Abstract
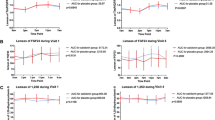
The effects of short term administration of 200 MRC U of synthetic salmon calcitonin (sCT) daily on carbohydrate metabolism were investigated in 10 patients with various bone diseases, 3 of whom had type II diabetes mellitus and 3 of whom had impaired glucose tolerance. Blood glucose levels during the nocturnal postabsorptive period, blood glucose and blood insulin (IRI) levels and the ratio of the area under the insulin curve to the area under the glucose curve (AI/AG) after a mixed meal were determined before and after 15 days of treatment. The values before and after sCT treatment were not significantly different, suggesting that high doses of sCT are not diabetogenic and can be given to patients with impaired glucose tolerance or to diabetics, without any risk of deteriorating metabolic control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ziegler R., Rave F., Molz G., Minne H. Calcitonin and endocrine pancreas. In: Pecile A. (Ed.), Calcitonin 1980. Chemistry, physiology, pharmacology and clinical aspects. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, 1981, p. 314.
Passariello N., Giugliano D., Sgambato S., Torella R., D’Onofrio F. Calcitonin, a diabetogenic hormone? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 53: 318, 1981.
Petralito A., Lunetta M., Liuzzo A., Fiore C.E., Heynen G. Effects of salmon calcitonin on blood glucose and insulin levels under basal conditions and after intravenous glucose load. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2: 209, 1979.
Passariello N., Giugliano D., Coppola A., Sgambato S. Effetti della calcitonina sulla secrezione di insulina e C-peptide in soggetti normali e diabetici. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 3(Suppl. 1): 118, 1980.
Giugliano D., Passariello N., Sgambato S., Torella R., D’Onofrio F. Calcitonin modulation of insulin and glucagon secretion in man. Am. J. Physiol. 242: E 206, 1982.
Sgambato S., Carbone L, Giugliano D., Siniscalchi N., Varano R., D’Onofrio F. Effect of calcitonin on glucose stimulated insulin secretion in normal, obese and prediabetic subjects. Farmaco 33: 256, 1978.
Cantalamessa L, Catania A., Reschini E., Peracchi M. Inhibitory effect of calcitonin on growth hormone and insulin secretion in man. Metabolism 27: 987, 1978.
Lunetta M., Infantpne E., Spanti D., Mughini L. Effects of synthetic salmon calcitonin administration on gastrin, immunoreactive insulin and growth hormone release after protein meal in uremic patients. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 4: 185, 1981.
Blahos J., Svoboda Z., Hoschl C. The effect of calcitonin on glucose metabolism. Endokrinologie 68: 226, 1976.
Gattereau A., Bielmann D., Durivage J., Davignon J., Larochelle P. Effects of acute and chronic administration of calcitonin on serum glucose in patients with Paget’s disease of bone. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 51: 354, 1980.
Danowski T.S., Nolan S., Thorsten S., Ahmad V., Sunder J., Fisher E., Vester J. Effets du traitement a court et long terme par la calcito-nine. Mater. Med. Pol. 2:156, 1976.
Giugliano D., Passariello N., Sgambato S., Torella R., Ceriello A., D’Onofrio F. Glucose metabolism in patients receiving chronic calcitonin treatment. Diabete Metab. 8:213, 1982.
Thomas D.W., Frewin D.B., Jolley P.T. Deterioration in diabetic control during calcitonin therapy. Med. J. Aust. 2: 699, 1979.
National Diabetes Data Group Classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and other categories of glucose intolerance. Diabetes 28: 1039, 1979.
Evans I., Joplin G.F., Maclntyre I. Hyperglycemic effect of synthetic salmon calcitonin. Lancet 7: 280, 1978.
Porte D., Halter J.B. The endocrine pancreas and diabetes mellitus. In: Williams R.H. (Ed.), Textbook of endocrinology. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, 1981, p. 729.
Starke A., Keck E., Berger M., Zimmermann H. Effects of calcium and calcitonin on circulating levels of glucagon and glucose in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 20: 547, 1981.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giustina, G., Cerudelli, B., Cimino, A. et al. Synthetic salmon calcitonin is not diabetogenic in patients with normal or impaired glucose metabolism. J Endocrinol Invest 8, 19–23 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03350629
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03350629