Abstract
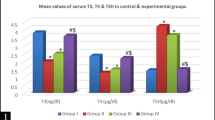
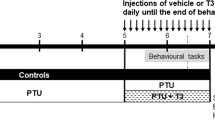
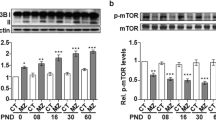
Adult-onset hypothyroidism causes cognitive dysfunctions of learning and memory, in which many synaptic proteins in hippocampus are involved. In our work, we studied the effect of adult-onset hypothyroidism on the expression of synaptotagmin 1 (syt 1) and SNAP-25 in dorsal hippocampus as well as its recovery by levothyroxine (L-T4) replacement therapy. Rats were divided into 4 groups: control, hypothyroidism, and hypothyroid rats treated with 5 μg T4/100 g body weight (BW) and 20 μg L-T4/100 g BW, respectively. Protein levels of syt 1 and SNAP-25 in dorsal hippocampus were determined by Western blot and immuno-histochemistry. The immunoblot analysis indicated that syt 1 was expressed at a significantly lower level in hypothyroid rats, while the level of SNAP-25 was much higher compared to controls. Furthermore, using immunostaining, we found that on the one hand, expression of syt 1 was significantly down-regulated in the examined layers of CA1 and CA3 sub-regions but not dentate gyrus (DG); however, on the other hand, expression of SNAP-25 was up-regulated in the layers of CA1, CA3, and DG. Two-week treatment with 20 μg L-T4/100 g BW fully restored the levels of syt 1 and SNAP-25 to the normal level, which was more effective than 5 μg L-T4/100 g BW that partially restored the levels of both proteins. These results suggest that adult-onset hypothyroidism caused down-regulation of syt 1 and up-regulation of SNAP-25 level in dorsal hippocampus, which could be restored by L-T4 treatment, and the recovery degree is related to the L-T4 dosage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Madeira MD, Sousa N, Lima-Andrade MT, Calheiros F, Cadete-Leite A, Paula-Barbosa MM. Selective vulnerability of the hippocampal pyramidal neurons to hypothyroidism in male and female rats. J Comp Neurol 1992, 322: 501–18.
Dugbartey AT. Neurocognitive aspects of hypothyroidism. Arch Intern Med 1998, 158: 1413–8.
Desouza LA, Ladiwala U, Daniel SM, Agashe S, Vaidya RA, Vaidya VA. Thyroid hormone regulates hippocampal neurogenesis in the adult rat brain. Mol Cell Neurosci 2005, 29: 414–26.
Alzoubi KH, Gerges NZ, Aleisa AM, Alkadhi KA. Levothyroxin restores hypothyroidism-induced impairment of hippocampus-dependent learning and memory: Behavioral, electrophysiological, and molecular studies. Hippocampus 2009, 19: 66–78.
Tong H, Chen GH, Liu RY, Zhou JN. Age-related learning and memory impairments in adult-onset hypothyroidism in Kunming mice. Physiol Behav 2007, 91: 290–8.
Liu YF, Chen HI, Yu L, et al. Upregulation of hippocampal TrkB and synaptotagmin is involved in treadmill exercise-enhanced aversive memory in mice. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2008, 90: 81–9.
Chapman ER. Synaptotagmin: a Ca(2+) sensor that triggers exocytosis? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2002, 3: 498–508.
Vara H, Martinez B, Santos A, Colino A. Thyroid hormone regulates neurotransmitter release in neonatal rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 2002, 110: 19–28.
Zhang HM, Su Q, Luo M. Thyroid hormone regulates the expression of SNAP-25 during rat brain development. Mol Cell Biochem 2008, 307: 169–75.
Wekking EM, Appelhof BC, Fliers E, et al. Cognitive functioning and well-being in euthyroid patients on thyroxine replacement therapy for primary hypothyroidism. Eur J Endocrinol 2005, 153: 747–53.
Capet C, Jego A, Denis P, et al. [Is cognitive change related to hypothyroidism reversible with replacement therapy?]. Rev Med Interne 2000, 21: 672–8.
Miller KJ, Parsons TD, Whybrow PC, et al. Memory improvement with treatment of hypothyroidism. Int J Neurosci 2006, 116: 895–906.
Samuels MH, Schuff KG, Carlson NE, Carello P, Janowsky JS. Health status, psychological symptoms, mood, and cognition in L-thyroxine-treated hypothyroid subjects. Thyroid 2007, 17: 249–58.
Alzoubi KH, Gerges NZ, Alkadhi KA. Levothyroxin restores hypothyroidism-induced impairment of LTP of hippocampal CA1: electrophysiological and molecular studies. Exp Neurol 2005, 195: 330–41.
Magnusson KR, Scruggs B, Zhao X, Hammersmark R. Age-related declines in a two-day reference memory task are associated with changes in NMDA receptor subunits in mice. BMC Neurosci 2007, 8: 43.
