Abstract
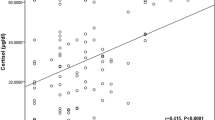
Six comatose patients hospitalized in an intensive care unit immediately following an acute trauma with severe brain injury (road or industrial accident) were examined throughout three consecutive 24-h cycles in the first week after trauma, when receiving intramuscularly 12 mg daily of dexamethasone-21-phosphate. Intravenous or enteral nutrition was supplied continuously. Plasma cortisol and aldosterone were measured on blood samples drawn at 4-h intervals. Data were analyzed both by conventional chronograms and by rhythmometric analysis according to the Coisinor procedures. A normally-synchronized circadian pattern of plasma cortisol was recognizable in all cases in the face of the lack of consciousness and of the pharmacological administration of dexamethasone. Acrophase was located at 08:56, with a 95% confidence region vastly overlapping the corresponding region of the controls. By contrast, the circadian pattern of plasma aldosterone appeared to be disrupted; irregular fluctuations were recorded along the entire day. The Cosinor analysis did not detect a significant rhythm of plasma aldosterone during the examined 24-h cycles. Data obtained with the present investigation demonstrate that comatose patients within a few days after severe head injury and given high-dose corticoid treatment do maintain the normal circadian organization of the plasma cortisol, whereas loose that of the plasma aldosterone. Our findings are compatible with the concept that glucocorticoid rhythmicity is particularly resistant to acute injury; the mineralo-corticoid rhythmicity appears more labile probably as a consequence of the plurifactorial modulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krieger D.T., Allen W., Rizzo F., Krieger H.P. Characterization of the normal pattern of plasma corticosteroid levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 32: 266, 1971.
Katz F.H., Romfh D., Smith J.A., Roper E.E., Barnes J.S., Boyd J.B. Diurnal variation of plasma aldosterone, cortisol and renin activity in supine man. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 40: 125, 1975.
Ambruster H., Vetter W., Beckerhoff R., Nussberger J., Vetter H., Siegenthaler H. Diurnal variations of plasma aldosterone in supine man: relationship to plasma renin activity and plasma cortisol. Acta Endocrinol. (Kbh.) 80: 95, 1975.
Bartter F.C., Chan J.C.M., Simpson H.W. Chronobiological aspects of plasma renin activity, plasma aldosterone, and urinary electrolytes. In: Krieger D.T. (Ed.), Endocrine rhythms. Raven Press, New York, 1979, p. 225.
Angeli A., Frairia R. Some physiological aspects of ACTH rhythmicities in man. In: Polleri A., Me Leod R.M. (Eds.), Neuroendocrinology: biological and clinical aspects. Academic Press, New York, 1979, p. 145.
Krieger D.T. Rhythms in CRF, ACTH, and corticosteroids. In: Krieger D.T. (Ed.), Endocrine rhythms. Raven Press, New York, 1979, p. 123.
Modlinger R.S., Sharif-Zadeh K., Ertel N.H., Gutkin M. The circadian rhythm of renin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 43: 1276, 1976.
Eik-Nes K.B., Clark D.L. Diurnal variations of plasma 17-hydroxycorticosteroids in subjects suffering from severe brain damage. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 18: 764, 1958.
Krieger D.T., Krieger H.P. Circadian variations of the plasma 17-hydroxycorticosteroids in central nervous system disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 26: 929, 1966.
Reinberg A. Human heritability of biological rhythms. Course in chronobiology, L’Aquila, Italy, March 4–10, 1979. Casa Editirice II Ponte, Milano, (in press.).
Baizola F., Urciuoli R., Boggio-Bertinet D. Problemi nutrizionali del paziente con danno cerebrale acuto. Minerva Med. 69: 1067, 1978.
Angeli A., Bisbocci D., Melö F., Frairia R., Gaidano G. Relative competition of corticosterone, cortisol, cortisone, 1-deoxycortisol and prednisolone with 1,2—3H-cortisol in various protein binding radioassay systems. Clin. Chim. Acta 61: 279, 1975.
Haiberg F., Tong Y.L., Johnson E.A. Circadian system phase, an aspect of temporal morphology: procedures and illustrative examples. In: Von Mayersbach H. (Ed.), The cellular aspects of biorhythms, Symposium on biorhythms. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1967, p. 20.
Haiberg F., Johnson E.A., Nelson W., Runge W., Sothern R. Autorhythmometry procedures for physiologic self-measurements and their analysis. Physiol. Teach. 1: 1, 1972.
Werk E.E., Choi Y., Sholiton L., Olinger C., Hague N. Interference in the effect of dexamethasone by diphenylhydantoin. N. Engl. J. Med. 281: 32, 1969.
Hague N., Thrasher K., Werk E.E., Knowles H.C., Sholiton L. Studies on dexamethasone metabolism in man: effect of diphenylhydantoin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 34: 44, 1972.
Sternholm M.R., Katz F.H. Effect of diphenylhydantoin, phenobarbital and diazepam on the metabolism of methylprednisolone and its sodium succinate. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 41: 887, 1975.
Andrews R.V., Folk G.E. Circadian metabolic patterns in cultured hamster adrenal glands. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 11: 393, 1964.
Meier A.H. Daily variation in concentration of plasma corticosterone in hypophysectomized rats. Endocrinology 98: 1475, 1976.
Ungar F., Haiberg. F. Circadian rhythm in the in vitro response adrenal to adrenocorticotropic hormone. Science 137: 1058, 1962.
Ottenweller J.E., Meier A.H., Ferrell B.R., Horseman N.D., Proctor A. Extrapituitary regulation of the circadian rhythm of plasma corticosteroid concentration in rats. Endocrinology 103: 1875, 1978.
Ferrari E., Bossolo P.A., Rea A., Vailati A., Martinelli I., Tamborini M., Demattei S., Bertulessi C. La risposta corticosurrenalica agli stimoli farmacologici specifici in ore diverse della giornata. In: Tronchetti F., Menchini-Fabris G.F. (Eds.), Giornate Endocrinolgiche Pisane. Pacini Editore, Pisa, 1978, vol. I, p. 431.
Haider W., Lackner F., Schlick W., Berzer H., Gerstenbrand F., Irsigler K., Korn A., Krystof G., Mayrhofer O. Metabolie changes in the course of severe acute brain damage. Eur. J. Intensive Care Med. 1: 19, 1975.
Carroll B.J., Mendels J. Neuroendocrine regulation in affective disorders. In: Sachar E.J. (Ed.), Hormones, behavior and psychopathology. Raven Press, New York, 1976, p. 193.
Brandt M., Wagner G., Walter W. Wachstumshormon, LH und FSH unter Funktionsdynamischen Bedingungen im Serum sowie Basale Kortisol — und Testosteron-Serumspiegel bei Schädelhirnverletzten unter Dexamethasonbehandlung. Neurochirurgia 20: 79, 1977.
Stoner H.B. Hypothalamic involvement in the response to injury. In: Richards J.R., Kinney J.M. (Eds.), Nutritional aspects of care in the critically ill. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, London and New York, 1977, p. 257.
Coghlan J.P., Blair-West J.R., Denton D.A., Fei D.T., Fernley R.T., Hardy K.J., Me Dougall J.G., Puy R., Robinson P.M., Scoggins B.A., Wright R.D. Control of aldosterone secretion. J. Endocrinol. 80: 55P, 1979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agrimonti, F., Boggio-Bertinet, D., Balzola, F. et al. Circadian profile of plasma cortisol and aldosterone in post-traumatic comatose patients under high-dose dexamethasone treatment. J Endocrinol Invest 4, 49–53 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03349414
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03349414