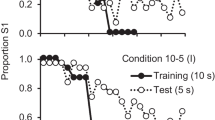
Abstract
Two experiments examined whether or not rats formed stimulus classes on a basis of same response (i.e., shared common response) during overtraining. In Experiment 1, rats were trained on two discriminations in a straight runway, then trained on conditional successive discriminations in a Y maze. Group C, in which rats were required to choose the same goal box when the original positive stimulus or the negative one was presented on the entrance of each goal box, learned shift problems faster than Group IC, in which rats were required to choose the right goal box when one of positive stimuli was presented and to choose the left goal box when the other was presented as well as negative stimuli, after overtraining, but not after criterion training. In Experiment 2, rats were trained on two discriminations in the Y maze, and then they were trained on either whole reversal (Group W) in which two tasks were reversed or partial reversal (Group P) in which one of two tasks was reversed in a straight runway. Group W learned their reversal faster than Group P after overtraining, but not after criterion training. These results indicate that the same response is a factor affecting stimulus classes formation in rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BHATT, R. S., WASSERMAN, E. A. (1989). Secondary generalization and categorization in pigeons. The Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 82, 213–224.
DELIUS, J. D., AMELING, M., LEA, S. E., STADDON, J. E. R. (1995). Reinforcement concordance induces and maintains stimulus associations in pigeons. The Psychological Record, 45, 283–297.
DUBE, W. V., CALLAHAN, T. D., MCILVANE, W. J. (1993), Serial reversal of concurrent auditory discriminations in rats. The Psychological Record, 43, 429–440.
EDWARDS, C. A., JAGIELO, J. A., ZENTALL, T. R., HOGAN, D. E. (1982). Acquired equivalence and distinctiveness in matching to sample by pigeons. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 8, 244–259.
FERSEN, L., von., & LEA, S. E. G. (1990). Category discrimination with polymorphous feature. The Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 54, 69–84.
HALL, G., RAY, E., BONARDI, C. (1993). Acquired equivalence between cues trained with a common antecedent. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 19, 391–399.
NAKAGAWA, E. (1978). The effect of overtraining on discrimination learning in white rats (in Japanese). Japanese Journal of Psychology, 49, 70–77.
NAKAGAWA, E. (1986). Overtraining, extinction and shift learning in a concurrent discrimination in rats. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 38B, 213–226.
NAKAGAWA, E. (1992). Effects of overtraining on reversal learning by rats in concurrent and single discriminations. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 44B, 37–56.
NAKAGAWA, E. (1993). Relational rule learning in the rat. Psychobiology, 21, 293–298.
NAKAGAWA, E. (1998). Stimulus classes formation in concurrent discriminations in rats as a function of overtraining. The Psychological Record, 48, 537–560.
SPRADLIN, J. E., COTTER, V. W., BAXLEY, N. (1973). Estabiishing a conditional discrimination without direct training: A study of transfer with retarded adolescents. America Journal of Mental Deficiency, 77, 556–566.
URCUIOLI, P. J., ZENTALL, T. R., JACKSON-SMITH, P., STEIRN, J. N. (1989). Evidence for common coding in many-to-one matching: Retention, intertriai interference, and transfer. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 15, 264–273.
VAUGHAN, W. (1988). Formation of equivalence sets in pigeons. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 14, 36–42.
VAUGHAN, W., HERRNSTEIN, R. J. (1987). Choosing among natural stimuli. The Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 47, 5–16.
ZENTALL, T. R., SHERBURNE, L. M., STEIRN, J. N., RANDALL, C. K., ROPER, K. L., URCUIOLI, P. J. (1992). Common coding in pigeons: Partial versus total reversals of one-to-many conditional discriminations. Animal Learning & Behavior, 20, 373–381.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakagawa, E. A Factor Affecting Stimulus Classes Formation in Concurrent Discriminations in Rats. Psychol Rec 49, 117–136 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395310
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395310