Abstract
Background
Overexpression of the Src homology 2 domain protein Shb in β-cells of transgenic mice has been shown to promote an increased β-cell mass. To investigate the mechanisms by which Shb controls the β-cell mass, we have presently studied the effects of Shb overexpression on the IRS-1–induced signaling pathway in mouse islet β-cells and in insulin-producing RINm5F cells and correlated these effects to growth and death patterns.
Materials and Methods
Shb overexpression was achieved in RINm5F cells by selection of stable clones or by FACS purification of transiently transfected cells. For Shb overexpression in primary mouse islet cells, a Shb-transgene mouse was used. Cell proliferation and death rates were determined using flow cytometry. Serum-, insulin-, and IGF-1-stimulated signaling events were studied by immunoblot, immunoprecipitation, and in vitro kinase procedures.
Results
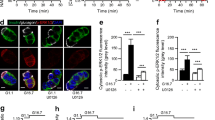
Transient Shb overexpression in RINm5F cells resulted in increased proliferation. Both Shb-overexpressing RINm5F cells and islet cells from transgenic mice (islet Shb) exhibited increased basal tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1. Shb overexpression resulted also in the assembly and activation of a multiunit complex consisting of at least Shb, IRS-1, IRS-2, FAK, and PI3K. Consequently, the phosphorylation of Akt was enhanced under basal conditions in Shb overexpressing cells. Finally, Shb overexpression did not affect insulin-induced phosphorylation of the PI3K-antagonist PTEN.
Conclusion
It is concluded that the Shb-induced alterations in the IRS-1/PI3K/Akt pathway may be relevant to the understanding of growth and death patterns of insulin-producing cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weir GC, Bonner-Weir S, Leahy JL. (1990) Islet mass and function in diabetes and transplantation. Diabetes 39: 401–405.
Brüning JC, Winnay J, Bonner-Weir S, Taylor SI, Accili D, Kahn CR. (1997) Development of a novel polygenic model of NIDDM in mice heterozygous for IR and IRS-1 null alleles. Cell 88: 561–572.
Withers DJ, Gutierrez JS, Towery H, et al. (1998) Disruption of IRS-2 causes type 2 diabetes in mice Nature 391: 900–904.
Withers DJ, Burks DJ, Towery HH, Altamuro SL, Flint CL, White MF. (1999) Irs-2 coordinates Igf-1 receptor-mediated beta-cell development and peripheral insulin signalling. Nature Gen. 23: 32–40.
Leibiger IB, Leibiger B Moede T, Berggren PO. (1998) Exocytosis of insulin promotes insulin gene transcription via the insulin receptor/PI-3 kinase/p70 s6 kinase and CaM kinase pathways. Mol. Cell 1: 933–938.
Kulkarni RN, Brüning JC, Winnay JN, Postic C, Magnuson MA, Kahn CR. (1999) Tissue-specific knockout of the insulin receptor in pancreatic beta cells creates an insulin secretory defect similar to that in type 2 diabetes. Cell 96: 329–339.
Whitman M, Downes CP, Keeler M, Keller T, Cantley L. (1988) Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature 332: 644–646.
Franke TF, Kaplan DR, Cantley LC, Toker A. (1997) Direct regulation of the Akt proto-oncogene product by phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate. Science 275: 665–668.
Stokoe D, Stephens LR, Copeland T, et al. (1997) Dual role of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate in the activation of protein kinase B. Science 277: 567–570.
Franke TF, Kaplan D, Cantley L. (1997) PI3K: downstream AKTion blocks apoptosis. Cell 88: 435–437.
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, et al. (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91: 231–241.
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, et al. (1998) Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 282: 1318–1321.
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, et al. (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96: 857–868.
Maehama T, Dixon JE. (1998) The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 13375–13378.
Cantely LC, Neel BG. (1999) New insights into tumor suppression: PTEN suppresses tumor formation by restraining the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96: 4240–4245.
Welsh M, Mares J, Karlsson T, Lavergne C, Bréant B, Claesson-Welsh L. (1994) Shb is a ubiquitously expressed Src homology 2 protein. Oncogene 9: 19–27.
Welsh M, Songyang Z, Frantz D, et al. (1998) Stimulation through the T cell receptor leads to interactions between SHB and several signaling proteins Oncogene 16: 891–902.
Karlsson T, Songyang Z, Landgren E, et al. (1995) Molecular interactions of the Src homology 2 domain protein Shb with phosphotyrosine residues, tyrosine kinase receptors and Src homology 3 domain proteins Oncogene 10: 1475–1483.
Lindholm CK, Gylfe E, Zhang W, Samelson LE, Welsh M. (1999) Requirement of the Src homology 2 domain protein Shb for T cell receptor-dependent activation of the interleukin-2 gene nuclear factor for activation of T cells element in Jurkat T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 28050–28057.
Karlsson T, Welsh M. (1996) Apoptosis of NIH3T3 cells overexpressing the Src homology 2 domain protein Shb. Oncogene 13: 955–961.
