Abstract
The bidirectional effects of the common bean (Phaseolus vul-garis) onto rust disease (Uromyces appendiculatus) epidemics and vice versa were studied in controlled growth chamber experiments. Bean plants of the variety ‘Dufrix” were inoculated with a suspension of 1 × 105 urediniospores ml-1 at one of three plant ages, designated as I1, I2 or I3, respectively, or left non-inoculated. Plant ages at inoculation were 22, 29, and 36 days after sowing (DAS) in experiment A, and 25, 32 and 39 DAS in experiment B.
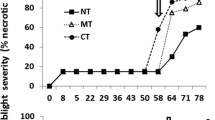
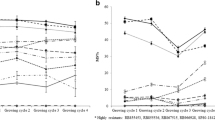
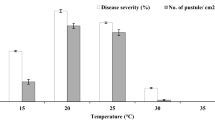
Effects of leaf position and age on bean rust epidemics were evident whereby up to 10 fold more disease was found on the first two trifoliates as compared to the unifoliate leaves. The respective proportions of diseased leaf area on a plant basis 10 and 18 days after inoculation were 0.06 and 0.25 for I3 compared with 0.16 and 0.33 for I1 (experiment A). Bean rust epidemics affected the maximum leaf area of Phaseolus beans, the highest effect (38% reduction) recorded from plants inoculated at I1 in experiment B.
Bean rust negatively affected actual yield of Phaseolus beans with averaged yield losses of 65.5, 34.4 and 14.0% (pooled data of experiments A and B) from treatments I1, I2 and I3, respectively. Host-disease-yield relationship was well explained by a multiple regression model consisting of the predictor variables mean total leaf area and total lesion area and predicted an average yield loss of 4.25% for each 1% increase of mean rust severity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrios GN, 2005. Plant Pathology, 5th edition. San Diego, California, Academic Press.
Allen DJ, 1983. The Pathology of Tropical Food Legumes. New York, John Wiley & Sons.
Alten von H, 1983. The effect of temperature, light and leaf age on the frequency of appressoria formation and infection with Uromyces phaseoli (Pers.) Wint. Phytopathol Z 107, 327–335.
Bassanezi BR, Amorim L, Bergamin Filho A, Hau B & Berger RD, 2001. Accounting for photosynthetic efficiency of bean leaves with rust, angular leaf spot and anthracnose to assess crop damage. Plant Pathol 50, 443–452.
Berger RD, Hau B, Weber GE, Bacchi LMA, Bergamin Filho A & Amorim L, 1995. A simulation model to describe epidemics of rust of Phaseolus beans. I: Development of the model and sensitivity analysis. Phytopathology 85, 715–721.
Bergamin Filho A, Carneiro SMTPG, Godoy CV, Amorim L, Berger RD & Hau B, 1997. Angular leaf spot of Phaseolus beans: Relationships between disease, healthy leaf area, and yield. Phytopathology 87, 506–515.
Boote JK, Jones JW, Mishoe JW & Berger RD, 1983. Coupling pests to crop growth simulators to predict yield reductions. Phytopathology 73, 1581–1587.
Burdon JJ, 1993. The structure of pathogen populations in natural plant communities. Annu Rev Phytopathol 20, 143–166.
Campbell CL & Madden LV, 1990. Introduction to Plant Disease Epidemiology. New York, John Wiley & Sons.
Charles-Edwards DA, 1982. Physiological Determinants of Crop Growth. San Diego, London, Academic Press.
Daly JM, Bell AA & Krupka LR, 1961. Respiratory changes during development of rust diseases. Phytopathology 51, 461–471.
Develey-Rivière MP & Galiana E, 2007. Resistance to pathogens and host developmental stage: a multifaceted relationship within the plant kingdom. New Phytol 175, 405–416.
Godoy CV, Carneiro SMBG, Iamauti MT, Amorim L, Berger RD & Bergamin Filho A, 1997. Diagrammatic scales for bean diseases: Development and validation. Phytopathol Z 104, 336–345.
Habtu A & Zadoks JC, 1994. Crop growth, disease and yield components of rusted Phaseolus beans in Ethiopia. J Phyto-pathol 143, 391–401.
Hagedorn DJ & Inglis DA, 1986. Handbook of Bean Diseases. University of Wisconsin, Cooperative Extension Publication No. A3374, Madison, Wisconsin.
Imhoff MW, Main CE & Leonard KJ, 1981. Effects of temperature, dew period, and age of leaves, spores and source of pustule on germination of bean rust urediospores. Phytopathology 71, 577–583.
Jesus Junior WC, do Vale FXR, Coelho RR, Hau B, Zambolim L, Costa LC & Bergamin Filho A, 2001. Effects of angular leaf spot and rust on yield loss of Phaseolus vulgaris. Phytopathology 91, 1045–1053.
Jesus Junior WC, do Vale FXR, Coelho RR, Paul PA, Hau B, Bergamin Filho A, Zambolim L & Berger RD, 2003. Relationships between angular leaf spot, healthy leaf area, effective leaf area and yield of Phaseolus vulgaris. Eur J Plant Pathol 109, 625–632.
Kranz J & Jörg E, 1989. The synecological approach in plant disease epidemiology. Rev Trop Plant Pathol 6, 27–38.
Kranz J, 2003. Comparative Epidemiology of Plant Diseases. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, Springer.
Livne A & Daly JM, 1966. Translocation in healthy and rust affected beans. Phytopathology 56, 170–175.
Lopes DB & Berger RD, 2000. The effects of rust and anthrac-nose on the photosynthetic competence of diseased bean leaves. Phytopathology 91, 212–220.
Lucas JA, 1998. Plant Pathology and Plant Pathogens, 3rd edition. Oxford, Blackwell Science.
Madden LV & Nutter FW, 1995. Modeling crop losses at the field scale. Can J Plant Pathol 17, 124–137.
Melching JS, Dowler WM, Koogle DL & Royer MH, 1988. Effect of plant and leaf age on susceptibility of soybean to soybean rust. Can J Plant Pathol 10, 30–35.
Mendes BMJ & Bergamin Filho A, 1989. Influence of temperature, wetness duration, and leaf type on the quantification of monocyclic parameters of bean rust. Phytopathol Z 126, 183–189.
Mersha Z & Hau B, 2008. Effects of bean rust (U. appendicula-tus) on host dynamics of Phaseolus beans. Plant Pathol 57, 674–686.
Schwartz HF, Correa VF, Pineda DPA, Otoya MM & Katherman MJ, 1981. Dry bean yield losses caused by Ascochyta, Angular, and White leaf spots in Colombia. Plant Dis 65, 494–496.
Stavely JR, 1991. Rust. In: Hall, R (Ed.) 1991: Compendium of Bean diseases. American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, MN. 24–25.
Voegele RT & Mendgen K, 2003. Research review on rust haustoria: nutrient uptake and beyond. New Phytol 159, 93–100.
Waggoner PE & Berger RD, 1987. Defoliation, disease and growth. Phytopathology 77, 393–398.
Wagner S & Boyle C, 1995. Changes in carbohydrate, protein and chlorophyll content, and enzyme activity during the switch from uredinio- to teliospore sporulation in the bean-rust fungus Uromyces appendiculatus (Pers.) Link. J Phytopath 143, 633–638.
Yarwood CE, 1959. Predisposition. In: Horsfall, JG and Diamond, AE (Eds.) 1959: Plant Pathology, an advanced treatise, Vol. 1, Academic Press, London. 521–562.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mersha, Z., Hau, B. Reciprocal effects of host and disease dynamics in the bean rust pathosystem. J Plant Dis Prot 118, 54–62 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356382
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356382