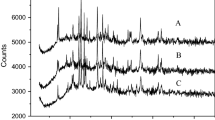
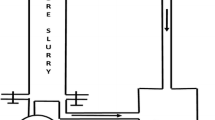
Abstract
A microbial survey of Jamnagar bauxite mines in Gujarat, India, revealed the indigenous presence of a variety of autotrophic and heterotrophic bacteria and fungi associated with the ore body and water ponds in the vicinity. Among these, bacteria belonging to the genera Thiobacillus, Bacillus and Pseudomonas are implicated in the weathering of aluminosilicates; the precipitation of iron oxy hydroxides; the dissolution and conversion of alkaline metal species; and the formation of alumina, silica and calcite minerals. Fungi belonging to the genus Cladosporium can reduce ferric iron and dissolve alumina silicates. Biogenesis thus plays a significant role in bauxite mineralization. Various types of bacteria and fungi, such as Bacillus polymyxa, Bacillus coagulans and Aspergillus niger, were found to be efficient in significant calcium solubilization and partial iron removal from bauxite ore. Probable mechanisms in the biobeneficiation process are analyzed. Biobeneficiation is shown to be an effective technique for the removal of iron and calcium from bauxite ores for use in refractories and ceramics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexopoulos, C.J., 1962, Introductory Mycology, John Wiley and Sons Inc., New York.
Bencke, E.S., 1958, Medical Mycology Laboratory Manual, Burgess Publ. Co., Minneapolis, MN, p. 34.
Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 1974, R. E. Buchanan and M. E. Gibbons, eds., 8th Ed. The Williams and Wilkins Co., Baltimore, MD.
Bromfield, S.M., 1954, “Reduction of ferric compounds by soil bacteria,” J. Gen. Microbiol., Vol. 11, pp. 1–6.
Brugstaller, W., and Schinner, F., 1993, “Leaching of metals with fungi,” J. Biotechnol., 27, pp. 91–116.
Ehrlich, H. L., 1990., Geomicrobiology, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Groudev, S.N., Groudeva, V.I., Genchev, F.N., Mochev, D.J., and Petrov, E.C., 1985, “Biological removal of iron from quartz sands, kaolins and clay,” Proceedings of XV International Mineral Process Congress, Vol II, Flotation, Hydrometallurgy, Cannes, France, pp. 378–387.
Groudeva, V.I., and Groudev, S.N., 1983, “Bauxite dressing by means of Bacillus circulans,” Travaux ICSOBA, 13, pp. 257–263.
Karavaiko, G.I., Avakyan, Z.A., Ogurtsova, L.V., and Safonova, O.F., 1989, “Microbiological processing of bauxite,” Biohydrometallurgy 1989, J. Salley, R.G.L McGready and L. Wichlacz, eds., CANMET, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, pp. 93–103.
Khalid, A.M., Bhatti, T.M., and Umar, M., 1993. “An improved solid medium for isolation, enumeration and genetic investigations of autotrophic iron and sulphur oxidising bacteria,” Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 39, pp. 259–263.
Lovely, D.R., 1987., “Organic matter mineralization with reduction of ferric iron: A review,” Geomicrobiology J., 5, pp. 375–399.
Mishra, A.K., Roy Mahapatra, S.S., Roy, P., Mohanty, B.K., Majumdar, S. and Ray, P.K., 1986, “Bioleaching of silica from magnesite ore,” Ind. J. of Tech., Vol. 24, pp. 770–772.
Natarajan, K.A., 1992, “Bioprocessing of minerals,” Proc. Int. Symp. Thermochemistry and Chemical Processes, C.K. Mathews, ea., BRNS, Bombay, India, pp. 229–237.
Natarajan, K.A., 1995., “Biomineral beneficiation,” Mineral Processing: Recent Advances and Future Trends, S.P. Mehrotra and R. Shekhar, eds., Allied Publishers, New Delhi, India, pp. 489–502.
Phalguni, A., Modak, J.M., and Natarajan, K.A., 1996, “Biobeneficiation of bauxite using Bacillus polymyxa Calcium and iron removal,” Int. J. Mineral Proc., 48, pp.
Raper, K.B., and Fennell, D. I., 1965, The Genus Aspergillus, Williams and Wilkins Company, Baltimore, MD.
Silverman, M.P., and Lundgren, D.G., 1959. “Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacteria Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans 1 — An improved medium and a harvesting procedure for securing high yields,” J. Bacter., Vol. 77, pp. 642–647.
Smith, J.E., and Pateman, J. A., 1977, Genetics and Physiology of Aspergillus, Academic Press, New York.
Vogel, A.I., 1985, Textbook of Quantitative Analysis, E.L.B.S, London.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
SME nonmeeting paper 96-638
Discussion of this peer-reviewed and approved paper is invited and must be submitted to SME prior to Aug. 31, 1997.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Natarajan, K.A., Modak, J.M. & Anand, P. Some microbiological aspects of bauxite mineralization and beneficiation. Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration 14, 47–53 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03402759
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03402759