Abstract
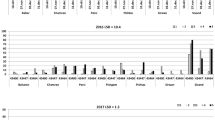
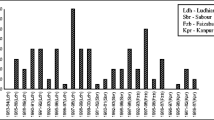
In plant disease development, temperature, relative humidity and rainfall are critical factors. To determine how specific environmental variables affect French bean rust, we determined the effect of these variables on disease development. Higher relative humidity (> 85%), moderate temperature (20–25 °C) and 18–24 h leaf wetness were found optimum for disease development. Effect of different meteorological factors on disease progress was studied under natural epiphytotic conditions and found that the disease was initiated in the second week of August and reached at peak in mid September. Multiple correlation coefficients between disease severity and these environmental factors suggested that 92.36% rust severity was due to mean temperature, average relative humidity and cumulative rainfall while rest of the variation may be attributed to the factors not included in the investigations. The multiple linear regression equation was fitted to the data and the equation arrived for all the weather parameters was, Y = − 52.4852 + 1.2535 X1 + 0.8008 X2 − 0.2862 X3 + 0.4622 X4 − 0.7755 X5 + 0.2428 X6. With the step, down procedure, three variable i.e., maximum temperature (X1), cumulative rainfall (X5) and wind speed (X6) were eliminated and final equation fitted to the data is Y = − 37.4111 + 1.0622 X2 + 0.5299 X3 − 0.2868 X4.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelotti F, Scapin CR, Tessmann DJ, Vida JB, Canteri MG (2013) The effect of temperature, leaf wetness and light on development of grapevine rust. Australas Plant Pathol 43:9–13
Ballantyne BJ (1978) The genetic bases of resistance to rust, caused by Uromyces appendiculatus in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Ph.D. Dissertation. University of Sydney, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia
Coelho RR, do Vale FXR, de Jesus Junior WC, Paul PA, Zambolin L, Barreto RW (2003) Determination of the climatic conditions favorable to the development of rust and angular leaf spot on common bean. Fitopatologia Brasileira 28:508–514
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agricultural research, 2nd edn. John Wiley, New York, p 680
Gupta SK, Shyam KR (1996) Angular leaf spot of French bean. Kisan World 23:43
Gupta SK, Jarial K, Kumar M (2008) Occurrence of French bean rust in Himachal Pradesh. J Mycol Plant Pathol 38:352–353
Harter LL, Andrus CF, Zaumeyer WJ (1935) Studies on bean rust caused by Uromyces phaseoli typica. J Agric Res 50:737–759
Hirst JM (1953) Changes in atmospheric spore content: diurnal periodicity and the effects of weather. Trans Br Mycol Soc 36:375–393
Imhoff MW, Leonard KJ, Main CE (1982) Patterns of bean rust lesion size increase and spore production. Phytopathology 72:441–446
Mendes BMJ, Bergamin-Filho A (1989) Influence of temperature, wetness duration and leaf type on the quantification of monocyclic parameters of bean rust. J Phytopathol 126:183–189
Rey G, Lozano JC (1961) Physiological studies on rust of bean (P. vulgaris) caused by Uromyces appendiculatus. Acta Agron Palmira 11:147–186
Schwartz HF, Steadman JR, Lindgren DT (2004) Rust of dry beans. Fort Collins, CO., USA: Colorado State University: Cooperative extension report no. 2
Shands WA, Schein RD (1962) Time–temperature interactions of Uromyces phaseoli during spore germination and tube elongation. Phytopathology 52:27
Shaner G, Finney RE (1977) The effect of nitrogen fertilization on the expression of slow-mildewing resistance in Knox wheat. Phytopathology 67:1051–1056
Sharma SR (1989) Yield losses caused by rust in French beans. Plant Dis Res 4:92–94
Sharma AK (1998) Epidemiology and management of rust disease of French bean. Veg Sci 25:85–88
Sharma SR, Sohi HS (1989) Diseases of French bean in India and their control. Indian Rev Life Sci 9:153–168
Silva SR, Rios GP, Silva SC (2001) Influence of genetic resistance and wetness period on infection and lesion development of common bean rust. Fitopatologia Brasileira 26:726–731
Stavely JR (2005) Rust. In: Schwartz HF, Steadman JR, Hall R, Forster RL (eds) Compendium of bean diseases, 2nd edn. APS Press, St. Paul, pp 38–39
Stavely JR, Pastor-Corrales MA (1989) Rust. In: Schwartz HF, Pastor-Corrales MA (eds) Bean production problems in the tropics, 2nd edn. Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT), Cali
Van der Plank JE (1963) Plant diseases: epidemics and control. Academic Press, New York, p 349p
Zeng YS, Wang ZZ, Zhao ZC (1999) Studies on conditions for sporulation and inoculation of uredospores of cowpea rust pathogen. China Veg 3:10–13
Yarwood CE (1961) Uredospore production by Uromyces phaseoli. Phytopathology 51:22–27
Zaumeyer WJ, Thomas HR (1957) A monographic study of bean diseases and methods for their control. U S Dep Agric Tech Bull 868:255
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, G., Gupta, S.K. Role of temperature, relative humidity and rainfall in the development of French bean rust ( Uromyces appendiculatus). Indian Phytopathology 72, 271–280 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-019-00133-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42360-019-00133-w