1706.01295] [INSPIRE].
W. Broniowski and E. Ruiz Arriola, Partonic quasidistributions of the proton and pion from transverse-momentum distributions, Phys. Rev. D 97 (2018) 034031 [arXiv:1711.03377] [INSPIRE].
Y.-Q. Ma and J.-W. Qiu, Exploring partonic structure of hadrons using ab initio lattice QCD calculations, Phys. Rev. Lett. 120 (2018) 022003 [arXiv:1709.03018] [INSPIRE].
K.-F. Liu and S.-J. Dong, Origin of difference between \( \overline{d} \) and ū partons in the nucleon, Phys. Rev. Lett. 72 (1994) 1790 [hep-ph/9306299] [INSPIRE].
G.S. Bali et al., Pion distribution amplitude from Euclidean correlation functions: exploring universality and higher-twist effects, Phys. Rev. D 98 (2018) 094507 [arXiv:1807.06671] [INSPIRE].
R.S. Sufian et al., Pion valence quark distribution from matrix element calculated in lattice QCD, arXiv:1901.03921 [INSPIRE].
H.-W. Lin et al., Parton distributions and lattice QCD calculations: a community white paper, Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 100 (2018) 107 [arXiv:1711.07916] [INSPIRE].
K. Cichy and M. Constantinou, A guide to light-cone PDFs from lattice QCD: an overview of approaches, techniques and results, arXiv:1811.07248 [INSPIRE].
C. Monahan, Recent developments in x-dependent structure calculations, PoS(LATTICE 2018)018 [arXiv:1811.00678] [INSPIRE].
LP3 collaboration, Improved parton distribution functions at the physical pion mass, Phys. Rev. D 98 (2018) 054504 [arXiv:1708.05301] [INSPIRE].
G. Backus and F. Gilbert, The resolving power of gross Earth data, Geophys. J. Int. 16 (1968) 169.
S.A. Teukolsky, W.T. Vetterling and B.P. Flannery, Numerical recipes in C: the art of scientific computing, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge U.K. (1992).
B.B. Brandt, A. Francis, H.B. Meyer and D. Robaina, Pion quasiparticle in the low-temperature phase of QCD, Phys. Rev. D 92 (2015) 094510 [arXiv:1506.05732] [INSPIRE].
R.-A. Tripolt, P. Gubler, M. Ulybyshev and L. Von Smekal, Numerical analytic continuation of Euclidean data, Comput. Phys. Commun. 237 (2019) 129 [arXiv:1801.10348] [INSPIRE].
J. Liang, K.-F. Liu and Y.-B. Yang, Lattice calculation of hadronic tensor of the nucleon, EPJ Web Conf. 175 (2018) 14014 [arXiv:1710.11145] [INSPIRE].
M.V. Ulybyshev, C. Winterowd and S. Zafeiropoulos, Direct detection of metal-insulator phase transitions using the modified Backus-Gilbert method, EPJ Web Conf. 175 (2018) 03008 [arXiv:1710.06675] [INSPIRE].
M. Ulybyshev, C. Winterowd and S. Zafeiropoulos, Collective charge excitations and the metal-insulator transition in the square lattice Hubbard-Coulomb model, Phys. Rev. B 96 (2017) 205115 [arXiv:1707.04212] [INSPIRE].
S. Forte, L. Garrido, J.I. Latorre and A. Piccione, Neural network parametrization of deep inelastic structure functions, JHEP 05 (2002) 062 [hep-ph/0204232] [INSPIRE].
NNPDF collaboration, Parton distributions from high-precision collider data, Eur. Phys. J. C 77 (2017) 663 [arXiv:1706.00428] [INSPIRE].
NNPDF collaboration, Parton distributions for the LHC Run II, JHEP 04 (2015) 040 [arXiv:1410.8849] [INSPIRE].
R.D. Ball et al., A first unbiased global NLO determination of parton distributions and their uncertainties, Nucl. Phys. B 838 (2010) 136 [arXiv:1002.4407] [INSPIRE].
NNPDF collaboration, Reweighting NNPDFs: the W lepton asymmetry, Nucl. Phys. B 849 (2011) 112 [Erratum ibid. B 854 (2012) 926] [arXiv:1012.0836] [INSPIRE].
J. Rojo, Machine Learning tools for global PDF fits, talk given at the 13th Conference on Quark Confinement and the Hadron Spectrum (Confinement XIII), July 31–August 6, Maynooth, Ireland (2018), arXiv:1809.04392 [INSPIRE].
J. Skilling and S.F. Gull, Bayesian maximum entropy image reconstruction, Lecture Notes — Monograph Series volume 20, Institute of Mathematical Statistics, Hayward, U.S.A. (1991).
M. Asakawa, T. Hatsuda and Y. Nakahara, Maximum entropy analysis of the spectral functions in lattice QCD, Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 46 (2001) 459 [hep-lat/0011040] [INSPIRE].
A. Rothkopf, Improved maximum entropy analysis with an extended search space, J. Comput. Phys. 238 (2013) 106 [arXiv:1110.6285] [INSPIRE].
Y. Burnier and A. Rothkopf, Bayesian approach to spectral function reconstruction for euclidean quantum field theories, Phys. Rev. Lett. 111 (2013) 182003 [arXiv:1307.6106] [INSPIRE].
A. Buckley et al., LHAPDF6: parton density access in the LHC precision era, Eur. Phys. J. C 75 (2015) 132 [arXiv:1412.7420] [INSPIRE].
B. Carpenter et al., Stan: a probabilistic programming language, J. Stat. Softw. 76 (2017).
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0), which permits any use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ArXiv ePrint: 1901.05408
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
To view a copy of this licence, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Karpie, J., Orginos, K., Rothkopf, A. et al. Reconstructing parton distribution functions from Ioffe time data: from Bayesian methods to neural networks. J. High Energ. Phys. 2019, 57 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP04(2019)057
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP04(2019)057