Gould E, Allan MD, McEwen BS. Dendritic spine density of adult hippocampal pyramidal cells is sensitive to thyroid hormone. Brain Res 1990, 525: 327–9.
Perin MS, Brose N, Jahn R, Südhof TC. Domain structure of synaptotagmin (p65). J Biol Chem 1991, 266: 623–9.
Quintanar JL, Salinas E. Effect of hypothyroidism on synaptosomal-associated protein of 25 kDa and syntaxin-1 expression in adenohypophyses of rat. J Endocrinol Invest 2002, 25: 754–8.
Mehta PP, Battenberg E, Wilson MC. SNAP-25 and synaptotagmin involvement in the final Ca(2+)-dependent triggering of neurotransmitter exocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996, 93: 10471–6.
de Wit H, Walter AM, Milosevic I, et al. Synaptotagmin-1 docks secretory vesicles to syntaxin-1/SNAP-25 acceptor complexes. Cell 2009, 138: 935–46.
Zhang X, Kim-Miller MJ, Fukuda M, Kowalchyk JA, Martin TF. Ca2+-dependent synaptotagmin binding to SNAP-25 is essential for Ca2+-triggered exocytosis. Neuron 2002, 34: 599–611.
Miyamoto T, Hashizume K, Ichikawa K, et al. Effect of thyroid hormone on the protein inhibitors for Ca2+-dependent proteinase in brain: evidence for the induction by thyroidectomy of irreversible changes in immature rats. Endocrinology 1988, 123: 1916–22.
Ando K, Kudo Y, Takahashi M. Negative regulation of neurotransmitter release by calpain: a possible involvement of specific SNAP-25 cleavage. J Neurochem 2005, 94: 651–8.
Hepp R, Grant NJ, Espliguero G, et al. Adrenal gland SNAP-25 expression is altered in thyroid hormone receptor knock-out mice. Neuroreport 2001, 12: 1427–30.
Baldini IM, Vita A, Mauri MC, et al. Psychopathological and cognitive features in subclinical hypothyroidism. Prog Neuropsycho-pharmacol Biol Psychiatry 1997, 21: 925–35.
Jensovsky J, Ruzicka E, Spackova N, Hejdukova B. Changes of event related potential and cognitive processes in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism after thyroxine treatment. Endocr Regul 2002, 36: 115–22.
Zhu DF, Wang ZX, Zhang DR, et al. fMRI revealed neural substrate for reversible working memory dysfunction in subclinical hypothyroidism. Brain 2006, 129: 2923–30.
Leentjens AF, Kappers EJ. Persistent cognitive defects after corrected hypothyroidism. Psychopathology 1995, 28: 235–7.
Ruiz-Marcos A, Cartagena-Abella P, Martinez-Galan JR, Calvo R, Morreale de Escobar G, Escobar del Rey F. Thyroxine treatment and the recovery of pyramidal cells of the cerebral cortex from changes induced by juvenile-onset hypothyroidism. J Neurobiol 1994, 25: 808–18.
Constantinou C, Margarity M, Valcana T. Region-specific effects of hypothyroidism on the relative expression of thyroid hormone receptors in adult rat brain. Mol Cell Biochem 2005, 278: 93–100.
Diez D, Grijota-Martinez C, Agretti P, et al. Thyroid hormone action in the adult brain: gene expression profiling of the effects of single and multiple doses of triiodo-L-thyronine in the rat striatum. Endocrinology 2008, 149: 3989–4000.
Hodel A. Snap-25. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1998, 30: 1069–73.
Ambrogini P, Cuppini R, Ferri P, et al. Thyroid hormones affect neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult rat. Neuroendocrinology 2005, 81: 244–53.
Montero-Pedrazuela A, Venero C, Lavado-Autric R, et al. Modulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis by thyroid hormones: implications in depressive-like behavior. Mol Psychiatry 2006, 11: 361–71.
Dratman MB, Crutchfield FL, Futaesaku Y, Goldberger ME, Murray M. [125I] triiodothyronine in the rat brain: evidence for neural localization and axonal transport derived from thaw-mount film autoradiography. J Comp Neurol 1987, 260: 392–408.
Dratman MB, Crutchfield FL, Axelrod J, Colburn RW, Thoa N. Localization of triiodothyronine in nerve ending fractions of rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1976, 73: 941–4.
Dratman MB, Crutchfield FL. Synaptosomal [125I]triiodothyronine after intravenous [125I]thyroxine. Am J Physiol 1978, 235: E638–47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
C.L. Liu and Y.X. Xu contributed to this work equally
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C.L., Xu, Y.X., Zhan, Y. et al. Effect of thyroxine on synaptotagmin 1 and SNAP-25 expression in dorsal hippocampus of adult-onset hypothyroid rats. J Endocrinol Invest 34, 280–286 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347086
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347086