Welsh M, Christmansson L, Karlsson T, Sandler S, Welsh N. (1999) Transgenic mice expressing Shb adaptor protein under the control of rat insulin promoter exhibit altered viability of pancreatic islet cells. Mol. Med. 5: 169–180.
Andersson A. (1978) Isolated mouse pancreatic islets in culture: effects of serum and different culture media on the insulin production of the islets. Diabetologia 14: 397–404.
Saldeen J, Curiel DT, Eizirik DL, et al. (1996) Efficient gene transfer to dispersed human pancreatic islet cells in vitro using adenovirus-polylysine/DNA complexes or polycationic liposomes. Diabetes 45: 1197–1203.
Saldeen J, Lee JC, Welsh N. (2001) Role of p38 mitogenactivated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) in cytokine-induced rat islet cell apoptosis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 61:1561–1569.
Welsh N. (1996) Interleukin-1 beta-induced ceramide and diacylglycerol generation may lead to activation of the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and the transcription factor ATF2 in the insulin-producing cell line RINm5F J. Biol. Chem. 271: 8307–8312.
Traynor-Kaplan AE, Thompson BL, Harris AL, Taylor P, Omann GM, Sklar LA. (1989) Transient increase in phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol trisphosphate during activation of human neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem. 264:15668–15673.
Homqvist K, Cross M, Riley D, Welsh M. (in press) The Shb adaptor protein causes Sic-dependent cell spreading and activation of focal adhesion kinase in murine brain endothelial cells. Cell. Signal.
Sonoda Y, Watanabe S, Matsumoto Y, Aizu-Yokota E, Kasahara T. (1999) FAK is the upstream signal protein of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt survival pathway in hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis of a human glioblastoma cell line. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 10566–10570.
Lebrun P, Mothe-Satney I, Delahaye L, Obberghen EV, Baron V. (1998) Insulin receptor substrate-1 as a signaling molecule for focal adhesion kinase pp125(FAK) and pp60(src). J. Biol. Chem. 273: 32244–32253.
Chen HC, Appeddu PA, Isoda H, Guan JL. (1996) Phosphorylation of tyrosine 397 in focal adhesion kinase is required for binding phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol. Chem. 271: 26329–26334.
Hungersford JE, Compton MT, Matter ML, Hoffstrom BG, Otey CA. (1996) Inhibition of pp125FAK in cultured fibroblasts results in apoptosis. J. Cell. Biol. 135: 1383–1390.
Ueno H, Honda H, Nakamoto T, et al. (1997) The phosphatidylinositol 3′ kinase pathway is required for the survival signal of leukocyte tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 14: 3067–3072.
Zhou LF, Xu SQ, Dews M, Baserga R. (1997) Co-operation of simian virus 40 T antigen and insulin receptor substrate-1 in protection from apoptosis induced by interleukin-3 withdrawal. Oncogene 15: 961–970.
Schneller M, Vuori K, Ruoslahti E. (1997) Alphavbeta3 integrin associates with activated insulin and PDGFbeta receptors and potentiates the biological activity of PDGF. EMBO J. 16: 5600–5607.
Anneren C. (2002) Dual role of the tyrosine kinase GTK and the adaptor protein SHB in beta-cell growth: enhanced beta-cell replication after 60% pancreatectomy and increased sensitivity to streptozotocin. J. Endocrinol. 172: 145–153.
Vazquez F, Ramaswamy S, Nakamura R, Sellers WR. (2000) Phosphorylation of the PTEN tail regulates protein stability and function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 5010–5018.
Torres J, Pulido R. (2001) The tumor suppressor PTEN is phosphorylated by the protein kinase CK2 at its C terminus. Implications for PTEN stability to proteasome-mediated degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 993–998.
Rothenberg PL, Willison LD, Simon J, Wolf BA. (1995) Glucose-induced insulin receptor tyrosine phosphorylation in insulin-secreting beta-cells. Diabetes 44: 802–809.
Kwon G, Xu G, Marshall CA, McDaniel ML. (1999) Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced pancreatic beta-cell insulin resistance is mediated by nitric oxide and prevented by 15–de-oxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 and aminoguanidine. A role for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activation and inos expression. J. Biol. Chem. 274: 18702–18708.
Acknowledgments
The excellent technical assistance of Ing-Marie Mörsare and Ing-Britt Hallgren is gratefully acknowledged. This work was supported by grants from the Swedish Medical Research Council (12X-109, 12X-11564, 31X-10822, 72P-12995), the Swedish Diabetes Association, the Nordic Insulin Fund, the Juvenile Diabetes Foundation International, the Wallenberg Foundation, and the Family Ernfors Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contributed by D. Steiner.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Welsh, N., Makeeva, N. & Welsh, M. Overexpression of the Shb SH2 Domain-Protein in Insulin-Producing Cells Leads to Altered Signaling Through the IRS-1 and IRS-2 Proteins. Mol Med 8, 695–704 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03402033
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03402033